|
Introduction
Obscurin is a giant protein expressed in striated muscle cells. It`s one of the three giant scaffold proteins of the striated muscles (the others are titin and nebulin [1] the encoding gene is localized on chromosome 1 (1q42) and the protein product is about 800 kDa with multiple splice variants of different sizes. The protein architecture resembles the modular organization of titin and is composed of multiple Ig-like domains and Fibronectin-like domains arranged in tandem, most of them are encoded on single exons [2]. The Obscurin gene (OBSCN) encodes for at least two splice variants, obscurin A and obscurin B[3] the common part of the two variants is composed of 67 Ig-like and fibronectin type III domains (Fn3). The COOH-terminal of the protein contains a calmodulin-binding IQ motif, an SH3 domain and a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor followed by a non-modular sequence with multiple phosphorylation sites at the extreme COOH-terminal. In the obscurin B variant, the skipping of exons 90 and 91 links the Ob67 domain to kinase exons leading to the formation of longer variants with two additional Ser/Thr kinase domains[4].
As scaffold protein of the sarcomere obscurin has several binding partners, mechanical and signaling functions; obscurin seems to be involved in the correct organization of myofibrils localized in different regions of the sarcomere at different stages of myofibrillogenesis, starting with the subsarcolemmal sarcomeres in early developing hearts [5]. In developing muscles, obscurin is predominantly found at the Z-disk. Later in development, several line of evidence showed the predominant localization of the protein in the M-band of mature striated muscles. Both localizations seem predominantly determined by the interaction with titin [6]. The presence of the GEF domain in the COOH-terminal suggests a role as a linker between sarcomeric proteins and the G-protein regulated pathways in myofibrils. Moreover, an involvement of obscurin in the lateral alignment of myofibrils and the M-band associated Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR) has been suggested [7] due to the highly stable complex formed by the N-terminal domains of obscurin, the C-terminal M10 domain of titin and the linker region of myomesin, which drives the correct alignment of the M-band and SR [8] [9]. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated a peripheral localization with respect to the myofibrillar proteins, and therefore a transverse orientation of obscurin with respect to the filament axis, which can then form a link between the myofibril and the SR lipid membranes [10].
Sequence annotation
The aminoacid sequence of human Obscurin from UniProt database (Q5VST9). The sequence provided in Figure 1 is based on the analysis of the human gene in the cardiac library [11]. Based on different splice variants, 4 isoforms are predicted: 2 long isoforms, two shorter isoforms in the extremely C-terminal part are possible but currently uncharacterized.
Schematic domain structure
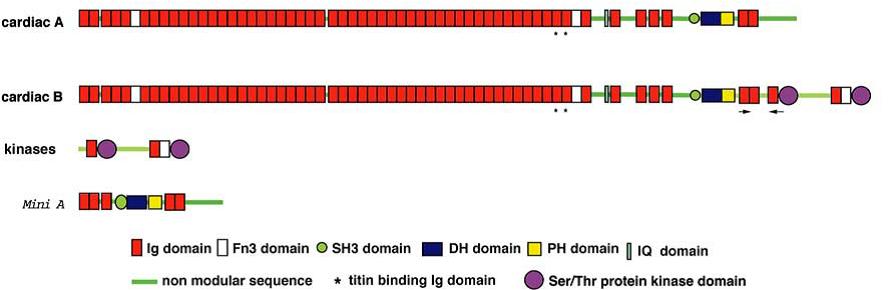 Schematic representation of obscurin domains in different isoforms according to Fukuzawa et al., 2005 [12]
Schematic representation of obscurin domains in different isoforms according to Fukuzawa et al., 2005 [12]
Protein structure
Obscurin is ~800kDa protein expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Its modular structure resembles the architecture of titin, indeed the NH2-terminal half of the protein consists of 49 Ig-like domains (with the characteristic β-sandwich shape) and 2 Fn3 domains, each ones with a length of 88-92 amino acids residues and no linker sequences between subsequent domains (except between Ob2-Ob3 and Ob24-Ob25). Two clusters of these Ig domains are 70-90% homologous at the protein level; these are Ob36-42 and Ob9-18. As for the other sarcomeric proteins the Ig domains present a highly stable structural scaffold that is necessary for the mechanical stability and a versatile surface which fits well with the role of binding site for other proteins [13]. The COOH-terminus shows a less ordered architecture with an non-modular 417 amino acid sequence with several consensus phosphorylation motifs for ERK-kinase (SPXR) [14]. A PH domain is located upstream of the last tandem Ig domains Ob56-57, very close to the DH/RhoGEF domain. After the Ob51 Ig domain a non-modular structure includes an IQ domain, so called for the conserved Ile-Gln that is a well-characterized binding motif for calmodulin or calmodulin-like protein as myosin light chain. In the isoform obscurin B an additional COOH-terminal part includes two more Ser/Thr Kinase domains, 2 Ig like domains and an Fn3 domain [15]. This isoform does not include the extremely COOH-terminal with non-modular structure that characterized the isoform A.
PDB entries for solved obscurin domain structures
1v1c - Solution structure os SH3 domain of obscurin, residues 5601-5668
2cr6 – Solution structure of the Ig domain (2998-3100) of human obscurin
2dku – Solution structure of the third Ig-like domain of human KIAA1556 protein
2dm7 – Solution structure of the 14th Ig-like domain of human KIAA1556 protein
2e7b – Solution structure of the 6th Ig-like domain from human KIAA1556
2gqh – Solution structure of the 15th Ig-like domain of human KIAA1556 protein
2edf – Solution structure of the second Ig-like domain (2826-2915) from human obscurin
2edh – Solution structure of the PDz domain (3614-3713) from human obscurin
2edl – Solution structure of the Ig-like domain (3801-3897) of human obscurin
2edq – Solution structure of the Ig-like domain (3713-3806) of human obscurin
2edr – Solution structure of the Ig-like domain (3361-3449) of human obscurin
2edw – Solution structure of the I-set domain (3537-3630) of human obscurin
2eny – Solution structure of the Ig-like domain (2735-2825) of human obscurin
2eo1 – Solution structure of the Ig-like domain of human OBSCN protein
2yz8 – Crystal structure of the 32th Ig-like domain of human obscurin (KIAA1556)
Obscurin binding partners in the sarcomere
Obscurin binding partners in the sarcomere
The main feature of the giant scaffold proteins of the sarcomere is to be involved in several interactions with the other proteins that form the muscle cytoskeleton, these networks are essential to obtain the mechanical stability and strength resistance required in muscle contractions. The first documented interaction of obscurin is detected in the Z-disk, between Titin Ig domains Z9/Z10 and obscurin Ig domains Ob 58/59 [16] (in according with the new nomenclature proposed by Fukuzawa et al. [17]); this observation is in contrast with the prevalent M-band localization in the adult skeletal muscle and the predicted maximum extension achieved by the complete elongation of the protein is not sufficient to cover the distance between Z-disk and M-band. Despite that, obscurin-titin complex in the Z-disk is formed during myofibrillogenesis and seems one of the key events for the correct assembly of the thin filaments. The same binding site is able to interact with the Ig-21 domain of the smaller titin isoform Novex-3 [18]; this protein span from the Z-disk to the I-band and seems to form a dynamic complex with obscurin that moves out of the Z-disk with the increasing length of the sarcomere. In adult myocytes obscurin has a prominent localization in the M-band [19]; the three extremely NH2-terminal Ig domain of obscurin binds the titin COOH-terminal domain M10 while Ig3 interact with the linker region between myomesin My4 and My5 [20]. The correct targeting of obscurin at the M-band seems to depend on these interactions, in agreement with the protein stabilizing role of the entire M-bands complex.
The interactions with different isoforms of membrane-associated proteins ankyrin (Ank1.5, Ank1.9, Ank2.2) suggest a key role for obscurin in the linkage of the SR to the myofibrils cytoskeleton [21]; the correct alignment of these crucial structures in myocytes has been an intriguing task and obscurin seems to play a pivotal role [22]. Showing the direct binding of integral membrane proteins with a sarcomeric component, a bridge has been provided on the linkage between lipidic membranes and mechanical apparatus assemblies during myofibrillogenesis. Obscurin is the major ligand of the cytoplasmic domain of Ank1.5 although different ankyrin proteins are able to bind with different affinities the COOH-terminal region of obscurin. Ank1.5 shows the strongest obscurin binding capacity with an affinity of 130 nM, however controversial data on the binding region due to the presence of multiple ankyrin binding sites on obscurin are available [23] [24].
The obscurin GEF domain is one of the most intriguing feature of this protein; GEF proteins have the ability to activates small GTPase involved in strictly regulated signaling pathways suggesting an obscurin role as a signal regulatory protein. This domain is able to bind the protein RanBP9 that is also able to interact with two NH2-terminal domains of titin [25]. This interaction takes place in the Z-disk and although there are no clear evidences, the interaction between titin and obscurin seems involved in the correct integration and maintenance of the Z-disk during myofibrillogenesis. Also the PH domain has a role in the GTP pathway regulation; this domain is able to bind the mammalian protein RhoA in tandem with DH domain. This interaction takes place in the M-band and activates the effector Rho kinase (ROCKs) [26]; this is not the only binding partner of the obscurin GEF domain, indeed it also interacts with the small GTPase TC10 [27].
Obscurin knockout mice and proposed physiological roles
In order to fully investigate the role of obscurin in vivo, mice knockout for OBSCN gene have been generated [28]. Despite the intriguingly expression pattern of this protein during myofibrillogenesis, with the protein localizing in both Z-disk and M-band, the lack of obscurin doesn’t affect the correct Z-disk organization. This is probably due to the redundancy of function between the N-terminal Ig domain of obscurin and obscurin like-1 [29]. On the other hand Kontrogianni-Kostantopoulos et al. proposed an essential role for obscurin not only in the SR anchorage to the sarcomere periphery via the interaction with ankyrin protein family [30], but also in the M-band organization and the myosin filament assembly in the A-band region [31].
Phatology
Up to date the involvement if obscurin in myopathies has been reported in the development of hereditary cardiac or skeletal muscle myopathies in human [32] [33], even though the knock-out mice failed to show typical signs of cardiomyophaties. Therefore the role of the protein in diseases remains unclear.
References
- ↑ Yap SV, Vafiadaki E, Strong J, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A. HAX-1: a multifaceted antiapoptotic protein localizing in the mitochondria and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of striated muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1266-79. Epub 2009 Nov 11. PMID:19913549 doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.028
- ↑ Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M. Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):123-36. PMID:11448995
- ↑ Fukuzawa A, Idowu S, Gautel M. Complete human gene structure of obscurin: implications for isoform generation by differential splicing. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2005;26(6-8):427-34. PMID:16625316 doi:10.1007/s10974-005-9025-6
- ↑ Fukuzawa A, Idowu S, Gautel M. Complete human gene structure of obscurin: implications for isoform generation by differential splicing. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2005;26(6-8):427-34. PMID:16625316 doi:10.1007/s10974-005-9025-6
- ↑ Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M. Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):123-36. PMID:11448995
- ↑ Fukuzawa A, Lange S, Holt M, Vihola A, Carmignac V, Ferreiro A, Udd B, Gautel M. Interactions with titin and myomesin target obscurin and obscurin-like 1 to the M-band: implications for hereditary myopathies. J Cell Sci. 2008 Jun 1;121(Pt 11):1841-51. Epub 2008 May 13. PMID:18477606 doi:10.1242/jcs.028019
- ↑ Lange S, Ouyang K, Meyer G, Cui L, Cheng H, Lieber RL, Chen J. Obscurin determines the architecture of the longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 2009 Aug 1;122(Pt 15):2640-50. Epub 2009 Jul 7. PMID:19584095 doi:10.1242/jcs.046193
- ↑ Fukuzawa A, Lange S, Holt M, Vihola A, Carmignac V, Ferreiro A, Udd B, Gautel M. Interactions with titin and myomesin target obscurin and obscurin-like 1 to the M-band: implications for hereditary myopathies. J Cell Sci. 2008 Jun 1;121(Pt 11):1841-51. Epub 2008 May 13. PMID:18477606 doi:10.1242/jcs.028019
- ↑ Yap SV, Vafiadaki E, Strong J, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A. HAX-1: a multifaceted antiapoptotic protein localizing in the mitochondria and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of striated muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1266-79. Epub 2009 Nov 11. PMID:19913549 doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.028
- ↑ Lange S, Ouyang K, Meyer G, Cui L, Cheng H, Lieber RL, Chen J. Obscurin determines the architecture of the longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 2009 Aug 1;122(Pt 15):2640-50. Epub 2009 Jul 7. PMID:19584095 doi:10.1242/jcs.046193
- ↑ Nemes A, Geleijnse ML, van Geuns RJ, Caliskan K, Michels M, Soliman OI, McGhie JS, ten Cate FJ. Evaluation of pericardial hydatid cysts by different echocardiographic imaging modalities. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Oct;22(5):647-51. Epub 2006 Apr 20. PMID:16625312 doi:10.1007/s10554-006-9089-4
- ↑ Nemes A, Geleijnse ML, van Geuns RJ, Caliskan K, Michels M, Soliman OI, McGhie JS, ten Cate FJ. Evaluation of pericardial hydatid cysts by different echocardiographic imaging modalities. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Oct;22(5):647-51. Epub 2006 Apr 20. PMID:16625312 doi:10.1007/s10554-006-9089-4
- ↑ Otey CA, Dixon R, Stack C, Goicoechea SM. Cytoplasmic Ig-domain proteins: cytoskeletal regulators with a role in human disease. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Aug;66(8):618-34. PMID:19466753 doi:10.1002/cm.20385
- ↑ Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M. Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):123-36. PMID:11448995
- ↑ Nemes A, Geleijnse ML, van Geuns RJ, Caliskan K, Michels M, Soliman OI, McGhie JS, ten Cate FJ. Evaluation of pericardial hydatid cysts by different echocardiographic imaging modalities. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Oct;22(5):647-51. Epub 2006 Apr 20. PMID:16625312 doi:10.1007/s10554-006-9089-4
- ↑ Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M. Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):123-36. PMID:11448995
- ↑ Nemes A, Geleijnse ML, van Geuns RJ, Caliskan K, Michels M, Soliman OI, McGhie JS, ten Cate FJ. Evaluation of pericardial hydatid cysts by different echocardiographic imaging modalities. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Oct;22(5):647-51. Epub 2006 Apr 20. PMID:16625312 doi:10.1007/s10554-006-9089-4
- ↑ Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt CC, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S. The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res. 2001 Nov 23;89(11):1065-72. PMID:11717165
- ↑ Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M. Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):123-36. PMID:11448995
- ↑ Nemes A, Geleijnse ML, van Geuns RJ, Caliskan K, Michels M, Soliman OI, McGhie JS, ten Cate FJ. Evaluation of pericardial hydatid cysts by different echocardiographic imaging modalities. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Oct;22(5):647-51. Epub 2006 Apr 20. PMID:16625312 doi:10.1007/s10554-006-9089-4
- ↑ Bagnato P, Barone V, Giacomello E, Rossi D, Sorrentino V. Binding of an ankyrin-1 isoform to obscurin suggests a molecular link between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils in striated muscles. J Cell Biol. 2003 Jan 20;160(2):245-53. Epub 2003 Jan 13. PMID:12527750 doi:10.1083/jcb.200208109
- ↑ Yap SV, Vafiadaki E, Strong J, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A. HAX-1: a multifaceted antiapoptotic protein localizing in the mitochondria and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of striated muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1266-79. Epub 2009 Nov 11. PMID:19913549 doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.028
- ↑ Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Jones EM, Van Rossum DB, Bloch RJ. Obscurin is a ligand for small ankyrin 1 in skeletal muscle. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Mar;14(3):1138-48. PMID:12631729 doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-07-0411
- ↑ Bagnato P, Barone V, Giacomello E, Rossi D, Sorrentino V. Binding of an ankyrin-1 isoform to obscurin suggests a molecular link between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils in striated muscles. J Cell Biol. 2003 Jan 20;160(2):245-53. Epub 2003 Jan 13. PMID:12527750 doi:10.1083/jcb.200208109
- ↑ Bowman AL, Catino DH, Strong JC, Randall WR, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Bloch RJ. The rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor domain of obscurin regulates assembly of titin at the Z-disk through interactions with Ran binding protein 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Sep;19(9):3782-92. Epub 2008 Jun 25. PMID:18579686 doi:10.1091/mbc.E08-03-0237
- ↑ Ford-Speelman DL, Roche JA, Bowman AL, Bloch RJ. The rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor domain of obscurin activates rhoA signaling in skeletal muscle. Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Sep;20(17):3905-17. Epub 2009 Jul 15. PMID:19605563 doi:10.1091/mbc.E08-10-1029
- ↑ Coisy-Quivy M, Touzet O, Bourret A, Hipskind RA, Mercier J, Fort P, Philips A. TC10 controls human myofibril organization and is activated by the sarcomeric RhoGEF obscurin. J Cell Sci. 2009 Apr 1;122(Pt 7):947-56. Epub 2009 Mar 3. PMID:19258391 doi:10.1242/jcs.040121
- ↑ Lange S, Ouyang K, Meyer G, Cui L, Cheng H, Lieber RL, Chen J. Obscurin determines the architecture of the longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 2009 Aug 1;122(Pt 15):2640-50. Epub 2009 Jul 7. PMID:19584095 doi:10.1242/jcs.046193
- ↑ Fukuzawa A, Lange S, Holt M, Vihola A, Carmignac V, Ferreiro A, Udd B, Gautel M. Interactions with titin and myomesin target obscurin and obscurin-like 1 to the M-band: implications for hereditary myopathies. J Cell Sci. 2008 Jun 1;121(Pt 11):1841-51. Epub 2008 May 13. PMID:18477606 doi:10.1242/jcs.028019
- ↑ Lange S, Ouyang K, Meyer G, Cui L, Cheng H, Lieber RL, Chen J. Obscurin determines the architecture of the longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 2009 Aug 1;122(Pt 15):2640-50. Epub 2009 Jul 7. PMID:19584095 doi:10.1242/jcs.046193
- ↑ Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Catino DH, Strong JC, Sutter S, Borisov AB, Pumplin DW, Russell MW, Bloch RJ. Obscurin modulates the assembly and organization of sarcomeres and the sarcoplasmic reticulum. FASEB J. 2006 Oct;20(12):2102-11. PMID:17012262 doi:10.1096/fj.06-5761com
- ↑ Arimura T, Matsumoto Y, Okazaki O, Hayashi T, Takahashi M, Inagaki N, Hinohara K, Ashizawa N, Yano K, Kimura A. Structural analysis of obscurin gene in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Oct 19;362(2):281-7. Epub 2007 Aug 13. PMID:17716621 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.183
- ↑ Fukuzawa A, Lange S, Holt M, Vihola A, Carmignac V, Ferreiro A, Udd B, Gautel M. Interactions with titin and myomesin target obscurin and obscurin-like 1 to the M-band: implications for hereditary myopathies. J Cell Sci. 2008 Jun 1;121(Pt 11):1841-51. Epub 2008 May 13. PMID:18477606 doi:10.1242/jcs.028019
|



