Sandbox Reserved 390
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==INTRODUCTION == | ==INTRODUCTION == | ||
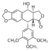
| - | The research team described the structural basis by which an anticancer drug etoposide kills cancer cells by interacting with its cellular targets human DNA topoisomerase type II<ref>PMID: 21778401</ref>. In the close-up representation of the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/21'>etoposide-binding site(s),</scene> cartoon-and-stick representation shows the insertion of two etoposide molecules into two cleavage sites [etoposide surrounded by orange mesh that represent active site (etoposide in red & grey representation), the DNA chain is in red and blue, and the magnesium is in green]. | + | The research team described the structural basis by which an anticancer drug etoposide kills cancer cells by interacting with its cellular targets human DNA topoisomerase type II<ref>PMID: 21778401</ref>. In the close-up representation of the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/21'>etoposide-binding site(s),</scene> cartoon-and-stick representation shows the insertion of two etoposide molecules into two cleavage sites [etoposide surrounded by orange mesh that represent active site (etoposide in red & grey representation), the DNA chain is in red and blue, and the magnesium is in green]. The neighboring magnesium’s are believed to be use at both the ATP-binding domain and in the cleavage core. In the nucleotide-binding pocket magnesium has been shown to contact all of the phosphate groups and it’s possible that the change in magnesium can be linked to a diminishing in the nucleotide-binding pocket. |
==ENZYME== | ==ENZYME== | ||
Type II topoisomerases (TOP2s) are abundant enzymes that play an essential role in <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/5'>DNA</scene> replication and transcription and are important targets for cancer chemotherapeutic drugs. These enzymes briefly cleave a pair of opposing phosphodiester bonds four base pairs apart, generating a TOP2-DNA cleavage complex. | Type II topoisomerases (TOP2s) are abundant enzymes that play an essential role in <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/5'>DNA</scene> replication and transcription and are important targets for cancer chemotherapeutic drugs. These enzymes briefly cleave a pair of opposing phosphodiester bonds four base pairs apart, generating a TOP2-DNA cleavage complex. | ||
Revision as of 23:09, 19 November 2012
Human topoisomerase IIbeta in complex with DNA and etoposide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117
- ↑ Kathryn L. Gilroy, Chrysoula Leontiou, Kay Padget, Jeremy H. Lakey and Caroline A. Austin* "mAMSA resistant human topoisomerase IIβ mutation G465D has reduced ATP hydrolysis activity” Oxford JournalsLife Sciences Nucleic Acids Research Volume 34, Issue 5Pp. 1597-1607. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl057
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117