This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1jch
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="1jch" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1jch, resolution 3.02Å" /> '''Crystal Structure of...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1jch.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1jch" size=" | + | [[Image:1jch.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1jch" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="1jch, resolution 3.02Å" /> | caption="1jch, resolution 3.02Å" /> | ||
'''Crystal Structure of Colicin E3 in Complex with its Immunity Protein'''<br /> | '''Crystal Structure of Colicin E3 in Complex with its Immunity Protein'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
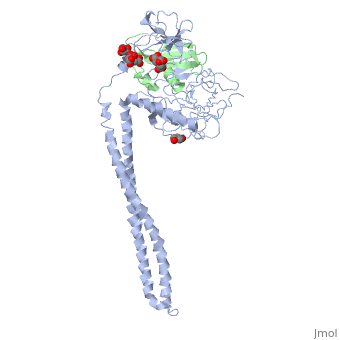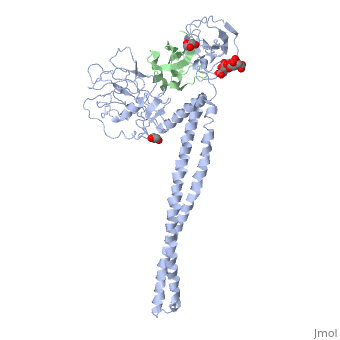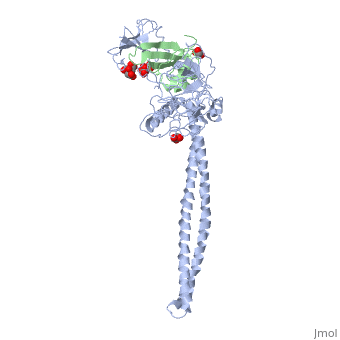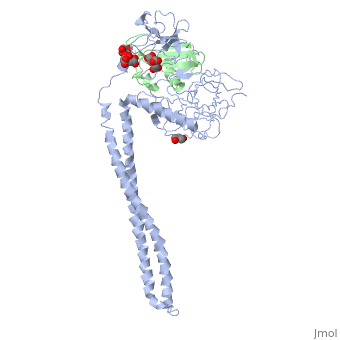
| - | Colicins kill E. coli by a process that involves binding to a surface | + | Colicins kill E. coli by a process that involves binding to a surface receptor, entering the cell, and, finally, intoxicating it. The lethal action of colicin E3 is a specific cleavage in the ribosomal decoding A site. The crystal structure of colicin E3, reported here in a binary complex with its immunity protein (IP), reveals a Y-shaped molecule with the receptor binding domain forming a 100 A long stalk and the two globular heads of the translocation domain (T) and the catalytic domain (C) comprising the two arms. Active site residues are D510, H513, E517, and R545. IP is buried between T and C. Rather than blocking the active site, IP prevents access of the active site to the ribosome. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1JCH is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_complex Protein complex] structure of sequences from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] with CIT and GOL as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligands ligands]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1JCH is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_complex Protein complex] structure of sequences from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] with <scene name='pdbligand=CIT:'>CIT</scene> and <scene name='pdbligand=GOL:'>GOL</scene> as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligands ligands]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1JCH OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category: translocation domain is a beta-jellyroll]] | [[Category: translocation domain is a beta-jellyroll]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 13:21:05 2008'' |
Revision as of 11:21, 21 February 2008
|
Crystal Structure of Colicin E3 in Complex with its Immunity Protein
Overview
Colicins kill E. coli by a process that involves binding to a surface receptor, entering the cell, and, finally, intoxicating it. The lethal action of colicin E3 is a specific cleavage in the ribosomal decoding A site. The crystal structure of colicin E3, reported here in a binary complex with its immunity protein (IP), reveals a Y-shaped molecule with the receptor binding domain forming a 100 A long stalk and the two globular heads of the translocation domain (T) and the catalytic domain (C) comprising the two arms. Active site residues are D510, H513, E517, and R545. IP is buried between T and C. Rather than blocking the active site, IP prevents access of the active site to the ribosome.
About this Structure
1JCH is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Escherichia coli with and as ligands. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of colicin E3: implications for cell entry and ribosome inactivation., Soelaiman S, Jakes K, Wu N, Li C, Shoham M, Mol Cell. 2001 Nov;8(5):1053-62. PMID:11741540
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 13:21:05 2008
Categories: Escherichia coli | Protein complex | Jakes, K. | Li, C. | Shoham, M. | Soelaiman, S. | Wu, N. | CIT | GOL | The receptor-binding domain is a coiled coil | The rnase domain is a six-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet. the immunity protein is a four-stranded antiparallel beta sheet flanked by 3 helices on one side of the sheet | Translocation domain is a beta-jellyroll