Xavière Lornage/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
Merlin shares certain properties with the ERM family : they both have a subcellular localization to cortical actin structures and they both bind to adhesion receptors.These receptors are CD44 <ref>PMID:9330869</ref> and E-cadherin <ref>PMID:12695331</ref>. | Merlin shares certain properties with the ERM family : they both have a subcellular localization to cortical actin structures and they both bind to adhesion receptors.These receptors are CD44 <ref>PMID:9330869</ref> and E-cadherin <ref>PMID:12695331</ref>. | ||
| - | However Merlin-1 has some properties not shared with ERM proteins. | + | However Merlin-1 has some properties not shared with ERM proteins. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 23:22, 23 December 2012
Human Merlin FERM Domain
|
Contents |
Introduction
The merlin-1 protein is encoded by the Neurofibromatosis-2(Nf2) gene. Neurofibromatosis type 2 is an inheritable autosomal dominant disorder. Patients develop tumors of the nervous system : meningiomas, schwannomas, neurofibromas.[1] Mutations in the Nf2 gene lead to tumor proliferation as well in humans as in mice. Therefore Merlin-1 is a tumor suppressor protein. To know more about the type of Nf2 mutations and the related deseases you can follow the link that leads you to the Portal to Swiss-Prot diseases and variants the Portal to Swiss-Prot diseases and variants
ERM Proteins
The merlin-1 protein belongs to the band 4.1 superfamily of membrane-cytoskeletal linkers [2]. Within this superfamily merlin-1 is closer to ezrin,radixin and moesin (the ERM proteins). ERM proteins link Adhrens Junctions to the actin cytoskeleton,and are able to remodel Adherens Junctions during epithelial morphogenesis. They also maintain the organization of apical surfaces on the plasma membrane [3].
Structural organization
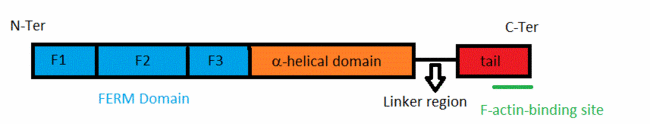
All these proteins have an about 300-residue globular plasma membrane-associated FERM domain(four-point-one ezrin, radixin, moesin).This FERM domain is a highly conserved domain. This domain is divided into three subdomains (F1, F2, and F3). ERM proteins are composed of a FERM domain followed by a long region with a high α-helical propensity and terminating in a C-terminal domain[4].
Regulation of the activity
The acitivity of ERM proteins is caused by the association of different regions within the protein. The C-terminal tail domain contains an F-actin binding site in the last 30 residues. This domain interacts with the FERM domain as an extended, meandering polypeptide beginning with a β-strand associated with β5 in F3 followed by four helices. The two first helices bind l and the two second lobe F3. The FERM-tail complex represents an inactive form of the protein in which membrane protein and active binding sites are masked.[5] The ERM proteins are regulated by changing from a closed conformation to an open, active state. This is due to severing of intramolecular head–tail interactions,and also of interactions between their FERM domain and α-helical domains[6].Conformational changes modify the intramolecular contacts, allowing these proteins to bind to their partners. The protein is in an active state.The FERM domain has a fundamental role because it allows ERM proteins to interact with integral proteins of the plasma membrane[7].
Regulators of the activity
Phosphorylation of a C-terminal threonine by Rho kinase and binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and protein partners, is necessary for full activation of ERM proteins [8]. They disrupt the head to tail interactions. The phosphorylations and/binding(s) determine the cellular localization and the cellular function of each specific ERM protein[9].
Merlin shares certain properties with the ERM family : they both have a subcellular localization to cortical actin structures and they both bind to adhesion receptors.These receptors are CD44 [10] and E-cadherin [11].
However Merlin-1 has some properties not shared with ERM proteins.