We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===Phe-Pro-p-amidinobenzylamine=== | ===Phe-Pro-p-amidinobenzylamine=== | ||
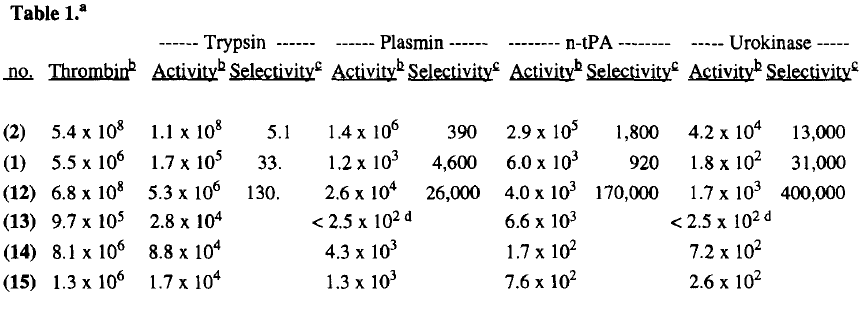
An early experiment to find a better thrombin inhibitor yielded a structure that was able to bond to the P1 and P2 sites of Thrombin effectively. In 1996 Lilly research laboratories created D-Phe-Pro-p-amidinobenzylamine by making improvements on the previous structure D-Phe-Pro-Agmatine. The new compound they created bonded to thrombin 130x more than it did to trypsin (also a serine protease), and it was highly selective of thrombin over fibrinolytic enzymes which break down fibrin clots. The inhibitor bound with Thrombin at rates 26,000x greater than with plasmin,<ref> http://voices.yahoo.com/what-fibrinolytic-enzymes-6186058.html?cat=68</ref>, 170,000x greater than with t-Pa, and 400,000x greater than with urokinase. | An early experiment to find a better thrombin inhibitor yielded a structure that was able to bond to the P1 and P2 sites of Thrombin effectively. In 1996 Lilly research laboratories created D-Phe-Pro-p-amidinobenzylamine by making improvements on the previous structure D-Phe-Pro-Agmatine. The new compound they created bonded to thrombin 130x more than it did to trypsin (also a serine protease), and it was highly selective of thrombin over fibrinolytic enzymes which break down fibrin clots. The inhibitor bound with Thrombin at rates 26,000x greater than with plasmin,<ref> http://voices.yahoo.com/what-fibrinolytic-enzymes-6186058.html?cat=68</ref>, 170,000x greater than with t-Pa, and 400,000x greater than with urokinase. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:1996 inhibitor rates.png|center 300]] |
Its selectivity was gained by binding its nitrogens on the benzamidine group by hydrogen bonding to Asp 189, and by fitting its benzamidine benzene into a hydrophobic pocket with Ser 214-Glu 217 and Asp 189-Glu 192 on the other side. The proline residue is in another hydrophobic pocket made up of His 57, Tyr 60A, Leu 99, and Trp 60D. The rest of this structure is unimportant on review of inhibitor 65 because only the amidinobenzylamine which occupies R1 and the proline which occupies the R2 sit are the same residues on inhibitor 65.<ref> M. R. Wiley, N. Y. Chirgadze, D. K. Clawson, T. J. Craft, D. S. GiffordMoore, N. D. Jones, J. L. Olkowski, L. C. Weir, G. F. Smith, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 2387. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0960894X96004428 </ref> | Its selectivity was gained by binding its nitrogens on the benzamidine group by hydrogen bonding to Asp 189, and by fitting its benzamidine benzene into a hydrophobic pocket with Ser 214-Glu 217 and Asp 189-Glu 192 on the other side. The proline residue is in another hydrophobic pocket made up of His 57, Tyr 60A, Leu 99, and Trp 60D. The rest of this structure is unimportant on review of inhibitor 65 because only the amidinobenzylamine which occupies R1 and the proline which occupies the R2 sit are the same residues on inhibitor 65.<ref> M. R. Wiley, N. Y. Chirgadze, D. K. Clawson, T. J. Craft, D. S. GiffordMoore, N. D. Jones, J. L. Olkowski, L. C. Weir, G. F. Smith, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 2387. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0960894X96004428 </ref> | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 15 November 2012
| |||||||||||
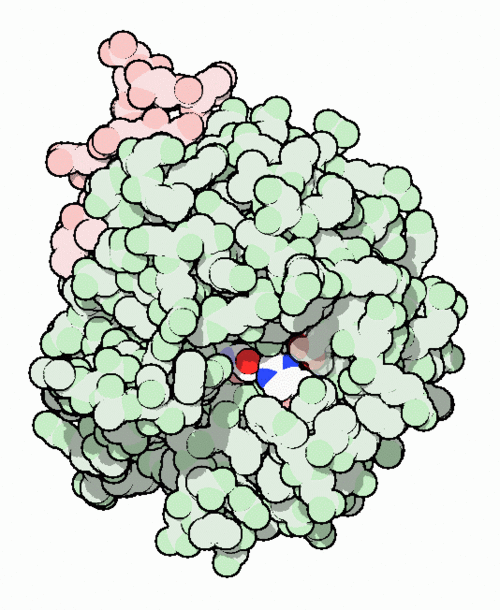
This is the of thrombin
References
- ↑ January 2002 Molecule of the Month by David Goodsell http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/101/motm.do?momID=25
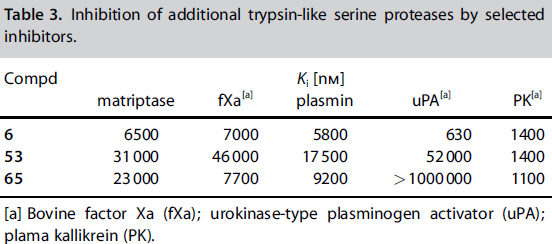
- ↑ Steinmetzer T, Baum B, Biela A, Klebe G, Nowak G, Bucha E. Beyond Heparinization: Design of Highly Potent Thrombin Inhibitors Suitable for Surface Coupling. ChemMedChem. 2012 Aug 20. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201200292. PMID:22907907 doi:10.1002/cmdc.201200292
- ↑ http://voices.yahoo.com/what-fibrinolytic-enzymes-6186058.html?cat=68
- ↑ M. R. Wiley, N. Y. Chirgadze, D. K. Clawson, T. J. Craft, D. S. GiffordMoore, N. D. Jones, J. L. Olkowski, L. C. Weir, G. F. Smith, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 2387. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0960894X96004428