We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox UC 10
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
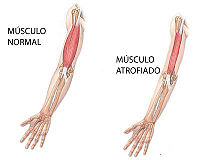
== N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN == | == N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN == | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1dq8' size='500' side='right' caption='N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN (PDB entry [[1dxx]])' scene=''>Dystrophin is an essential component of skeletal muscle cells. Its N-terminal domain binds to F-actin and its C terminus binds to the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (DAG) complex in the membrane.<scene name='1xjo/Active_site/3'>active site</scene> | + | <StructureSection load='1dq8' size='500' side='right' caption='N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN (PDB entry [[1dxx]])' scene=''>[[Image:1dxx.png|200px|left|thumb|Crystal Structure of Human dystrophin, [[1dxx]]]]Dystrophin is an essential component of skeletal muscle cells. Its N-terminal domain binds to F-actin and its C terminus binds to the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (DAG) complex in the membrane.<scene name='1xjo/Active_site/3'>active site</scene> |
[[Image:1dxx.png|200px|center|thumb|Crystal Structure of Human dystrophin, [[1dxx]]]] | [[Image:1dxx.png|200px|center|thumb|Crystal Structure of Human dystrophin, [[1dxx]]]] | ||
Revision as of 20:19, 19 December 2012
N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN
| |||||||||||
QUIZ TIME !!
Referencias
- ↑ Norwood FL, Sutherland-Smith AJ, Keep NH, Kendrick-Jones J. The structure of the N-terminal actin-binding domain of human dystrophin and how mutations in this domain may cause Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy. Structure. 2000 May 15;8(5):481-91. PMID:10801490
- ↑ Nadeau D, Marchand C. Change in the kinetics of sulphacetamide tissue distribution in Walker tumor-bearing rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 1975 Nov-Dec;3(6):565-76. PMID:1234
- ↑ Rubinstein MH. A new granulation method for compressed tablets [proceedings]. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;28 Suppl:67P. PMID:12345