Sandbox Reserved 715
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:1uyp asr r 500.jpg | 232 px |left|thumb|'''EC 3.2.1.26.''']] |
Revision as of 23:51, 31 December 2012
Please, do not delete or modify any text or image. Thank you.
Thermotoga maritima β-fructosidase (invertase)
Contents |
Introduction
The β-fructosidase (β-D-fructofuranosidase EC 3. 2. 1. 26.) of the thermophilic baterium Thermotoga maritima is an enzyme which hydrolyzes sucrose to release fructose and glucose. 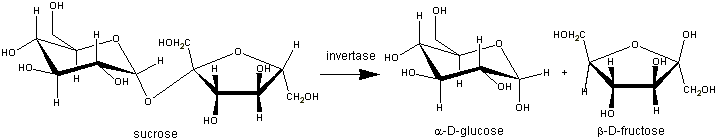
This enzyme achieves the hydrolysis with a retention molecular mechanism. Actually, the invertase hydrolyses the D-sucrose to form the D-fructose and the D-glucose. So, the substrate anomeric configuration is conserved in products. The β-fructosidase belongs to the GH32 (Glycoside hydrolysases 32) according to the sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolysases.
Glycoside Hydrolases and GH32 family
Glycoside Hydrolysases
Glycoside hydrolases (GH) constitute a widespread enzyme group presenting a huge variety of protein folds and substrate specificities. They are classified into EC 3.2.1 as enzymes catalyzing the hydrolysis of O-, N- and S-linked glycosides. The enzymatic hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds can be realised by two ways : inversion or retention of the product anomeric configuration compared with the substrate anomeric configuration. So we can classify Glycoside hydrolases according to these mechanismes. But we can alson make a classification depending on three-dimensional structure or on sequence. The classification based on sequence allowed to define more than 120 families of Glycoside hydrolases : GH9, GH14... The Thermotoga maritima β-fructosidase belongs to the GH32 family.GH32 Family
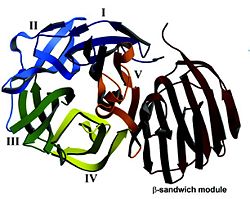
The GH32 family includes over 370 members from plants, fungi and bacteria. This family contains not only invertases but other fructofuranosidases like insulinase, transfructosidase or inulinase. Family GH32 enzymes are retaining enzymes, so the Thermotoga maritima β-fructosidase is a retaining enzyme as we said in the introduction.This molecular mechanism appears conserved in the sequences of the different GH32 family members. Members of the GH32 family share a common feature which are two important amino acid residues. These two amino acid residues constitute the catalytic machinery accountable to the glycosidic bond cleavage. And they have been identified as an aspartate situated near the N-terminus and acting as the nucleophile, and a glutamate acting as the general acide/base. The GH32 family enzymes present a particular three-dimensional structure. The core of this structure is built of a five-bladed β-propeller (I to V) appended to a β-sandwich, consisting of two sheets of six β-strands.
Thermotoga maritima β-fructosidase structure
Global organisation
The Thermotoga maritima β-fructosidase (invertase) is consists of 432 residues. One molecule of this β-fructosidase is composed, like the other GH32 family enzymes, of two modules :
- a five-bladed β-propeller module, from residu 1 to 295. It is the catalytic module.The β-strands forming the blades in the five β-propeller are stronly twisted, forming an angle of about 90° between the first and the last β-strand of a blade.
- a β-sandwich module , from residu 306 to 432, in C-terminal region.
These two modules are linked by a ten residue linker. After purification, the Thermotoga maritima invertase is a monomer in solution and have a size of about 30 kDa. A monomer of this invertase has an elleptical shape. The dimensions of this elleptical monomere are about 63 Å x 43 Å x 45 Å. And there is a negatively charged surface depression at the center of the β-propeller. But before purifcation, six copies of the invertase are rallied together. The ensemble of six bi-modular molecules are arranged into three dimers and display two-fold symetry each. A dimer is arranged around a pseudo-twofold axis and brigs the β-sandwich domain of a monomer A in contact with the β-propeller domain of a monomer b and vice-versa.