1gzx
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
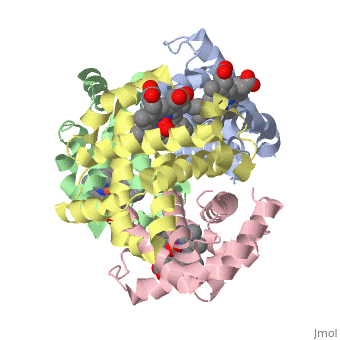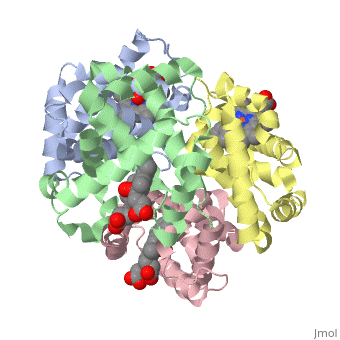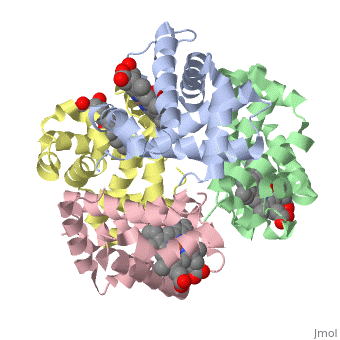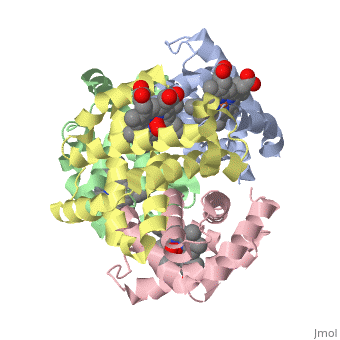
| - | The cooperative binding of oxygen by haemoglobin results from restraints | + | The cooperative binding of oxygen by haemoglobin results from restraints on ligand binding in the T state. The unfavourable interactions made by the ligands at the haems destabilise the T state and favour the high affinity R state. The T <==> R equilibrium leads, in the presence of a ligand, to a rapid increase in the R state population and therefore generates cooperative binding. There is now considerable understanding of this phenomenon, but the interactions that reduce ligand affinity in the T state have not yet been fully explored, owing to the difficulties in preparing T state haemoglobin crystals in which all the subunits are oxygenated. A protocol has been developed to oxygenate deoxy T state adult human haemoglobin (HbA) crystals in air at 4 C at all four haems without significant loss of crystalline order. The X-ray crystal structure, determined to 2.1 A spacing, shows significant changes in the alpha and beta haem pockets as well as changes at the alpha(1)beta(2) interface in the direction of the R quaternary structure. Most of the shifts and deviations from deoxy T state HbA are similar to, but larger than, those previously observed in the T state met and other partially liganded T state forms. They provide clear evidence of haem-haem interaction in the T state. |
==Disease== | ==Disease== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category: transport]] | [[Category: transport]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 12:55:50 2008'' |
Revision as of 10:55, 21 February 2008
|
OXY T STATE HAEMOGLOBIN: OXYGEN BOUND AT ALL FOUR HAEMS
Contents |
Overview
The cooperative binding of oxygen by haemoglobin results from restraints on ligand binding in the T state. The unfavourable interactions made by the ligands at the haems destabilise the T state and favour the high affinity R state. The T <==> R equilibrium leads, in the presence of a ligand, to a rapid increase in the R state population and therefore generates cooperative binding. There is now considerable understanding of this phenomenon, but the interactions that reduce ligand affinity in the T state have not yet been fully explored, owing to the difficulties in preparing T state haemoglobin crystals in which all the subunits are oxygenated. A protocol has been developed to oxygenate deoxy T state adult human haemoglobin (HbA) crystals in air at 4 C at all four haems without significant loss of crystalline order. The X-ray crystal structure, determined to 2.1 A spacing, shows significant changes in the alpha and beta haem pockets as well as changes at the alpha(1)beta(2) interface in the direction of the R quaternary structure. Most of the shifts and deviations from deoxy T state HbA are similar to, but larger than, those previously observed in the T state met and other partially liganded T state forms. They provide clear evidence of haem-haem interaction in the T state.
Disease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Erythremias, alpha- OMIM:[141800], Erythremias, beta- OMIM:[141900], Erythrocytosis OMIM:[141850], HPFH, deletion type OMIM:[141900], Heinz body anemia OMIM:[141850], Heinz body anemias, alpha- OMIM:[141800], Heinz body anemias, beta- OMIM:[141900], Hemoglobin H disease OMIM:[141850], Hypochromic microcytic anemia OMIM:[141850], Methemoglobinemias, alpha- OMIM:[141800], Methemoglobinemias, beta- OMIM:[141900], Sickle cell anemia OMIM:[141900], Thalassemia, alpha- OMIM:[141850], Thalassemia-beta, dominant inclusion-body OMIM:[141900], Thalassemias, alpha- OMIM:[141800], Thalassemias, beta- OMIM:[141900]
About this Structure
1GZX is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens with and as ligands. Known structural/functional Site: . Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of T state haemoglobin with oxygen bound at all four haems., Paoli M, Liddington R, Tame J, Wilkinson A, Dodson G, J Mol Biol. 1996 Mar 8;256(4):775-92. PMID:8642597
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 12:55:50 2008
Categories: Homo sapiens | Protein complex | Dodson, G. | Liddington, R. | Paoli, M. | Tame, J. | Wilkinson, A. | HEM | OXY | Cooperativity | Haem protein | Oxygen binding | Transport