We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox UC 19
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
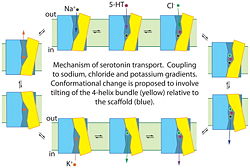
[[Image:Mecanismo.jpg|250px|center]] | [[Image:Mecanismo.jpg|250px|center]] | ||
'''Proposed mechanism for serotonin transport by SERT'''. Binding of serotonin (5-HT+), Na+ and Cl− to the transporter from the cell exterior allows a conformational change, shown here as the tilting of a 4-helix bundle (yellow), that closes the extracellular substrate permeation pathway and opens a cytoplasmic pathway. After dissociation of Na+, Cl− and 5-HT+ to the cytoplasm, the transporter binds a K+ ion (or a proton, see (96)) to allow the reverse conformational change, leading to extracellular K+ dissociation and another cycle of transport. | '''Proposed mechanism for serotonin transport by SERT'''. Binding of serotonin (5-HT+), Na+ and Cl− to the transporter from the cell exterior allows a conformational change, shown here as the tilting of a 4-helix bundle (yellow), that closes the extracellular substrate permeation pathway and opens a cytoplasmic pathway. After dissociation of Na+, Cl− and 5-HT+ to the cytoplasm, the transporter binds a K+ ion (or a proton, see (96)) to allow the reverse conformational change, leading to extracellular K+ dissociation and another cycle of transport. | ||
| - | + | Sesdsdfsdfasdfsdafasdfsdf <StructureSection load='2q6h' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of the SERT Homologue LeuT, ([[2q6h]])' scene='Serotonin_Transporter/Opening/2'>sdfsdfdfsdfsdfsdfsdf | |
Revision as of 20:06, 19 December 2012
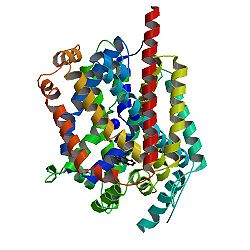
Leucine transporter LeuT in complex with sertraline
Recent high-resolution crystal structures of several transporters from protein families that were previously thought to be unrelated show common structural features indicating a large structural family representing transporters from all kingdoms of life.
Content
| |||||||||||