This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 390
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==COMPOUND ACTIVE SITE== | ==COMPOUND ACTIVE SITE== | ||
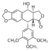
| - | This molecule has 36 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/3'>alpha helices</scene> represented with magenta helices and 40 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/2'>beta sheets</scene> represented with blue arrows in the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/4'>secondary structures</scene>. At the active site we can see how the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/14'>ligand</scene> (in green) is stabilized. The detail view of the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/5'>active site</scene> show how the ligand is stabilized by amino acid <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Arg/1'>arginine</scene> (at position 503B in blue), <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/4'>aspartic acid </scene> (at position 479B in yellow with hydrogen bond interaction), <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Gln/1'>glutamine</scene> (at position 778B in purple), also by nucleoside <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/7'>thymidine</scene>(in light blue at position 9F) and <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/6'>deoxyguanosine</scene> (in green at possition 13D showing a Pi-Pi interaction) | + | This molecule has 36 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/3'>alpha helices</scene> represented with magenta helices and 40 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/2'>beta sheets</scene> represented with blue arrows in the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/4'>secondary structures</scene>. At the active site we can see how the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Top/14'>ligand</scene> (in green) is stabilized. The detail view of the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/5'>active site</scene> show how the ligand is stabilized by amino acid <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Arg/1'>arginine</scene> (at position 503B in blue), <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/4'>aspartic acid </scene> (at position 479B in yellow with hydrogen bond interaction), <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/Gln/1'>glutamine</scene> (at position 778B in purple), also by nucleoside <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/7'>thymidine</scene> (in light blue at position 9F) and <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_390/New/6'>deoxyguanosine</scene> (in green at possition 13D showing a Pi-Pi interaction) |
==ETOPOSIDE RESISTANCE== | ==ETOPOSIDE RESISTANCE== | ||
Revision as of 00:27, 20 November 2012
Human topoisomerase IIbeta in complex with DNA and etoposide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117
- ↑ Kathryn L. Gilroy, Chrysoula Leontiou, Kay Padget, Jeremy H. Lakey and Caroline A. Austin* "mAMSA resistant human topoisomerase IIβ mutation G465D has reduced ATP hydrolysis activity” Oxford JournalsLife Sciences Nucleic Acids Research Volume 34, Issue 5Pp. 1597-1607. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl057
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117