This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1tc3
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="1tc3" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1tc3, resolution 2.450Å" /> '''TRANSPOSASE TC3A1-6...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1tc3.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1tc3" size=" | + | [[Image:1tc3.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1tc3" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="1tc3, resolution 2.450Å" /> | caption="1tc3, resolution 2.450Å" /> | ||
'''TRANSPOSASE TC3A1-65 FROM CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS'''<br /> | '''TRANSPOSASE TC3A1-65 FROM CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
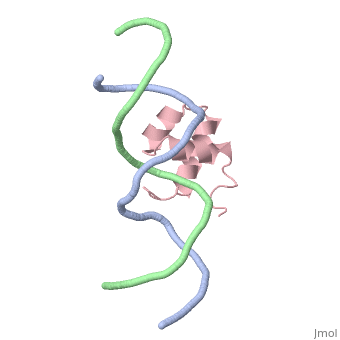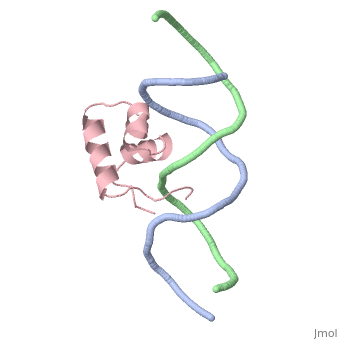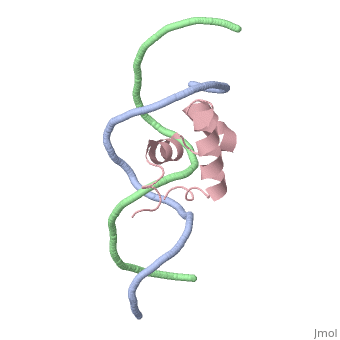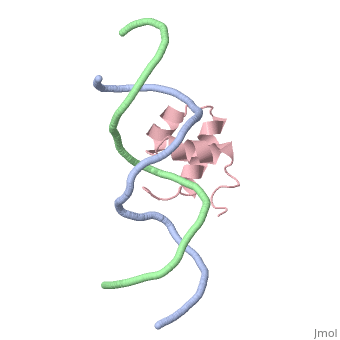
| - | The crystal structure of the complex between the N-terminal DNA-binding | + | The crystal structure of the complex between the N-terminal DNA-binding domain of Tc3 transposase and an oligomer of transposon DNA has been determined. The specific DNA-binding domain contains three alpha-helices, of which two form a helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif. The recognition of transposon DNA by the transposase is mediated through base-specific contacts and complementarity between protein and sequence-dependent deformations of the DNA. The HTH motif makes four base-specific contacts with the major groove, and the N-terminus makes three base-specific contacts with the minor groove. The DNA oligomer adopts a non-linear B-DNA conformation, made possible by a stretch of seven G:C base pairs at one end and a TATA sequence towards the other end. Extensive contacts (seven salt bridges and 16 hydrogen bonds) of the protein with the DNA backbone allow the protein to probe and recognize the sequence-dependent DNA deformation. The DNA-binding domain forms a dimer in the crystals. Each monomer binds a separate transposon end, implying that the dimer plays a role in synapsis, necessary for the simultaneous cleavage of both transposon termini. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1TC3 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans Caenorhabditis elegans]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1TC3 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans Caenorhabditis elegans]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1TC3 OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Category: Caenorhabditis elegans]] | [[Category: Caenorhabditis elegans]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Ketting, R | + | [[Category: Ketting, R F.]] |
[[Category: Perrakis, A.]] | [[Category: Perrakis, A.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Plasterk, R | + | [[Category: Plasterk, R H.A.]] |
| - | [[Category: Pouderoyen, G | + | [[Category: Pouderoyen, G Van.]] |
| - | [[Category: Sixma, T | + | [[Category: Sixma, T K.]] |
[[Category: complex (transposase/dna)]] | [[Category: complex (transposase/dna)]] | ||
[[Category: dna binding]] | [[Category: dna binding]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category: transposase]] | [[Category: transposase]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 15:12:00 2008'' |
Revision as of 13:12, 21 February 2008
|
TRANSPOSASE TC3A1-65 FROM CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS
Overview
The crystal structure of the complex between the N-terminal DNA-binding domain of Tc3 transposase and an oligomer of transposon DNA has been determined. The specific DNA-binding domain contains three alpha-helices, of which two form a helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif. The recognition of transposon DNA by the transposase is mediated through base-specific contacts and complementarity between protein and sequence-dependent deformations of the DNA. The HTH motif makes four base-specific contacts with the major groove, and the N-terminus makes three base-specific contacts with the minor groove. The DNA oligomer adopts a non-linear B-DNA conformation, made possible by a stretch of seven G:C base pairs at one end and a TATA sequence towards the other end. Extensive contacts (seven salt bridges and 16 hydrogen bonds) of the protein with the DNA backbone allow the protein to probe and recognize the sequence-dependent DNA deformation. The DNA-binding domain forms a dimer in the crystals. Each monomer binds a separate transposon end, implying that the dimer plays a role in synapsis, necessary for the simultaneous cleavage of both transposon termini.
About this Structure
1TC3 is a Single protein structure of sequence from Caenorhabditis elegans. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of the specific DNA-binding domain of Tc3 transposase of C.elegans in complex with transposon DNA., van Pouderoyen G, Ketting RF, Perrakis A, Plasterk RH, Sixma TK, EMBO J. 1997 Oct 1;16(19):6044-54. PMID:9312061
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 15:12:00 2008