1s9v
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | Celiac disease, also known as celiac sprue, is a gluten-induced | + | Celiac disease, also known as celiac sprue, is a gluten-induced autoimmune-like disorder of the small intestine, which is strongly associated with HLA-DQ2. The structure of DQ2 complexed with an immunogenic epitope from gluten, QLQPFPQPELPY, has been determined to 2.2-A resolution by x-ray crystallography. The glutamate at P6, which is formed by tissue transglutaminase-catalyzed deamidation, is an important anchor residue as it participates in an extensive hydrogen-bonding network involving Lys-beta71 of DQ2. The gluten peptide-DQ2 complex retains critical hydrogen bonds between the MHC and the peptide backbone despite the presence of many proline residues in the peptide that are unable to participate in amide-mediated hydrogen bonds. Positioning of proline residues such that they do not interfere with backbone hydrogen bonding results in a reduction in the number of registers available for gluten peptides to bind to MHC class II molecules and presumably impairs the likelihood of establishing favorable side-chain interactions. The HLA association in celiac disease can be explained by a superior ability of DQ2 to bind the biased repertoire of proline-rich gluten peptides that have survived gastrointestinal digestion and that have been deamidated by tissue transglutaminase. Finally, surface-exposed proline residues in the proteolytically resistant ligand were replaced with functionalized analogs, thereby providing a starting point for the design of orally active agents for blocking gluten-induced toxicity. |
==Disease== | ==Disease== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[Category: Bergseng, E.]] | [[Category: Bergseng, E.]] | ||
[[Category: Khosla, C.]] | [[Category: Khosla, C.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Kim, C | + | [[Category: Kim, C Y.]] |
[[Category: Quarsten, H.]] | [[Category: Quarsten, H.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Sollid, L | + | [[Category: Sollid, L M.]] |
[[Category: EDO]] | [[Category: EDO]] | ||
[[Category: hla-dq2]] | [[Category: hla-dq2]] | ||
[[Category: immune system]] | [[Category: immune system]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 14:59:20 2008'' |
Revision as of 12:59, 21 February 2008
|
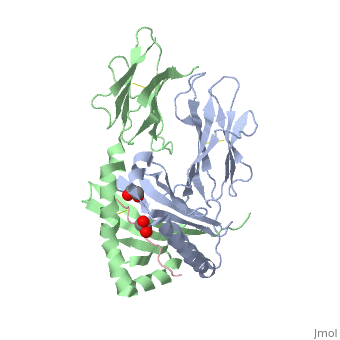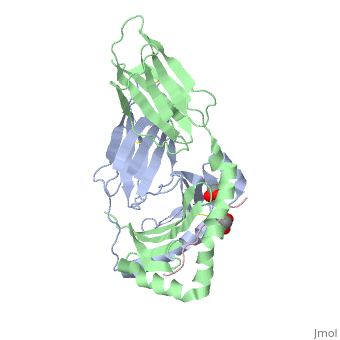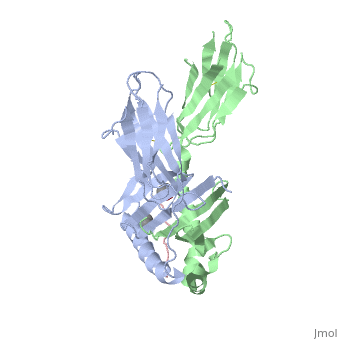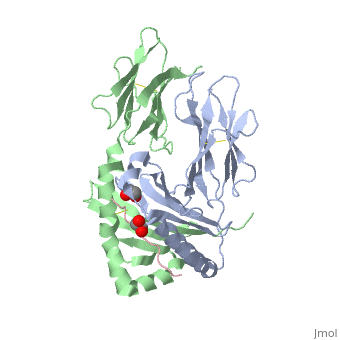
Crystal structure of HLA-DQ2 complexed with deamidated gliadin peptide
Contents |
Overview
Celiac disease, also known as celiac sprue, is a gluten-induced autoimmune-like disorder of the small intestine, which is strongly associated with HLA-DQ2. The structure of DQ2 complexed with an immunogenic epitope from gluten, QLQPFPQPELPY, has been determined to 2.2-A resolution by x-ray crystallography. The glutamate at P6, which is formed by tissue transglutaminase-catalyzed deamidation, is an important anchor residue as it participates in an extensive hydrogen-bonding network involving Lys-beta71 of DQ2. The gluten peptide-DQ2 complex retains critical hydrogen bonds between the MHC and the peptide backbone despite the presence of many proline residues in the peptide that are unable to participate in amide-mediated hydrogen bonds. Positioning of proline residues such that they do not interfere with backbone hydrogen bonding results in a reduction in the number of registers available for gluten peptides to bind to MHC class II molecules and presumably impairs the likelihood of establishing favorable side-chain interactions. The HLA association in celiac disease can be explained by a superior ability of DQ2 to bind the biased repertoire of proline-rich gluten peptides that have survived gastrointestinal digestion and that have been deamidated by tissue transglutaminase. Finally, surface-exposed proline residues in the proteolytically resistant ligand were replaced with functionalized analogs, thereby providing a starting point for the design of orally active agents for blocking gluten-induced toxicity.
Disease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Celiac disease, susceptibility to OMIM:[146880], Celiac disease, susceptibility to OMIM:[604305], Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, variant, resistance to OMIM:[604305], Multiple sclerosis, susceptibility to OMIM:[604305]
About this Structure
1S9V is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens with as ligand. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Structural basis for HLA-DQ2-mediated presentation of gluten epitopes in celiac disease., Kim CY, Quarsten H, Bergseng E, Khosla C, Sollid LM, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 23;101(12):4175-9. Epub 2004 Mar 12. PMID:15020763
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 14:59:20 2008
Categories: Homo sapiens | Protein complex | Bergseng, E. | Khosla, C. | Kim, C Y. | Quarsten, H. | Sollid, L M. | EDO | Hla-dq2 | Immune system