SecA PBD motions
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
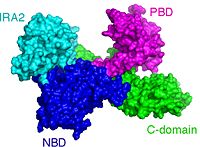
PBD is the site where signal peptides of preproteins dock <ref>pmid 18022369</ref> and from there they control ATP hydrolysis at the NBD-IRA2 interface <ref>pmid 17525736</ref>. | PBD is the site where signal peptides of preproteins dock <ref>pmid 18022369</ref> and from there they control ATP hydrolysis at the NBD-IRA2 interface <ref>pmid 17525736</ref>. | ||
So far no functional role has been unequivocally atributed to this rotational motion. It has been suggested that PBD rotates to allow the opening of a clamp-like structure. This clamp has been shown to be the site where preprotein chains are located during their translocation <ref>pmid 18923516</ref><ref>pmid 19933328</ref>. | So far no functional role has been unequivocally atributed to this rotational motion. It has been suggested that PBD rotates to allow the opening of a clamp-like structure. This clamp has been shown to be the site where preprotein chains are located during their translocation <ref>pmid 18923516</ref><ref>pmid 19933328</ref>. | ||
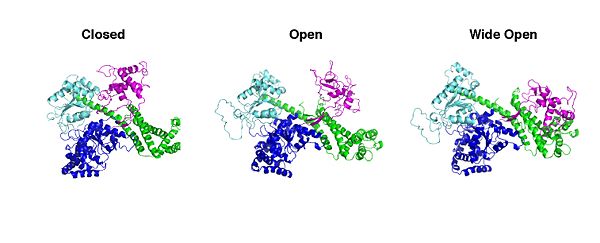
| - | SecA has been visualized in a Wide Open <ref>pmid 12242434</ref>; an Open <ref>pmid 17229438</ref> and a Closed conformation <ref>pmid 18022369</ref>. | + | |
| + | SecA has been visualized in a Wide Open <ref>pmid 12242434</ref>; an Open <ref>pmid 17229438</ref> and a Closed conformation <ref>pmid 18022369</ref>, according to the position of the PBD. | ||
There are a few testable working hypotheses about the importance of this PBD swiveling motion. PBD motion could be the ATP-driven mechanical event that pushes preproteins through the SecYEG pore or it could prevent their backsliding. The implementation of single molecule techniques (e.g. single molecule FRET analysis) could provide us with high resolution information about the functional role of this extremelly dynamic domain. | There are a few testable working hypotheses about the importance of this PBD swiveling motion. PBD motion could be the ATP-driven mechanical event that pushes preproteins through the SecYEG pore or it could prevent their backsliding. The implementation of single molecule techniques (e.g. single molecule FRET analysis) could provide us with high resolution information about the functional role of this extremelly dynamic domain. | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 6 September 2012
SecA PBD motion
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Papanikou E, Karamanou S, Economou A. Bacterial protein secretion through the translocase nanomachine. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007 Nov;5(11):839-51. PMID:17938627 doi:nrmicro1771
- ↑ Sardis MF, Economou A. SecA: a tale of two protomers. Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jun 1;76(5):1070-81. Epub 2010 Apr 23. PMID:20444093 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07176.x
- ↑ Gelis I, Bonvin AM, Keramisanou D, Koukaki M, Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Economou A, Kalodimos CG. Structural basis for signal-sequence recognition by the translocase motor SecA as determined by NMR. Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):756-69. PMID:18022369 doi:S0092-8674(07)01269-X
- ↑ Karamanou S, Gouridis G, Papanikou E, Sianidis G, Gelis I, Keramisanou D, Vrontou E, Kalodimos CG, Economou A. Preprotein-controlled catalysis in the helicase motor of SecA. EMBO J. 2007 Jun 20;26(12):2904-14. Epub 2007 May 24. PMID:17525736 doi:7601721
- ↑ Zimmer J, Nam Y, Rapoport TA. Structure of a complex of the ATPase SecA and the protein-translocation channel. Nature. 2008 Oct 16;455(7215):936-43. PMID:18923516 doi:10.1038/nature07335
- ↑ Bauer BW, Rapoport TA. Mapping polypeptide interactions of the SecA ATPase during translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 8;106(49):20800-5. Epub 2009 Nov 20. PMID:19933328 doi:10.1073/pnas.0910550106
- ↑ Hunt JF, Weinkauf S, Henry L, Fak JJ, McNicholas P, Oliver DB, Deisenhofer J. Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA. Science. 2002 Sep 20;297(5589):2018-26. PMID:12242434 doi:10.1126/science.1074424
- ↑ Papanikolau Y, Papadovasilaki M, Ravelli RB, McCarthy AA, Cusack S, Economou A, Petratos K. Structure of dimeric SecA, the Escherichia coli preprotein translocase motor. J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 9;366(5):1545-57. Epub 2006 Dec 23. PMID:17229438 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.049
- ↑ Gelis I, Bonvin AM, Keramisanou D, Koukaki M, Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Economou A, Kalodimos CG. Structural basis for signal-sequence recognition by the translocase motor SecA as determined by NMR. Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):756-69. PMID:18022369 doi:S0092-8674(07)01269-X