We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox UC 10
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
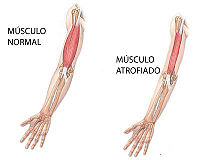
CONCLUSIONS: The dystrophin ABD structure reveals a previously uncharacterised arrangement of the CH domains within the ABD. This observation has implications for the mechanism of actin binding by dystrophin and related proteins. Examining the position of three pathogenic missense mutations within the structure suggests that they exert their effects through misfolding of the ABD, rather than through disruption of the binding to F-actin<ref>PMID 10801490</ref>[[Image:imag1gonzalo.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Comparacion de la degeneracion muscular, [[1dxx]]]] | CONCLUSIONS: The dystrophin ABD structure reveals a previously uncharacterised arrangement of the CH domains within the ABD. This observation has implications for the mechanism of actin binding by dystrophin and related proteins. Examining the position of three pathogenic missense mutations within the structure suggests that they exert their effects through misfolding of the ABD, rather than through disruption of the binding to F-actin<ref>PMID 10801490</ref>[[Image:imag1gonzalo.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Comparacion de la degeneracion muscular, [[1dxx]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
== Escenas == | == Escenas == | ||
| + | |||
<scene name='Sandbox_UC_10/Conservacion_evolutiva/1'>Zonas conservadas evolutivamente</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_UC_10/Conservacion_evolutiva/1'>Zonas conservadas evolutivamente</scene> | ||
{{Template:ColorKey_ConSurf}} | {{Template:ColorKey_ConSurf}} | ||
| - | + | <scene name='Sandbox_UC_10/Conservacion_evolutiva2/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | |
<scene name='Sandbox_UC_10/Escena2/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_UC_10/Escena2/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Current revision
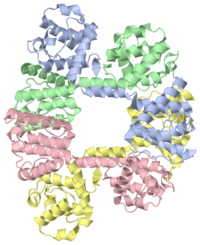
N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN
| |||||||||||
QUIZ TIME !!
Referencias
- ↑ Norwood FL, Sutherland-Smith AJ, Keep NH, Kendrick-Jones J. The structure of the N-terminal actin-binding domain of human dystrophin and how mutations in this domain may cause Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy. Structure. 2000 May 15;8(5):481-91. PMID:10801490