FK506 binding protein
From Proteopedia
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
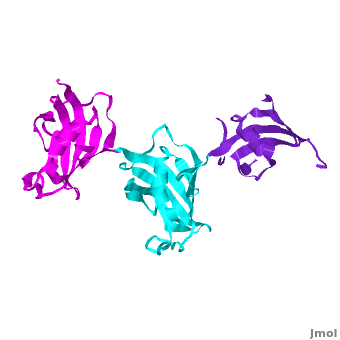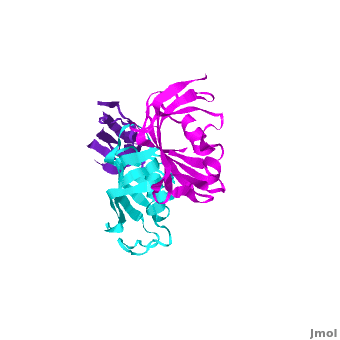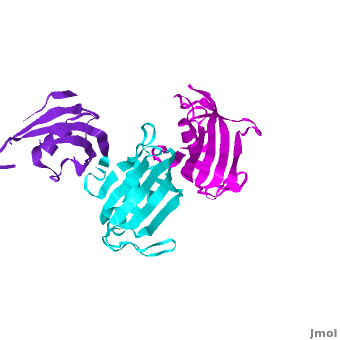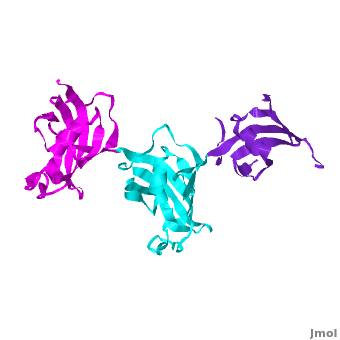
| - | It was shown that 12 conserved residues (for wFK73_1 domain they are Tyr67, Phe77, Asp78, Arg83, Phe87, Gln95, Val96, Ile97, Trp100, Tyr123, Ile132, and Phe140) of the FK1 domains of hFKBP12, 13, 25, 51 and 52, are involved in binding the FK506 or rapamycin. Since only the FK1 domains contain all the conserved amino acids (in contrast to FK2 and/or FK3 domains), only they exhibit PPIase activity, which can be inhibited by the binding of the drugs FK506, and rapamycin. These conserved residues form the hydrophobic cavity. The structure of hFKBP12 ([[2ppn]]) demonstrates a good example of this <scene name='3jym/Cavity/1'>cavity</scene>. All these residues are conserved in the wFK73_1 domain, it could be assumed that a similar cavity is also formed in wFK73_1, although some of these residues are missing electron density in the wFK73 structure and, therefore, it can not be seen. Domain <font color='magenta'><b>wFK73_3</b></font> has <scene name='3jym/Cavity/3'>narrower cavity</scene>, whereas <font color='cyan'><b>wFK73_2</b></font> <scene name='3jym/Cavity/4'>lacks this cavity at all</scene>. Conserved residues are colored yellow. So, the lack of drug binding of the wFK73_2 and wFK73_3 domains could be explained by the absence of the conserved drug binding residues. This is in agreement with the fact that the FK2 domains of hFKBP51 and hFKBP52 and the single FK domains of FKBP38, DmFKBP45 and AtFKBP42, all lacking the conserved residues, do not exhibit drug binding. | + | It was shown that 12 conserved residues (for wFK73_1 domain they are Tyr67, Phe77, Asp78, Arg83, Phe87, Gln95, Val96, Ile97, Trp100, Tyr123, Ile132, and Phe140) of the FK1 domains of hFKBP12, 13, 25, 51 and 52, are involved in binding the FK506 or rapamycin. Since only the FK1 domains contain all the conserved amino acids (in contrast to FK2 and/or FK3 domains), only they exhibit PPIase activity, which can be inhibited by the binding of the drugs FK506, and rapamycin. These conserved residues form the hydrophobic cavity. The structure of hFKBP12 ([[2ppn]]) demonstrates a good example of this <scene name='3jym/Cavity/1'>cavity</scene>. All these residues are conserved in the wFK73_1 domain, it could be assumed that a similar cavity is also formed in wFK73_1, although some of these residues are missing electron density in the wFK73 structure and, therefore, it can not be seen. Domain <font color='magenta'><b>wFK73_3</b></font> has <scene name='3jym/Cavity/3'>narrower cavity</scene>, whereas <font color='cyan'><b>wFK73_2</b></font> <scene name='3jym/Cavity/4'>lacks this cavity at all</scene>. Conserved residues are colored yellow. So, the lack of drug binding of the wFK73_2 and wFK73_3 domains could be explained by the absence of the conserved drug binding residues. This is in agreement with the fact that the FK2 domains of hFKBP51 and hFKBP52 and the single FK domains of FKBP38, DmFKBP45 and AtFKBP42, all lacking the conserved residues, do not exhibit drug binding. |
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Wheat FKBP73]]. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 20 August 2012
FK506 binding protein (FKBP) is a prolyl isomerase related to the cyclophilins. FKBP is a folding chaperone for proteins containing prolines. FKBP12 binds the immunosuppressor tacrolimus (FK506) which is used against organ rejection. For more details see Human FKBP52.
Contents |
Wheat FKBP73 and its comparison with human FKBP52[1]
| |||||||||||
SlyD[2]
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of FKBP
FKPB3
3kz7 – hFKBP FK506-binding domain + immunosuppressant - human
FKPB4
1q1c – hFKBP
1n1a – hFKBP N terminal
1p5q - hFKBP C terminal
1qz2 – hFKBP + Hsp90 peptide
FKBP5
3o5d, 3o5e, 3o5f – hFKBP
3o5g, 3o5i, 3o5j, 3o5k - hFKBP FK506-binding domain
3o5l, 3o5m, 3o5o, 3o5p, 3p5q - hFKBP FK506-binding domain (mutant)
3o5r - hFKBP FK506-binding domain (mutant) + immunosuppressant
FKBP8
2f2d, 3ey6, 2awg - hFKBP FK506-binding domain
2d9f – hFKBP – NMR
2jwx - hFKBP N terminal - NMR
FKBP12
1eym – hFKBP (mutant)
1fkk – hFKBP
2gaq, 2pnu– hFKBP - NMR
1fkd, 1fkj, 2fke, 1qpf, 1qpl – hFKBP + immunosuppressant
2ppp, 2ppn, 2dg3, 1d6o – hFKBP
1j4h, 1j4i – hFKBP + inhibitor
1b6c – hFKBP + TGF-B superfamily receptor I
3fap – hFKBP + FKBP12-rapamycin associated protein
4fap - hFKBP + FKBP12-rapamycin associated protein + immunosuppressant
1tco - FKBP + Ser/Thr phosphatase B2 + immunosuppressant - bovine
1yat – FKBP + antagonist – yeast
FKBP26
3pr9, 3pra, 3prb, 3prd – FKBP – Methanocaldococcus jannaschii
FKBP59
1rot, 1rou – FKBP N terminal – NMR – rabbit
2kr7 – FKBP SlyD – NMR - Helicobacter pylori
2lgo – FKBP – NMR – Giardia lamblia
FKBP73
3jym - FKBP wheat
- ↑ Unger T, Dym O, Albeck S, Jacobovitch Y, Bernehim R, Marom D, Pisanty O, Breiman A. Crystal structure of the three FK506 binding protein domains of wheat FKBP73: evidence for a unique wFK73_2 domain. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2010 Jun;11(2):113-23. Epub 2010 Mar 20. PMID:20306145 doi:10.1007/s10969-010-9085-8
- ↑ Cheng T, Li H, Xia W, Sun H. Multifaceted SlyD from Helicobacter pylori: implication in [NiFe] hydrogenase maturation. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011 Nov 2. PMID:22045417 doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0855-y