This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 458
From Proteopedia
(→Structure) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
There are four major isozymes in the CK family and have been characterized on the basis of differences in gene and amino acid sequence, as well as tissue localization and immunogenicity. The four isozymes are the muscle (MM-CK), brain (BB-CK), mitochondrial ubiquitous (Miu-CK) and mitochondrial sarcomeric (Mis-CK). | There are four major isozymes in the CK family and have been characterized on the basis of differences in gene and amino acid sequence, as well as tissue localization and immunogenicity. The four isozymes are the muscle (MM-CK), brain (BB-CK), mitochondrial ubiquitous (Miu-CK) and mitochondrial sarcomeric (Mis-CK). | ||
| - | <Structure load='1QK1' size=' | + | |
| + | <Structure load='1QK1' size='200' frame='true' align='left' caption='Crystal Structure of Human Mitochondrial Ubiquitous Creatine Kinase' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| Line 23: | Line 28: | ||
<ref>McLeish, M. and Kenyon, G. ''Relating Structure to Mechanism in Creatine Kinase'' Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 40:1-20, 2005. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10409230590918577 DOI: 10.1080.10409230590918577]</ref> | <ref>McLeish, M. and Kenyon, G. ''Relating Structure to Mechanism in Creatine Kinase'' Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 40:1-20, 2005. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10409230590918577 DOI: 10.1080.10409230590918577]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref> Knopp, J. ''Knopp's Knotes'' p47, Fifth Edition. | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 2 May 2012
|
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
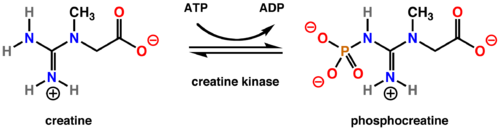
Creatine KinaseCreatine Kinase (CK), sometimes referred to as Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK), is an enzyme (EC 2.7.3.2). CK is classified as a transferase, which means it facilitates the transfer of a group from one molecule to another. AX + B ---> A + BX The first three numbers of its EC number indicate that it is a phosphotransferase with a nitrogenous group as the acceptor. CK is a very important enzyme for all organisms, as it catalyzes the conversion of creatine into phosphocreatine. Phosphocreatine is used as an energy source for high energy need cells such as smooth muscle cells. CK is clinically relevant in blood serum assays in that an elevated CK level might indicate muscle wasting or myocardial infarction.
StructureThere are four major isozymes in the CK family and have been characterized on the basis of differences in gene and amino acid sequence, as well as tissue localization and immunogenicity. The four isozymes are the muscle (MM-CK), brain (BB-CK), mitochondrial ubiquitous (Miu-CK) and mitochondrial sarcomeric (Mis-CK).
Mechanism
References |