This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 390
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
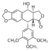
The interplay between the protein, the DNA, and the drug explains the structure-activity relations of etoposide derivatives and the molecular basis of drug-resistant mutations. This resistance occurs via two mechanisms: '''1)''' Decreased accumulation via increased P-glycoprotein; and '''2)''' Changes in target proteins (mutation or decreased expression of topoisomerase II or decreased apoptosis due to mutation of p53). | The interplay between the protein, the DNA, and the drug explains the structure-activity relations of etoposide derivatives and the molecular basis of drug-resistant mutations. This resistance occurs via two mechanisms: '''1)''' Decreased accumulation via increased P-glycoprotein; and '''2)''' Changes in target proteins (mutation or decreased expression of topoisomerase II or decreased apoptosis due to mutation of p53). | ||
| - | '''1.''' Decreased accumulation via increased P-glycoprotein | + | '''1.''' Decreased accumulation via increased P-glycoprotein (a multidrug resistance): This drug resistance mechanism is characterized by decreased intracellular accumulation of drug facilitated by overexpression of the human multidrug resistance (mdrl) gene, causing overproduction of P-glycoprotein. This cell membrane protein acts as an export pump for a wide variety of unrelated foreign natural products. By maintaining lower intracellular levels of drug, lower drug concentration would be available to the target, which is topoisomerase II. |
'''2.''' Changes in target proteins: This mechanism relates directly to the target enzyme; Either low enzyme levels or altered sensitivity of the enzyme for the drug confers resistance to that drug. This mechanism also confers a form of multidrug resistance; in that resistance to one topoisomerase II inhibitor through decreased or altered topoisomerase activity generally translates into resistance to most other topoisomerase II inhibitors. | '''2.''' Changes in target proteins: This mechanism relates directly to the target enzyme; Either low enzyme levels or altered sensitivity of the enzyme for the drug confers resistance to that drug. This mechanism also confers a form of multidrug resistance; in that resistance to one topoisomerase II inhibitor through decreased or altered topoisomerase activity generally translates into resistance to most other topoisomerase II inhibitors. | ||
Revision as of 02:53, 20 November 2012
Human topoisomerase IIbeta in complex with DNA and etoposide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117
- ↑ Kathryn L. Gilroy, Chrysoula Leontiou, Kay Padget, Jeremy H. Lakey and Caroline A. Austin* "mAMSA resistant human topoisomerase IIβ mutation G465D has reduced ATP hydrolysis activity” Oxford JournalsLife Sciences Nucleic Acids Research Volume 34, Issue 5Pp. 1597-1607. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl057
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117