Sandbox Reserved 705
From Proteopedia
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
The ERM proteins are regulated by changing from a closed conformation to an open, active state. This is due to intramolecular head–tail interactions,and also to interactions between their head and α-helical domains<ref name="utile2">PMID:22012890</ref>.Conformational changes modify the intramolecular contacts, allowing these proteins to bind to their partners. | The ERM proteins are regulated by changing from a closed conformation to an open, active state. This is due to intramolecular head–tail interactions,and also to interactions between their head and α-helical domains<ref name="utile2">PMID:22012890</ref>.Conformational changes modify the intramolecular contacts, allowing these proteins to bind to their partners. | ||
Phosphorylation of a C-terminal threonine by Rho kinase and binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and protein partners, is necessary for full activation of ERM proteins <ref>PMID:14993232</ref>. They disrupt the head to tail interactions. The phosphorylations and/binding(s) determine the cellular localization and the cellular function of each specific ERM protein. | Phosphorylation of a C-terminal threonine by Rho kinase and binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and protein partners, is necessary for full activation of ERM proteins <ref>PMID:14993232</ref>. They disrupt the head to tail interactions. The phosphorylations and/binding(s) determine the cellular localization and the cellular function of each specific ERM protein. | ||
| - | '''On précise que c'est le binding de PIP2 ?'''<ref> | + | '''On précise que c'est le binding de PIP2 ?'''<ref>PMCID:3133355</ref> |
Merlin shares certain properties with the ERM family : they both have a subcellular localization to cortical actin structures and they both bind to adhesion receptors.These receptors are CD44 <ref>PMID:9330869</ref> and E-cadherin <ref>PMID:12695331</ref>. | Merlin shares certain properties with the ERM family : they both have a subcellular localization to cortical actin structures and they both bind to adhesion receptors.These receptors are CD44 <ref>PMID:9330869</ref> and E-cadherin <ref>PMID:12695331</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 23 December 2012
Human Merlin FERM Domain
Contents |
Introduction
The merlin-1 protein is encoded by the Neurofibromatosis-2(Nf2) gene. Neurofibromatosis type 2 is an inheritable autosomal dominant disorder. Patients develop tumors of the nervous system : meningiomas, schwannomas, neurofibromas.[1] Mutations in the Nf2 gene lead to tumor proliferation as well in humans as in mice. Therefore Merlin-1 is a tumor suppressor protein. To know more about the type of Nf2 mutations and the related deseases you can follow the link that leads you to the Portal to Swiss-Prot diseases and variants the Portal to Swiss-Prot diseases and variants
ERM Proteins
The merlin-1 protein belongs to the band 4.1 superfamily of membrane-cytoskeletal linkers [2]. Within this superfamily merlin-1 is closer to ezrin,radixin and moesin (the ERM proteins). ERM proteins link Adhrens Junctions to the actin cytoskeleton,and are able to remodel Adherens Junctions during epithelial morphogenesis. They also maintain the organization of apical surfaces on the plasma membrane [3]. All these proteins have an about 300-residue globular plasma membrane-associated FERM domain(four-point-one ezrin, radixin, moesin).This FERM domain is a highly conserved domain. This domain is divided into three subdomains (F1, F2, and F3). ERM proteins are composed of a FERM domain followed by a long region with a high α-helical propensity and terminating in a C-terminal domain[4].
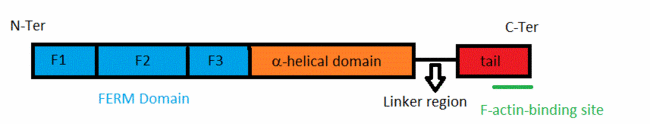
The acitivity of ERM proteins is caused by the association of different regions within the protein. Le domain FERM ne lie pas l'hélicale alpha? la head c pa le domaine FERM? Ce serait plus simple et il faudrai le citer pour que ça ait du sens The ERM proteins are regulated by changing from a closed conformation to an open, active state. This is due to intramolecular head–tail interactions,and also to interactions between their head and α-helical domains[5].Conformational changes modify the intramolecular contacts, allowing these proteins to bind to their partners. Phosphorylation of a C-terminal threonine by Rho kinase and binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and protein partners, is necessary for full activation of ERM proteins [6]. They disrupt the head to tail interactions. The phosphorylations and/binding(s) determine the cellular localization and the cellular function of each specific ERM protein. On précise que c'est le binding de PIP2 ?[7]
Merlin shares certain properties with the ERM family : they both have a subcellular localization to cortical actin structures and they both bind to adhesion receptors.These receptors are CD44 [8] and E-cadherin [9]. However Merlin-1 has some properties not shared with ERM proteins.
Specificity of merlin FERM domain
| |||||||
| 3u8z, resolution 2.64Å () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene: | NF2, SCH (Homo sapiens) | ||||||
| |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
As showed in the default scene, the structure 3U8Z has in total 4 chains. These are represented by 1 sequence-unique entity. The chains A,B and C possess 9
Alpha Helices and 15 Beta Strands and the chain D has only 9 Alpha Helicesand 14 Beta Strands . You can visualize their .
Structural differences
The overall architecture of merlin is similar to that of ERM proteins. Indeed they have almost the same organization : a FERM domain,a central α-helical rod, but lack a C-terminal actin-binding site[5]. The closed complex of the Merlin proteins corresponds to the tumor suppressor-active form. As the N-terminus FERM domain and C-terminus are maintained associated, Merlin is in a closed conformation and is able to promote nuclear translocation and inhibt growth[10]. More precisly,binding of the tail provokes dimerization and unfurling of the F2 motif of the FERM domain.The “closed” complex of merlin-1 is in fact an “open” dimer [4]. Ser-10 and Ser-518 phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA) and/or p21-activated kinase(PAK) trigger the "closed" complex [11]. Phosphorylation by PAK and PKA at Ser 518 renders the protein inactive. Revoir et compléter la dimérisation
CD44
CD44 is a cell-surface receptor for hyaluronan (HA a ligand). When HA binds to CD44 the complex promotes tumorigenesis it means it promotes tumor invasion and metastasis. Indeed, CD44 is a receptor presents in the TA3 carcinome mammaire cells and Tr6BC1 schwannoma cells and HA allows their growth. Lire ces deux articles pour savoir s'il faut les citer[12][13] Hydrophobic repartition Polar Savoir si on montre les hydrophobes etc et leur intérêt...puisqu'on a leur répartition. Faire un schéma pour la structural difference de merlin et ERM protein pour montrer que c'est plus court. Décrire CD44 role. Qu'ajouter de plus? As tu des idées de schémas que l'on peut faire ou imiter à partir d'une publi ou je sais pas? As tu des idées de structure 3D que l'on peut montrer? Peux tu me dire s'il y a des fautes dans le texte en anglais ( ce qui est le cas je le sais^^)
Applications
J'ai trouvé un article la dessus enfin qui l'évoque^^ je rédigerais ça demain ou bientôt^^
References
- ↑ Martuza RL, Eldridge R. Neurofibromatosis 2 (bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis). N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 17;318(11):684-8. PMID:3125435 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198803173181106
- ↑ Trofatter JA, MacCollin MM, Rutter JL, Murrell JR, Duyao MP, Parry DM, Eldridge R, Kley N, Menon AG, Pulaski K, et al.. A novel moesin-, ezrin-, radixin-like gene is a candidate for the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):826. PMID:8242753
- ↑ Brault E, Gautreau A, Lamarine M, Callebaut I, Thomas G, Goutebroze L. Normal membrane localization and actin association of the NF2 tumor suppressor protein are dependent on folding of its N-terminal domain. J Cell Sci. 2001 May;114(Pt 10):1901-12. PMID:11329377
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Fehon RG, McClatchey AI, Bretscher A. Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;11(4):276-87. doi: 10.1038/nrm2866. PMID:20308985 doi:10.1038/nrm2866
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Yogesha SD, Sharff AJ, Giovannini M, Bricogne G, Izard T. Unfurling of the band 4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin (FERM) domain of the merlin tumor suppressor. Protein Sci. 2011 Oct 19. doi: 10.1002/pro.751. PMID:22012890 doi:10.1002/pro.751
- ↑ Fievet BT, Gautreau A, Roy C, Del Maestro L, Mangeat P, Louvard D, Arpin M. Phosphoinositide binding and phosphorylation act sequentially in the activation mechanism of ezrin. J Cell Biol. 2004 Mar 1;164(5):653-9. PMID:14993232 doi:10.1083/jcb.200307032
- ↑ PMCID:3133355
- ↑ Vaheri A, Carpen O, Heiska L, Helander TS, Jaaskelainen J, Majander-Nordenswan P, Sainio M, Timonen T, Turunen O. The ezrin protein family: membrane-cytoskeleton interactions and disease associations. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997 Oct;9(5):659-66. PMID:9330869
- ↑ Lallemand D, Curto M, Saotome I, Giovannini M, McClatchey AI. NF2 deficiency promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis by destabilizing adherens junctions. Genes Dev. 2003 May 1;17(9):1090-100. Epub 2003 Apr 14. PMID:12695331 doi:10.1101/gad.1054603
- ↑ Li W, Cooper J, Karajannis MA, Giancotti FG. Merlin: a tumour suppressor with functions at the cell cortex and in the nucleus. EMBO Rep. 2012 Mar;13(3):204-15. PMID:22482125
- ↑ Laulajainen M, Muranen T, Carpen O, Gronholm M. Protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of the NF2 tumor suppressor protein merlin at serine 10 affects the actin cytoskeleton. Oncogene. 2008 May 22;27(23):3233-43. Epub 2007 Dec 10. PMID:18071304 doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210988
- ↑ Morrison H, Sherman LS, Legg J, Banine F, Isacke C, Haipek CA, Gutmann DH, Ponta H, Herrlich P. The NF2 tumor suppressor gene product, merlin, mediates contact inhibition of growth through interactions with CD44. Genes Dev. 2001 Apr 15;15(8):968-80. PMID:11316791 doi:10.1101/gad.189601
- ↑ Sainio M, Zhao F, Heiska L, Turunen O, den Bakker M, Zwarthoff E, Lutchman M, Rouleau GA, Jaaskelainen J, Vaheri A, Carpen O. Neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein colocalizes with ezrin and CD44 and associates with actin-containing cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 1997 Sep;110 ( Pt 18):2249-60. PMID:9378774
External Resources
- Li Q, Nance MR, Kulikauskas R, Nyberg K, Fehon R, Karplus PA, Bretscher A, Tesmer JJ. Self-masking in an intact ERM-merlin protein: an active role for the central alpha-helical domain. J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 2;365(5):1446-59. Epub 2006 Oct 26. PMID:17134719 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.075
- Hennigan RF, Moon CA, Parysek LM, Monk KR, Morfini G, Berth S, Brady S, Ratner N. The NF2 tumor suppressor regulates microtubule-based vesicle trafficking via a novel Rac, MLK and p38(SAPK) pathway. Oncogene. 2012 Apr 23. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.135. PMID:22525268 doi:10.1038/onc.2012.135
- Sun CX, Robb VA, Gutmann DH. Protein 4.1 tumor suppressors: getting a FERM grip on growth regulation. J Cell Sci. 2002 Nov 1;115(Pt 21):3991-4000. PMID:12356905
- Johnson KC, Kissil JL, Fry JL, Jacks T. Cellular transformation by a FERM domain mutant of the Nf2 tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene. 2002 Sep 5;21(39):5990-7. PMID:12203111 doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205693
- Li Q, Nance MR, Kulikauskas R, Nyberg K, Fehon R, Karplus PA, Bretscher A, Tesmer JJ. Self-masking in an intact ERM-merlin protein: an active role for the central alpha-helical domain. J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 2;365(5):1446-59. Epub 2006 Oct 26. PMID:17134719 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.075
- Surace EI, Haipek CA, Gutmann DH. Effect of merlin phosphorylation on neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) gene function. Oncogene. 2004 Jan 15;23(2):580-7. PMID:14724586 doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207142
- Mani T, Hennigan RF, Foster LA, Conrady DG, Herr AB, Ip W. FERM domain phosphoinositide binding targets merlin to the membrane and is essential for its growth-suppressive function. Mol Cell Biol. 2011 May;31(10):1983-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00609-10. Epub 2011 Mar , 14. PMID:21402777 doi:10.1128/MCB.00609-10
- Pearson MA, Reczek D, Bretscher A, Karplus PA. Structure of the ERM protein moesin reveals the FERM domain fold masked by an extended actin binding tail domain. Cell. 2000 Apr 28;101(3):259-70. PMID:10847681
