Traditionally, new drugs are developed by either making small changes to existing drugs or by individually testing thousands of compounds. Both of these methods require many hours of laborious chemical synthesis. However, new techniques are being applied in the drug industry which decrease the cost and time required to discover and develop new drugs.
Fragment-Based Drug Discovery
Fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) is a method of discovering new compounds by utilizing fragments that have some degree of binding affinity for a drug target, optimizing those fragments so as to increase their binding affinity, then linking them together to form a lead compound that has high affinity and selectivity for the drug target. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and x-ray crystallography can be used to analyze the fragments and drug targets in order to create three-dimensional images which can be used to obtain an analysis of molecular relationships. This allows developers to get a visual representation of how each fragment binds to the target and can also be useful in identifying the individual binding sites of the target.
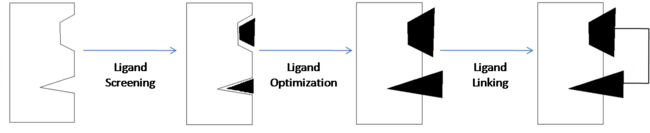
Fragment-Based Drug Discovery (Adapted from Fig. 1)
[1]
The development of using SAR by NMR is a classic example of FBDD. (Throughout this discussion ABT-737 will be used to illustrate the FBDD process.) This compound has been shown to effectively inhibit the over-expression of which is a protein that is commonly observed to be over-expressed in many types of cancers.[2] It acts an inhibitor of apoptosis and may also contribute to chemotherapy resistance. Bcl-xl inhibition by ABT-737 therefore, allows apoptosis to occur and helps to prevent chemo-resistance.
| SAR by NMR
|
| Structure-activity relationship (SAR) by NMR is one tool that is commonly used to design and develop new drugs. This is the process "in which small organic molecules that bind to proximal subsites of a protein are identified, optimized, and linked together to produce high-affinity ligands."[1] In other words, NMR is used to identify the components responsible for binding and analyze the relationship between the ligand and the biological target.
|
Ligand Screening
The first step of FBDD is to expose the potential drug target to a large number of small molecular fragments. This is usually done with a method known as high-throughput screening. High-throughput screening (HTS) is the process of using robotics to perform a large number of chemical tests. HTS is used to quickly identify fragments that have affinity for the target which are then analyzed to understand why they have affinity.
ABT-737: ligand screening
were found to have moderate affinity for Bcl-xl. is a fluorobiphenylcarboxylic acid. It occupies of Bcl-xl. The fluorobiphenyl portion of compound 1 is very hydrophobic. Therefore, Bcl-xl forms a around the fluorobiphenyl system. The of Bcl-xl.
is a napthalene-based alcohol which occupies . This particular fragment also is involved with hydrophobic interactions with Bcl-xl, although they are not as strong as in the case of compound 1.
Ligand Optimization
Once the fragments have been identified, they are then modified to increase their binding affinity. These modifications can include atom substitutions, the addition of substituents, or even the replacement of the entire fragment. Knowing and having an understanding of the structure of the biological target is useful in optimizing the fragments. The nature of the binding site is what determines how a ligand will bind (as in the case of the hydrophobic pocket formed around compound 1). This approach to designing drugs is referred to as structure-based drug design.
| Structure-Based Drug Design
|
| Structure-based drug design is utilized when the 3-D structure of a protein, or other drug target, is used to predict drug candidates. A visual representation of the structure allows developers to pinpoint binding sites and more effectively design a drug that will have high affinity for the target.
|
ABT-737: ligand optimization
Compounds 1 & 2 exhibited very poor binding affinity for Bcl-xl. The optimization of these two compounds resulted in . In order to improve the binding affinity, the carboxylic acid of compound 1 was substituted with an acyl sulfonamide to capitalize on the hydrophilic interaction with the protein. This thereby increasing the affinity for Bcl-xl. The substitution of the sulfonamide actually allows the acidic proton to get closer to Gly 142 than it could in the carboxylic acid, which is why it is able to bind stronger to the amino acid.
Compound 2 was important in identifying the hydrophobicity of binding site 2 but was substituted with a . This substitution more efficiently binds to site 2 through π stacking with Phe 101 and Tyr 199. This idea of using a known ligand to develop another ligand, and eventually drugs, is known as ligand-based drug design.
| Ligand-Based Drug Design
|
| "Ligand-based drug design (LBDD) techniques are applied when the structure of the receptor is unknown but when a series of compounds or ligands have been identified that show the biological activity of the interest."[3] In other words, once it is known how a ligand binds to a protein or any other molecule, new ligands, and eventually drugs, can be designed to bind in a similar manner and get the desired effect. It involves modifying a known ligand to develop another ligand with a higher binding affinity for the target.
|
Compound 3 required further optimization because the binding affinity for Bcl-xl is greatly reduced in the presence of human serum albumin (HSA). In order to decrease HSA affinity, and therefore increase Bcl-xl affinity, SAR by NMR was used to modify compound 3 by eliminating key binding groups of the compound to HSA without affecting Bcl-xl affinity.
| Modifying compound 2 to reduce HSA affinity
|
| Compound 2 has high affinity for Bcl-xl but has an even higher affinity for HSA. For this reason, when HSA is present, compound 2 and similar ligands are more likely to bind to HSA thereby decreasing the amount that can bind with Bcl-xl. In order to decrease the affinity for HSA while maintaining affinity for Bcl-xl, SAR by NMR was used to compare compound 2 with a , which also has high affinity for HSA. It was found that two hydrophobic portions of compound 2 had very strong hydrophobic interactions with HSA. Therefore, these portions were modified with polar substituents to decrease HSA affinity. To decrease hydrophobicity, the fluorobiphenyl system was substituted with a piperazine ring and a 2-dimethylaminoethyl group was added to the thioethylamino linkage group.
|
Ligand Linking
The final step in FBDD is to link all of the individual, optimized fragments together to form one compound with very high affinity for the target. The goal is for all of the high-binding affinity characteristics of the fragments to be represented in one final compound.

