This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 390
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='3qx3' size='600' side='right' caption='Structure of the human topoisomeraseIIbcore-DNA cleavage complex stabilized by the anticancer drug etoposide. (PDB entry 3QX3)' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3qx3' size='600' side='right' caption='Structure of the human topoisomeraseIIbcore-DNA cleavage complex stabilized by the anticancer drug etoposide. (PDB entry 3QX3)' scene=''> | ||
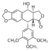
The purpose of this page is to explain a semisynthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin [[Image:PODO.png|thumb|right|50 px|Chemical structure of podophyllotoxin]] (etoposide) that demonstrates antitumor activity by inhibiting DNA topoisomerase II, thereby inhibiting DNA re-ligation which lead to apoptosis of the cancer cell and also, to describe the mechanisms of resistance of etoposide. | The purpose of this page is to explain a semisynthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin [[Image:PODO.png|thumb|right|50 px|Chemical structure of podophyllotoxin]] (etoposide) that demonstrates antitumor activity by inhibiting DNA topoisomerase II, thereby inhibiting DNA re-ligation which lead to apoptosis of the cancer cell and also, to describe the mechanisms of resistance of etoposide. | ||
| + | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
==INTRODUCTION == | ==INTRODUCTION == | ||
The research team described the structural basis by which an anticancer drug etoposide kills cancer cells by interacting with its cellular targets human DNA topoisomerase type II<ref>PMID: 21778401</ref>. In the close-up representation of the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/21'>etoposide-binding site(s),</scene> cartoon-and-stick representation shows the insertion of two etoposide molecules into two cleavage sites [etoposide surrounded by orange mesh that represent active site (etoposide in red & grey representation), the DNA chain is in red and blue, and the magnesium is in green]. | The research team described the structural basis by which an anticancer drug etoposide kills cancer cells by interacting with its cellular targets human DNA topoisomerase type II<ref>PMID: 21778401</ref>. In the close-up representation of the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/21'>etoposide-binding site(s),</scene> cartoon-and-stick representation shows the insertion of two etoposide molecules into two cleavage sites [etoposide surrounded by orange mesh that represent active site (etoposide in red & grey representation), the DNA chain is in red and blue, and the magnesium is in green]. | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 19 November 2012
Human topoisomerase IIbeta in complex with DNA and etoposide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117
- ↑ Kathryn L. Gilroy, Chrysoula Leontiou, Kay Padget, Jeremy H. Lakey and Caroline A. Austin* "mAMSA resistant human topoisomerase IIβ mutation G465D has reduced ATP hydrolysis activity” Oxford JournalsLife Sciences Nucleic Acids Research Volume 34, Issue 5Pp. 1597-1607. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl057
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117