We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Nuclear receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: == Nuclear Receptor == === Structure === ==== DBD (DNA Binding Domain) ==== ==== LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) ==== <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure ...) |
m |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==== DBD (DNA Binding Domain) ==== | ==== DBD (DNA Binding Domain) ==== | ||
==== LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) ==== | ==== LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) ==== | ||
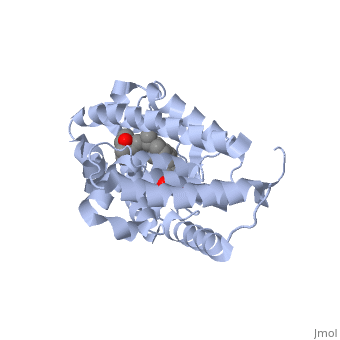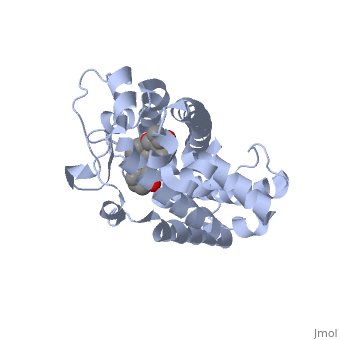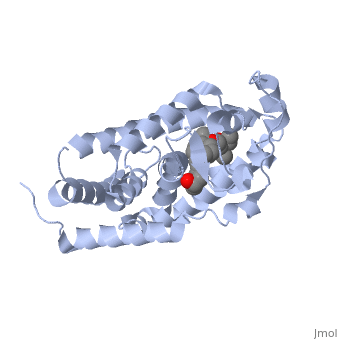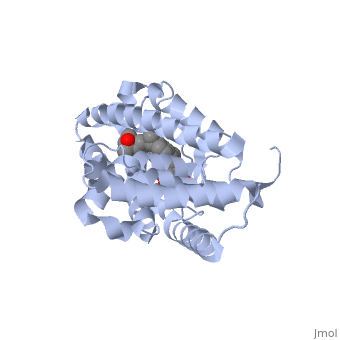
| - | <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of | + | <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of the LBD of a VDR (vitamin D receptor) complexed to 1alpha,25(OH)(2)D(3) and the 20-epi analogs(PDB entry [[1ie8]])' scene=''> |
| - | The LBD of | + | The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. |
| + | It is completely folded and composed of a beta-sheet, and 12 alpha-helices arranged in a three layered sandwich. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 08:14, 6 September 2012
Contents |
Nuclear Receptor
Structure
DBD (DNA Binding Domain)
LBD (Ligand Binding Domain)
| |||||||||||