We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Hox protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | =Hox- | + | =Hox Proteins Specifically Recognize the Sequence-Dependent Shape of the Minor Groove= |
| + | |||
| + | ==Biological Role of Hox Proteins= | ||
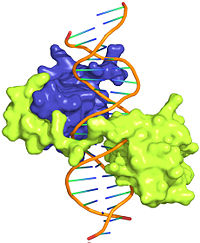
[[Image:Hox-intro.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Crystal structure of Exd-Scr-DNA ternary complex; PDB ID# 2R5Z (cite).]] | [[Image:Hox-intro.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Crystal structure of Exd-Scr-DNA ternary complex; PDB ID# 2R5Z (cite).]] | ||
Revision as of 04:55, 2 July 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 22 April 2012, through 31 August 2012 for use in the course "Protein DNA" taught by Remo_Rohs at the La Canada High School, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 169 through Sandbox Reserved 170. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Hox Proteins Specifically Recognize the Sequence-Dependent Shape of the Minor Groove
=Biological Role of Hox Proteins
Important for embryonic development across species. Recognize DNA with high binding specificity. Eight Drosophila Hox proteins. Bind with a co-factor. Shows crystal structure of Scr-Exd-DNA ternary complex.
</StructureSection>
|
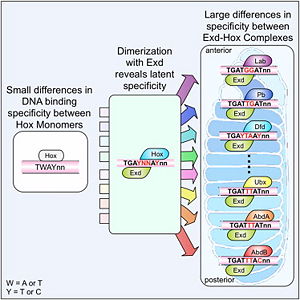
Image:Slattery-etal-Figure6.jpg
Caption (cite).
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Remo Rohs, Eric Martz, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Skyler Saleebyan, Julia Tam, Bailey Holmes, Sharon Kim, Alexander Berchansky, Iris Dror, Ana Carolina Dantas Machado, Masha Karelina, Keziah Kim, Jaime Prilusky, Angel Herraez