We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 714
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Structure == | ||
<Structure load='1s8o_mm1.pdb' size='400' frame='true' align='left' caption='X-ray crystal structure of hsEH' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='1s8o_mm1.pdb' size='400' frame='true' align='left' caption='X-ray crystal structure of hsEH' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structure == | ||
The Human soluble Epoxide hydrolase is a homodimer. Each subunit has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Catalytic_domains/1'>two catalytic domains</scene>, linked by a proline-rich section. | The Human soluble Epoxide hydrolase is a homodimer. Each subunit has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Catalytic_domains/1'>two catalytic domains</scene>, linked by a proline-rich section. | ||
| + | The C-terminal domain is called Cytosolic epoxide hydrolase 2: it catalyzes the trans-addition of water to epoxides in order to product glycols. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Cter_activesite/1'>active site</scene> is made of five residues. The two tyrosines (Y383 and Y466) plays a role. | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 30 December 2012
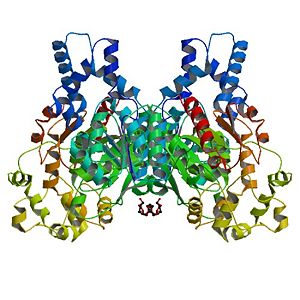
Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase: Biological assembly, 1s8o
Contents |
Overview
|
Structure
The Human soluble Epoxide hydrolase is a homodimer. Each subunit has , linked by a proline-rich section. The C-terminal domain is called Cytosolic epoxide hydrolase 2: it catalyzes the trans-addition of water to epoxides in order to product glycols. The is made of five residues. The two tyrosines (Y383 and Y466) plays a role.
Mechanism
Inhibitors
External ressources
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
DUTREUX Fabien, BONHOURE Anna

