1qrq
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="1qrq" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1qrq, resolution 2.80Å" /> '''STRUCTURE OF A VOLTA...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1qrq.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1qrq" size=" | + | [[Image:1qrq.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1qrq" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="1qrq, resolution 2.80Å" /> | caption="1qrq, resolution 2.80Å" /> | ||
'''STRUCTURE OF A VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT K+ CHANNEL BETA SUBUNIT'''<br /> | '''STRUCTURE OF A VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT K+ CHANNEL BETA SUBUNIT'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
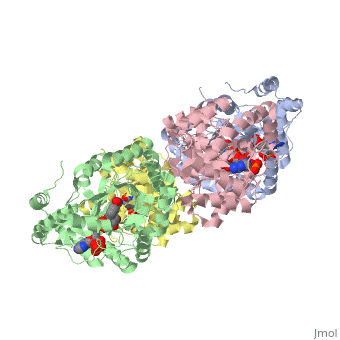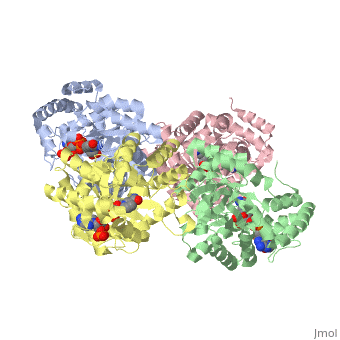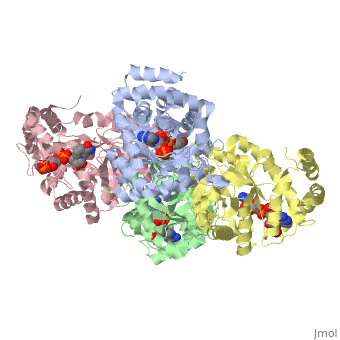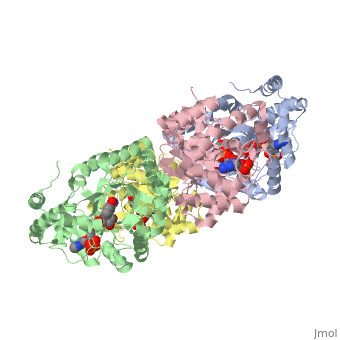
| - | The integral membrane subunits of many voltage-dependent potassium | + | The integral membrane subunits of many voltage-dependent potassium channels are associated with an additional protein known as the beta subunit. One function of beta subunits is to modify K+ channel gating. We have determined the structure of the conserved core of mammalian beta subunits by X-ray crystallography at 2.8 A resolution. Like the integral membrane component of K+ channels, beta subunits form a four-fold symmetric structure. Each subunit is an oxidoreductase enzyme complete with a nicotinamide co-factor in its active site. Several structural features of the enzyme active site, including its location with respect to the four-fold axis, imply that it may interact directly or indirectly with the K+ channel's voltage sensor. This structure suggests a mechanism for coupling membrane electrical excitability directly to chemistry of the cell. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1QRQ is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rattus_norvegicus Rattus norvegicus] with NDP as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1QRQ is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rattus_norvegicus Rattus norvegicus] with <scene name='pdbligand=NDP:'>NDP</scene> as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1QRQ OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Category: Rattus norvegicus]] | [[Category: Rattus norvegicus]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Gulbis, J | + | [[Category: Gulbis, J M.]] |
[[Category: MacKinnon, R.]] | [[Category: MacKinnon, R.]] | ||
[[Category: Mann, S.]] | [[Category: Mann, S.]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category: voltage-dependent potassium channel]] | [[Category: voltage-dependent potassium channel]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 14:43:00 2008'' |
Revision as of 12:43, 21 February 2008
|
STRUCTURE OF A VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT K+ CHANNEL BETA SUBUNIT
Overview
The integral membrane subunits of many voltage-dependent potassium channels are associated with an additional protein known as the beta subunit. One function of beta subunits is to modify K+ channel gating. We have determined the structure of the conserved core of mammalian beta subunits by X-ray crystallography at 2.8 A resolution. Like the integral membrane component of K+ channels, beta subunits form a four-fold symmetric structure. Each subunit is an oxidoreductase enzyme complete with a nicotinamide co-factor in its active site. Several structural features of the enzyme active site, including its location with respect to the four-fold axis, imply that it may interact directly or indirectly with the K+ channel's voltage sensor. This structure suggests a mechanism for coupling membrane electrical excitability directly to chemistry of the cell.
About this Structure
1QRQ is a Single protein structure of sequence from Rattus norvegicus with as ligand. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel beta subunit., Gulbis JM, Mann S, MacKinnon R, Cell. 1999 Jun 25;97(7):943-52. PMID:10399921
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 14:43:00 2008