We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 470
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_Robert_B_Rose_1}} | {{Sandbox_Reserved_Robert_B_Rose_1}} | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
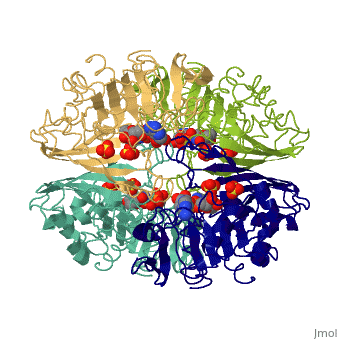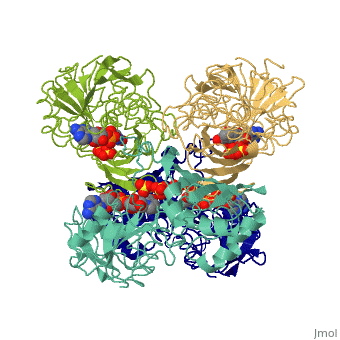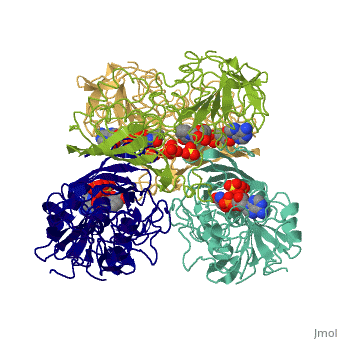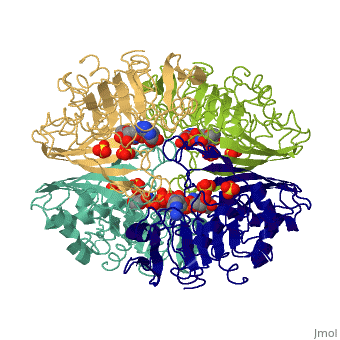
'''[[Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase]]''' | '''[[Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase]]''' | ||
<Structure load='3gpd' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />(abbreviated as GAPDH or the less common G3PDH) (EC 1.2.1.12) ~37kDa is a well-known [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme enzyme] which catalyzes the sixth step of [[glycolysis]], a reversible cytosolic process in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eukaryote eukaryotes] which involves the breakdown of glucose for energy and carbon molecules. Along with its role in glycolysis and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gluconeogenesis gluconeogenesis], recent research has determined that GAPDH is actually a multifunctional protein, as it has numerous defined, non-metabolic functions involved in multiple subcellular processes including [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription transcription] activation, ER to Golgi transportation, transcriptional control of histone [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_Expression gene expression], nuclear membrane fusion, neuronal initiation of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis], recognizing fraudulently incorporated nucleotides in DNA, and maintaining [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telomere telomere] structures. Research also shows that it possibly has a direct involvement in cellular phenotype of human [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurodegeneration neurodegenerative] disorders, especially those characterized by expansion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAG_Triplet_Repeat_Disorders CAG repeats]. | <Structure load='3gpd' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />(abbreviated as GAPDH or the less common G3PDH) (EC 1.2.1.12) ~37kDa is a well-known [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme enzyme] which catalyzes the sixth step of [[glycolysis]], a reversible cytosolic process in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eukaryote eukaryotes] which involves the breakdown of glucose for energy and carbon molecules. Along with its role in glycolysis and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gluconeogenesis gluconeogenesis], recent research has determined that GAPDH is actually a multifunctional protein, as it has numerous defined, non-metabolic functions involved in multiple subcellular processes including [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription transcription] activation, ER to Golgi transportation, transcriptional control of histone [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_Expression gene expression], nuclear membrane fusion, neuronal initiation of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis], recognizing fraudulently incorporated nucleotides in DNA, and maintaining [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telomere telomere] structures. Research also shows that it possibly has a direct involvement in cellular phenotype of human [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurodegeneration neurodegenerative] disorders, especially those characterized by expansion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAG_Triplet_Repeat_Disorders CAG repeats]. | ||
| + | ==Structure== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | GAPDH has two domains, a GAPDH-like, C-terminal domain, and an NAD Binding Domain. | ||
| + | *The NAD (Nucleotide) Binding Domain is an Alpha Beta 3-Layer(α-β-α) Sandwich, including amino acids 1-138 and 301-340 on chains O and Q . Its [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CATH CATH] reports a Rossmann fold and a classification as an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxidoreductase oxidoreductase]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The GAPDH-like, C-terminal domain (Catalytic domain) is an Alpha Beta 2-Layer(α-β) Sandwich, including amino acids 139 - 300 on chains O and Q . Its CATH reports a holo-D-Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, (domain 2) and a classification as an oxidoreductase (aldehyde(D)-NAD(A)). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Importance== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Role in Glycolysis:''' | '''Role in Glycolysis:''' | ||
| Line 30: | Line 39: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
#↑"GAPDH glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [Homo sapiens] - Gene - NCBI." National Center for Biotechnology Information. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''<ref>'''"GAPDH glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [Homo sapiens] - Gene - NCBI." National Center for Biotechnology Information. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''[<http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2597>]'''. '''<ref/>''' | #↑"GAPDH glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [Homo sapiens] - Gene - NCBI." National Center for Biotechnology Information. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''<ref>'''"GAPDH glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [Homo sapiens] - Gene - NCBI." National Center for Biotechnology Information. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''[<http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2597>]'''. '''<ref/>''' | ||
| + | #↑"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase." Stanford University. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2012. '''<ref>'''"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase." Stanford University. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2012. '''[<http://www.stanford.edu/~mmogri/bio/gapdh/structure.html>]'''. '''</ref>''' | ||
#↑"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1." European Bioinformatics Institute | Homepage | EBI. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''<ref>'''"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1." European Bioinformatics Institute | Homepage | EBI. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''[<http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/potm/2004_2/Page3.htm>]'''.'''</ref>''' | #↑"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1." European Bioinformatics Institute | Homepage | EBI. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''<ref>'''"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1." European Bioinformatics Institute | Homepage | EBI. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''[<http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/potm/2004_2/Page3.htm>]'''.'''</ref>''' | ||
#↑"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''<ref>'''"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''[<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glyceraldehyde_3-phosphate_dehydrogenase>]'''. '''</ref>''' | #↑"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''<ref>'''"Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 May 2012. '''[<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glyceraldehyde_3-phosphate_dehydrogenase>]'''. '''</ref>''' | ||
Revision as of 01:15, 3 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
IntroductionGlyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase
StructureGAPDH has two domains, a GAPDH-like, C-terminal domain, and an NAD Binding Domain.
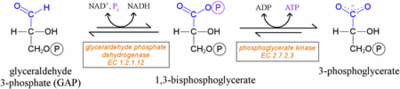
ImportanceRole in Glycolysis:
GAPDH catalyzes the conversion of glyceraldyhyde-3-phosphate at carbon 1 to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG).
Other roles:
GAPDH was also found to be involved in ER to Golgi transport because it is recruited by rab2 to vesicular-tubular clusters of the endoplasmic reticulum where it helps form COP 1 vesicles.
Use in the lab:
References
|