Sandbox Reserved 714
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
=== N-terminal domain === | === N-terminal domain === | ||
| - | The N-terminal domain is responsible of the Mg<sup>2+</sup> dependant hydrolysis of dihydroxy lipid phosphates <ref>PMID:15096040</ref>. Indeed, the aliphatic substrate binds the protein on its hydrophobic tunnel, as it has been described previously. The specificity of this enzyme has been tested for several lipid molecules, and the best substrate found is the monophosphate of dihydroxy stearic acid (threo-9/10-phosphonoxy-hydroxy-octadecanoic acid) <ref>PMID:12574510</ref>. | + | The N-terminal domain is responsible of the Mg<sup>2+</sup> dependant hydrolysis of dihydroxy lipid phosphates <ref>PMID:15096040</ref>. Indeed, the aliphatic substrate binds the protein on its hydrophobic tunnel, as it has been described previously. The specificity of this enzyme has been tested for several lipid molecules, and the best substrate found is the monophosphate of dihydroxy stearic acid (threo-9/10-phosphonoxy-hydroxy-octadecanoic acid) <ref>PMID:12574510</ref>. Indeed, the catalytic values for this substrate are K<sub>m</sub> = 21 +/- 0.3 μ�M, V<sub>Max</sub> = 338 �+/- 12 nmol.�min�<sup>-1</sup>�.mg�<sup>-1</sup>, and k<sub>cat</sub> =� 0.35 +/-� 0.01 s<sup>-�1</sup>. |
In the example of this substrate, the reaction follows this equation: | In the example of this substrate, the reaction follows this equation: | ||
Revision as of 10:14, 3 January 2013
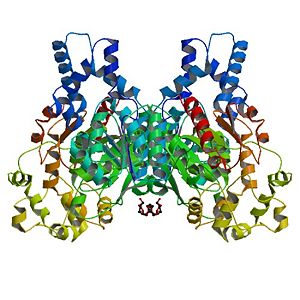
Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase: Biological assembly, 1s8o
Contents |
Overview
| |||||||||||
Additional 3D Structures of hsEH
1vj5 - hsEH + N-cyclohexyl-N'-(4-iodophenyl)urea complex
1zd2,1zd3, 1zd4,1zd5 - hsEH + 4-(3-cyclohexyluriedo)-carboxylic acids
3ant - Hydrolase domain + synthetic inhibitor
3pdc - Hydrolase domain + benzoxazole inhibitor
External ressources
Protein Data Bank entry on 1S8O
Uniprot link on Bifunctional epoxyde hydrolase 2
Wikipedia page on Epoxyde hydrolase 2
References
- ↑ Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Epoxide hydrolases: mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:311-33. PMID:15822179 doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.095920
- ↑ Gomez GA, Morisseau C, Hammock BD, Christianson DW. Structure of human epoxide hydrolase reveals mechanistic inferences on bifunctional catalysis in epoxide and phosphate ester hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 2004 Apr 27;43(16):4716-23. PMID:15096040 doi:10.1021/bi036189j
- ↑ Newman JW, Morisseau C, Harris TR, Hammock BD. The soluble epoxide hydrolase encoded by EPXH2 is a bifunctional enzyme with novel lipid phosphate phosphatase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Feb 18;100(4):1558-63. Epub 2003 Feb 6. PMID:12574510 doi:10.1073/pnas.0437724100
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
DUTREUX Fabien, BONHOURE Anna

