SecA PBD motions
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== SecA PBD motion == | == SecA PBD motion == | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='SecA from B. subtilis in the Closed conformation (PDB entry [[1M6N]])' scene='SecA_PBD_motions/Seca_pbd_motions/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='SecA from B. subtilis in the Closed conformation (PDB entry [[1M6N]])' scene='SecA_PBD_motions/Seca_pbd_motions/1'> | ||
| - | + | ===PBD moves=== | |
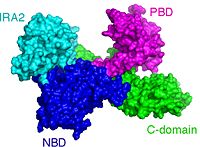
[[Image:SecA.jpg|left|thumb|200px|alt=text|SecA from ''E.coli'']] | [[Image:SecA.jpg|left|thumb|200px|alt=text|SecA from ''E.coli'']] | ||
| - | |||
Protein secretion is essential for all organisms. Bacteria have evolved a plethora of secretion systems to handle the various proteins that need to be exported from the cytoplasm <ref>pmid 17938627</ref>. Most of these proteins bear an amino terminal extension termed signal peptide and they are called preproteins. The Sec secretion system is uniquitus and essential for cell viability. In bacteria, the Sec system consists of the membrane embedded heterotrimeric complex SecYEG that forms the channel through which preproteins are threaded and the cytoplasmic nanomotor SecA. SecA spends chemical energy to produce mechanical work that somehow pushes and threads preproteins through SecYEG. | Protein secretion is essential for all organisms. Bacteria have evolved a plethora of secretion systems to handle the various proteins that need to be exported from the cytoplasm <ref>pmid 17938627</ref>. Most of these proteins bear an amino terminal extension termed signal peptide and they are called preproteins. The Sec secretion system is uniquitus and essential for cell viability. In bacteria, the Sec system consists of the membrane embedded heterotrimeric complex SecYEG that forms the channel through which preproteins are threaded and the cytoplasmic nanomotor SecA. SecA spends chemical energy to produce mechanical work that somehow pushes and threads preproteins through SecYEG. | ||
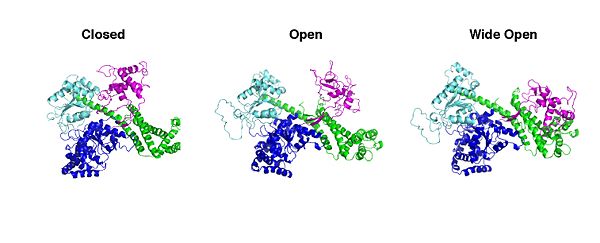
SecA constists of 4 domains; the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Nbd/1'>Nucleotide Binding Domain</scene>(NDB); the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Pbd/1'>Preprotein Binding Domain</scene>(PBD); the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Ira2/1'>Intramolecular Regulator of ATP hydrolysis 2</scene> (IRA2) and the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Cdomain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> (C-domain). SecAs from different organisms have been visualized <ref>pmid 20444093</ref>. The most prominent difference between the protomers of visualized SecAs is an 80o rotational and translational movement of the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Pbdmagenta/1'>PBD</scene> around its <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Stem/1'>stem</scene> that connects it with NBD. | SecA constists of 4 domains; the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Nbd/1'>Nucleotide Binding Domain</scene>(NDB); the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Pbd/1'>Preprotein Binding Domain</scene>(PBD); the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Ira2/1'>Intramolecular Regulator of ATP hydrolysis 2</scene> (IRA2) and the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Cdomain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> (C-domain). SecAs from different organisms have been visualized <ref>pmid 20444093</ref>. The most prominent difference between the protomers of visualized SecAs is an 80o rotational and translational movement of the <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Pbdmagenta/1'>PBD</scene> around its <scene name='SecA_PBD_motions/Stem/1'>stem</scene> that connects it with NBD. | ||
Revision as of 13:46, 6 September 2012
SecA PBD motion
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Papanikou E, Karamanou S, Economou A. Bacterial protein secretion through the translocase nanomachine. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007 Nov;5(11):839-51. PMID:17938627 doi:nrmicro1771
- ↑ Sardis MF, Economou A. SecA: a tale of two protomers. Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jun 1;76(5):1070-81. Epub 2010 Apr 23. PMID:20444093 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07176.x
- ↑ Gelis I, Bonvin AM, Keramisanou D, Koukaki M, Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Economou A, Kalodimos CG. Structural basis for signal-sequence recognition by the translocase motor SecA as determined by NMR. Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):756-69. PMID:18022369 doi:S0092-8674(07)01269-X
- ↑ Karamanou S, Gouridis G, Papanikou E, Sianidis G, Gelis I, Keramisanou D, Vrontou E, Kalodimos CG, Economou A. Preprotein-controlled catalysis in the helicase motor of SecA. EMBO J. 2007 Jun 20;26(12):2904-14. Epub 2007 May 24. PMID:17525736 doi:7601721
- ↑ Zimmer J, Nam Y, Rapoport TA. Structure of a complex of the ATPase SecA and the protein-translocation channel. Nature. 2008 Oct 16;455(7215):936-43. PMID:18923516 doi:10.1038/nature07335
- ↑ Bauer BW, Rapoport TA. Mapping polypeptide interactions of the SecA ATPase during translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 8;106(49):20800-5. Epub 2009 Nov 20. PMID:19933328 doi:10.1073/pnas.0910550106
- ↑ Hunt JF, Weinkauf S, Henry L, Fak JJ, McNicholas P, Oliver DB, Deisenhofer J. Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA. Science. 2002 Sep 20;297(5589):2018-26. PMID:12242434 doi:10.1126/science.1074424
- ↑ Papanikolau Y, Papadovasilaki M, Ravelli RB, McCarthy AA, Cusack S, Economou A, Petratos K. Structure of dimeric SecA, the Escherichia coli preprotein translocase motor. J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 9;366(5):1545-57. Epub 2006 Dec 23. PMID:17229438 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.049
- ↑ Gelis I, Bonvin AM, Keramisanou D, Koukaki M, Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Economou A, Kalodimos CG. Structural basis for signal-sequence recognition by the translocase motor SecA as determined by NMR. Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):756-69. PMID:18022369 doi:S0092-8674(07)01269-X