Sandbox Reserved 478
From Proteopedia
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Catalytic Domain=== | ===Catalytic Domain=== | ||
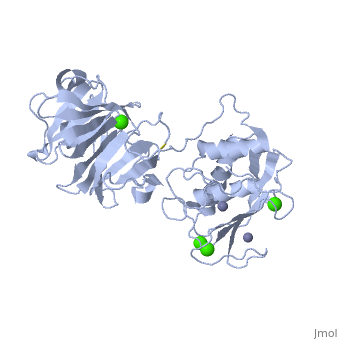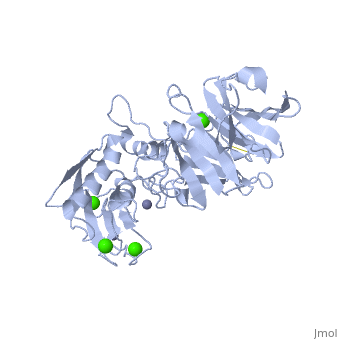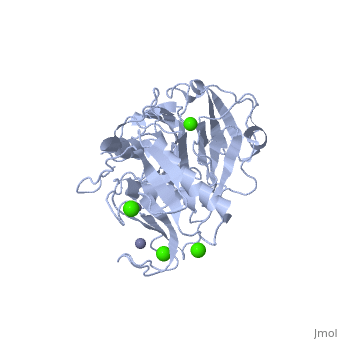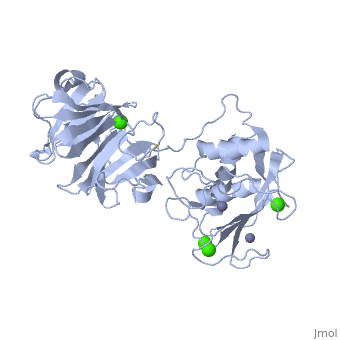
| - | + | Many of the MMPs share similar catalytic domain structures and this holds up for MMP-1. The Catalytic Domain is about 160 amino acid residues in length with the catalytic zinc ion residing in the C-terminal segment of this domain. The Domain consists of three α-helices, a highly twisted five-stranded β-sheet, and three calcium-binding sites, which are used for ligand binding. Except for one calcium that is held within monomer A, all of the calcium ions are coordinated with either four or five liganding residues. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
===Linker Region=== | ===Linker Region=== | ||
| - | + | The Catalytic Domain is followed by a linker region spanning 15-65 residues in all MMPs. The linker region connects the Catalytic Domain and the Hemopexin Domain of the enzyme. This leads to the MMP-1 being more stabilized overall, which is highly required for the mutual actions of two domains. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
===Hemopexin-like Domain=== | ===Hemopexin-like Domain=== | ||
Revision as of 06:53, 2 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
StructureThe Structure of MMP-1 and all other members of the Metalloproteinase family for that matter are formed from three domains. The structure comprises of the N-terminal catalytic domain, the linker region and the C-terminal hemopexin domain. The structure of human MMP-1 was determined with X-Ray Crystallography at a resolution of 2.67A to have two monomers (chains A and B). The catalytic domain of one monomer contacts the hemopexin domain of the other monomer. An interesting observation that has been noted is that the contact site used by the two monomers in the asymmetric unit to form the dimer is not the same as the dimerization site observed in the structure of the MMP-9 hemopexin domain. This difference shows that not all members of the Matrix Metalloproteinase family behave the same in their dimerization processes. Catalytic DomainMany of the MMPs share similar catalytic domain structures and this holds up for MMP-1. The Catalytic Domain is about 160 amino acid residues in length with the catalytic zinc ion residing in the C-terminal segment of this domain. The Domain consists of three α-helices, a highly twisted five-stranded β-sheet, and three calcium-binding sites, which are used for ligand binding. Except for one calcium that is held within monomer A, all of the calcium ions are coordinated with either four or five liganding residues. Linker RegionThe Catalytic Domain is followed by a linker region spanning 15-65 residues in all MMPs. The linker region connects the Catalytic Domain and the Hemopexin Domain of the enzyme. This leads to the MMP-1 being more stabilized overall, which is highly required for the mutual actions of two domains. Hemopexin-like Domainadlskflam adfafdaf afa f Mechanism of Actionsdfglkmsdfsd fasdf a sdf asf ads ff Medical Implicationslkmlml;kmlm
References |