Allosteric modulation of H-Ras GTPase
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Mutations == | == Mutations == | ||
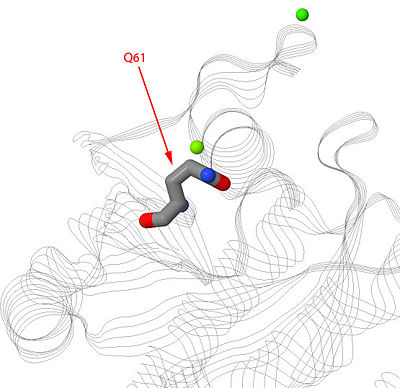
| - | [[Image:Q61Ras.jpg|400px|left]] | + | [[Image:Q61Ras.jpg|400px|left]] The residue Glutamine-61 (Q61) plays a large role in the mutation of the Ras protein. When the Q61 becomes mutated in stops the GTPase of the Ras causing the protein to continuously stay active. Mutated Q61 is found in many cancer patients. |
| + | Mutation of Q61 causes a shift in Loop 7 and Helix 3 causing the conformation of the amino acids and switch regions to change. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Reference == | ||
| + | <ref group="xtra">PMID:20194776</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Buhrman, G.]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Holzapfel, G.]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Mattos, C.]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Acetylation]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Cell membrane]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Disease mutation]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Golgi apparatus]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Gtp-binding]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Lipoprotein]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Membrane]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Methylation]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Nucleotide-binding]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Oncoprotein]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Palmitate]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Prenylation]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Protein-nucleotide complex]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Proto-oncogene]] | ||
| + | [[Category: S-nitrosylation]] | ||
Revision as of 02:54, 19 June 2012
| |||||||||
| 3k8y, resolution 1.30Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , | ||||||||
| Gene: | HRAS, HRAS1 (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| Related: | 2rge, 3k9n, 3k9l | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
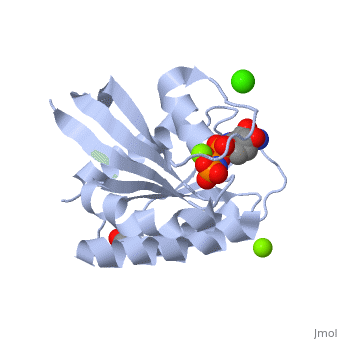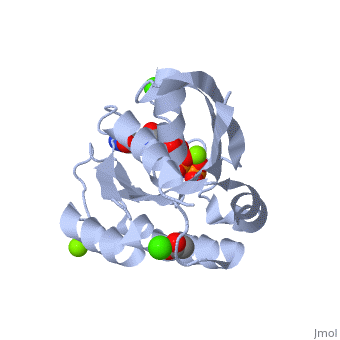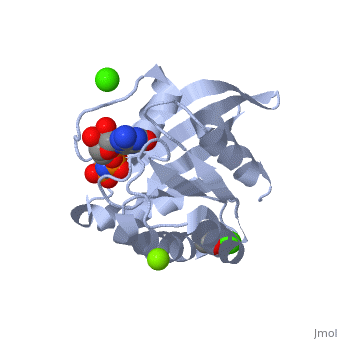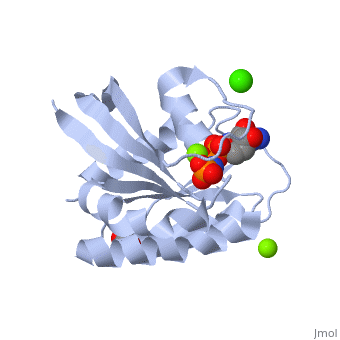
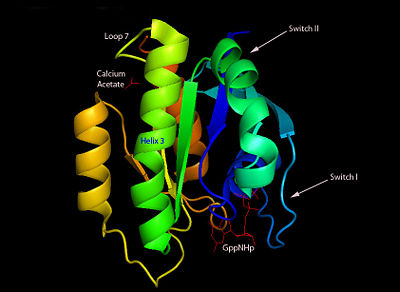
H-Ras is a small monomeric GTPase protein that is found inside of cells. It helps regulate cell division in cells through signal transduction pathways such as the Ras pathway. H-Ras is also known as a molecular switch, it contains two switch regions: Switch I and Switch II. Switch I is a Thymine 35 and switch II is a Glycine 60, both of these switches depend on the phosphate group on a GTP molecule to turn “on” and “off”. In the Ras catalytic cycle, Ras is activated when it attaches to a GTP molecule turning both switch regions “on”. This pathway also involves GTPase activating protein, which hydrolyzes the GTP attached to the Ras causing the switches to turn “off”.
Structure
H-Ras is 166 Amino Acids long with six beta sheets and six helices. One of the helix 2 is a 3/10 helix, unlike the rest of the helices. Also it contains a Calcium Acetate in the allosteric binding site that is located by the Loop 7 and Helix 3. The structure of Ras actually forms slightly different when it is and isn't bound to calcium acetate. The GTP molecule will then attach on the bottom of the protein inbetween the Switch I and Switch II region.Mutations
The residue Glutamine-61 (Q61) plays a large role in the mutation of the Ras protein. When the Q61 becomes mutated in stops the GTPase of the Ras causing the protein to continuously stay active. Mutated Q61 is found in many cancer patients.Mutation of Q61 causes a shift in Loop 7 and Helix 3 causing the conformation of the amino acids and switch regions to change.
Reference
- Buhrman G, Holzapfel G, Fetics S, Mattos C. Allosteric modulation of Ras positions Q61 for a direct role in catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 16;107(11):4931-6. Epub 2010 Mar 1. PMID:20194776
Categories: Homo sapiens | Buhrman, G. | Holzapfel, G. | Mattos, C. | Acetylation | Cell membrane | Disease mutation | Golgi apparatus | Gtp-binding | Lipoprotein | Membrane | Methylation | Nucleotide-binding | Oncoprotein | Palmitate | Prenylation | Protein-nucleotide complex | Proto-oncogene | S-nitrosylation