We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Grb10 SH2 Domain
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→Interaction Between Grb10 and E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Dimerization of the Grb10 SH2 Domain== | ==Dimerization of the Grb10 SH2 Domain== | ||
| - | The crystal structure of Grb10 SH2 domain (molecular mass = 12.4 kDa) was an important step to understanding how this protein interacts with IGF1 receptors, and although the SH2 domain functions as an independent segment, it forms a dimer in physiological environments. <ref name=Guan>PMID: 12551896 </ref> The <scene name='Grb10_SH2_Domain/Best_interface/1'>dimer interface</scene> exists due to the middle hydrophobic Phe515 and uncharged Thr504 (labeled blue) residues packed into its equivalent counter parter on the other protomer, designated as Phe515' and Thr504' (labeled red); Gln511 (blue) forms a hydrogen bond to the backbone of Asp514' (red) while the side chain of Asn519 forms two hydrogen bonds to the backbone of Lys505'. <ref name=Guan>PMID: 12551896 </ref> The interface ends with Leu518 and Phe-496' via hydrophobic interactions. <ref name=Guan>PMID: 12551896 </ref>. The structure of Grb10 SH2 forms similar SH2 domains found in other proteins, which have an <scene name='Grb10_SH2_Domain/Alpha_helix/1'>alpha helix</scene> on the outsides with anti-parallel <scene name='Grb10_SH2_Domain/Beta_sheet/1'>beta sheets</scene>. | + | The crystal structure of Grb10 SH2 (Src Homology) domain (molecular mass = 12.4 kDa) was an important step to understanding how this protein interacts with IGF1 receptors, and although the SH2 domain functions as an independent segment, it forms a dimer in physiological environments. <ref name=Guan>PMID: 12551896 </ref> The <scene name='Grb10_SH2_Domain/Best_interface/1'>dimer interface</scene> exists due to the middle hydrophobic Phe515 and uncharged Thr504 (labeled blue) residues packed into its equivalent counter parter on the other protomer, designated as Phe515' and Thr504' (labeled red); Gln511 (blue) forms a hydrogen bond to the backbone of Asp514' (red) while the side chain of Asn519 forms two hydrogen bonds to the backbone of Lys505'. <ref name=Guan>PMID: 12551896 </ref> The interface ends with Leu518 and Phe-496' via hydrophobic interactions. <ref name=Guan>PMID: 12551896 </ref>. The structure of Grb10 SH2 forms similar SH2 domains found in other proteins, which have an <scene name='Grb10_SH2_Domain/Alpha_helix/1'>alpha helix</scene> on the outsides with anti-parallel <scene name='Grb10_SH2_Domain/Beta_sheet/1'>beta sheets</scene>. |
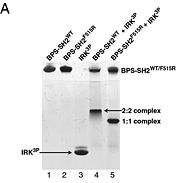
To ensure the crystallographic structure of Grb10 SH2 is indeed a dimer in solution, Evan Stein and colleagues substituted Phe515 at the dimer interface with arginine (electrically charged side chain) and found, using gel filtration chromatography (Picture 1), that the Grb10 SH2 dimer had indeed become independent monomers. | To ensure the crystallographic structure of Grb10 SH2 is indeed a dimer in solution, Evan Stein and colleagues substituted Phe515 at the dimer interface with arginine (electrically charged side chain) and found, using gel filtration chromatography (Picture 1), that the Grb10 SH2 dimer had indeed become independent monomers. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
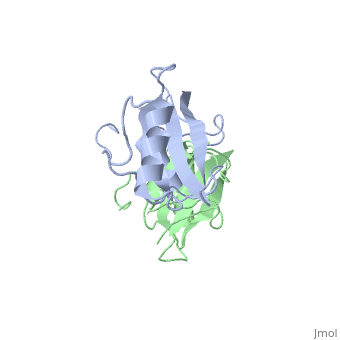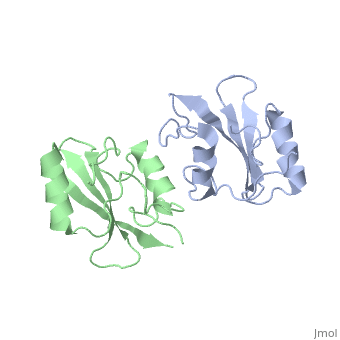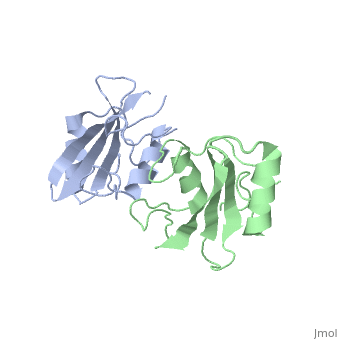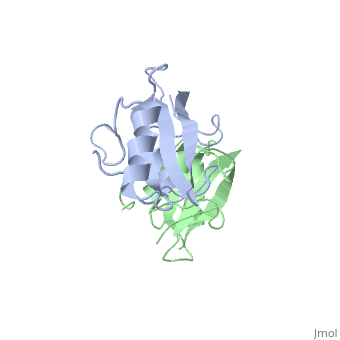
<Structure load='3M7F' size='350' frame='true' align='left' caption='Crystal structure of the Nedd4 C2/Grb10 SH2 complex PDB entry [[3M7F]])' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='3M7F' size='350' frame='true' align='left' caption='Crystal structure of the Nedd4 C2/Grb10 SH2 complex PDB entry [[3M7F]])' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Grb10 has now been shown to not only inhibit insulin receptors and IGF1R kinase activity, but also interacts via its SH2 domain with the C2 domain of E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 facilitating ubiquitation of IGF1R <ref>PMCID: PMC3009938</ref> | ||
There are 3 interfaces at chich Nedd4 C2 and Grb10 SH2 interact: | There are 3 interfaces at chich Nedd4 C2 and Grb10 SH2 interact: | ||
Revision as of 11:08, 8 November 2012
| |||||||||||
Interaction Between Grb10 and E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4
|
Grb10 has now been shown to not only inhibit insulin receptors and IGF1R kinase activity, but also interacts via its SH2 domain with the C2 domain of E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 facilitating ubiquitation of IGF1R [3]
There are 3 interfaces at chich Nedd4 C2 and Grb10 SH2 interact:
another interaction at interface I:
Interface II : Smallest interface
Interface III: medium size surface
Grb10 Gene Inhibition Affects Body Composition, and Insulin Signaling
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Stein EG, Ghirlando R, Hubbard SR. Structural basis for dimerization of the Grb10 Src homology 2 domain. Implications for ligand specificity. J Biol Chem. 2003 Apr 11;278(15):13257-64. Epub 2003 Jan 27. PMID:12551896 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M212026200
- ↑ He W, Rose DW, Olefsky JM, Gustafson TA. Grb10 interacts differentially with the insulin receptor, insulin-like growth factor I receptor, and epidermal growth factor receptor via the Grb10 Src homology 2 (SH2) domain and a second novel domain located between the pleckstrin homology and SH2 domains. J Biol Chem. 1998 Mar 20;273(12):6860-7. PMID:9506989
- ↑ PMCID: PMC3009938