Joe Granger Methionine Repressor: Escherichia coli
From Proteopedia
(→Reference) |
(→MET REPRESSOR/DNA COMPLEX + S-ADENOSYL-METHIONINE) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===MET REPRESSOR/DNA COMPLEX + S-ADENOSYL-METHIONINE=== | ===MET REPRESSOR/DNA COMPLEX + S-ADENOSYL-METHIONINE=== | ||
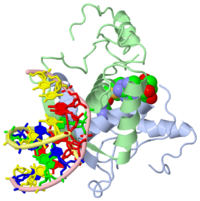
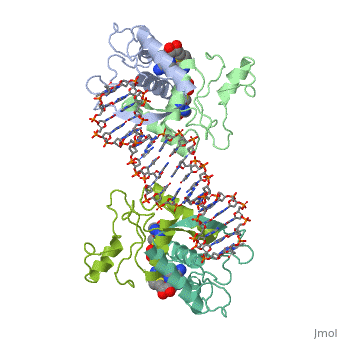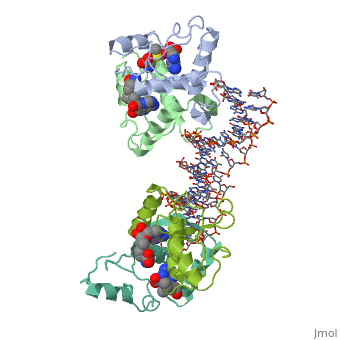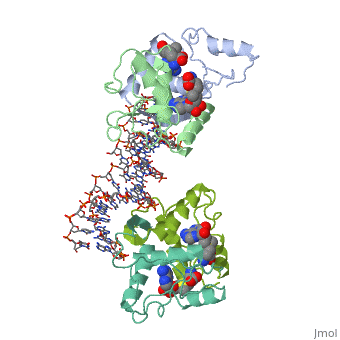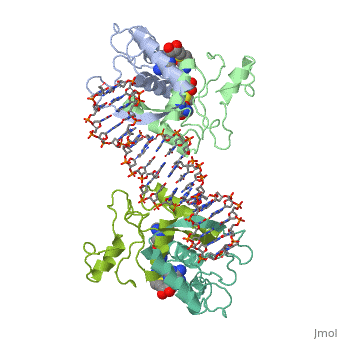
| - | {{ The Met Repressor Protein is involved with regulating the synthesis of methionine. This protein works to bind the DNA | + | {{ The Met Repressor Protein is involved with regulating the synthesis of methionine. This protein is a homodimer composed of 2 104 amino acid chains. works to bind the DNA operators that activate the transcription of genes that produce methionine. When this protein is bound to DNA, it prevents RNA polymerase'''II''' from binding and promoting transcription. The crystal structure of the met repressor-operator complex shows two dimeric repressor molecules bound to adjacent sites 8 base pairs apart on an 18-base-pair DNA fragment. The <scene name='User:Wally_Novak/Suface_of_the_protein/6'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> is bound tightly with The DNA operator in the major groove. What binds the to the DNA tightly is the two Beta sheets. While they are both from different monomers, they complex in an anti parallel fashion <scene name='User:Wally_Novak/Anti_parallel/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> . This complexed beta sheet not only connects the two dimers, but it is also involved with binding to the DNA conciseness Sequence AGACGTCT () ). The beta sheets then create the polar connections necessary to connect to the Conciseness sequence (). Sequence specificity to the concensious sequence is achieved by insertion of double-stranded antiparallel protein beta-ribbons into the major groove of B-form DNA, with direct hydrogen-bonding between amino-acid side chains and the base pairs. The repressor also recognizes sequence-dependent distortion or flexibility of the operator phosphate backbone, conferring specificity even for inaccessible base pairs. Ultimately, the specific amino acid sequence and shape allows for it to bind to its consensus sequence }} |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
Revision as of 01:36, 8 November 2012
| |||||||||
| 1cma, resolution 2.80Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
MET REPRESSOR/DNA COMPLEX + S-ADENOSYL-METHIONINE
{{ The Met Repressor Protein is involved with regulating the synthesis of methionine. This protein is a homodimer composed of 2 104 amino acid chains. works to bind the DNA operators that activate the transcription of genes that produce methionine. When this protein is bound to DNA, it prevents RNA polymeraseII from binding and promoting transcription. The crystal structure of the met repressor-operator complex shows two dimeric repressor molecules bound to adjacent sites 8 base pairs apart on an 18-base-pair DNA fragment. The is bound tightly with The DNA operator in the major groove. What binds the to the DNA tightly is the two Beta sheets. While they are both from different monomers, they complex in an anti parallel fashion . This complexed beta sheet not only connects the two dimers, but it is also involved with binding to the DNA conciseness Sequence AGACGTCT () ). The beta sheets then create the polar connections necessary to connect to the Conciseness sequence (). Sequence specificity to the concensious sequence is achieved by insertion of double-stranded antiparallel protein beta-ribbons into the major groove of B-form DNA, with direct hydrogen-bonding between amino-acid side chains and the base pairs. The repressor also recognizes sequence-dependent distortion or flexibility of the operator phosphate backbone, conferring specificity even for inaccessible base pairs. Ultimately, the specific amino acid sequence and shape allows for it to bind to its consensus sequence }}
About this Structure
1cma is a 4 chain structure with sequence from Escherichia coli. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
- Somers WS, Phillips SE. Crystal structure of the met repressor-operator complex at 2.8 A resolution reveals DNA recognition by beta-strands. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):387-93. PMID:1406951 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/359387a0
Santanu Maitra, and james S. Nowick. (2000) B-Sheet Interactions Between Proteins. University of Califonia Irvine. 15