Sandbox Reserved 716
From Proteopedia
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== '''3D structure''' == | == '''3D structure''' == | ||
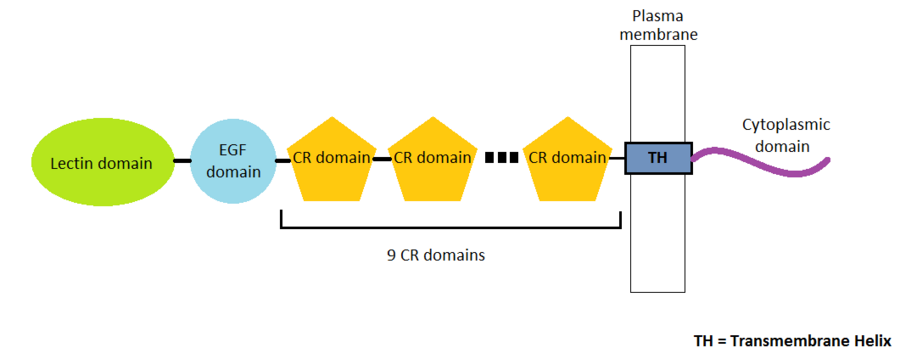
| - | P-Selectin is a protein composed by 162 amino-acids residues in 4 different chains A, B, C and D. There are many domains in this protein. Three domains represent the extracellular part of the protein : the '''EGF domain''', the '''lectin domain''' and nine '''consensus repeat (CR) domains'''. Finally, we find a transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic domain. | + | P-Selectin is a protein composed by 162 amino-acids residues in 4 different chains A, B, C and D. There are many domains in this protein. Three types of domains represent the extracellular part of the protein : the '''EGF domain''', the '''lectin domain''' and nine '''consensus repeat (CR) domains'''. Finally, we find a transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic domain. |
[[Image:Selectin_Structure.png|900px|center]] | [[Image:Selectin_Structure.png|900px|center]] | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
2. Somers WS, Tang J, Shaw GD, Camphausen RT. Insights into the molecular basis of leukocyte tethering and rolling revealed by structures of P- and E-selectin bound to SLe(X) and PSGL-1. Cell. 2000 Oct 27;103(3):467-79. PMID : [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11081633 11081633] | 2. Somers WS, Tang J, Shaw GD, Camphausen RT. Insights into the molecular basis of leukocyte tethering and rolling revealed by structures of P- and E-selectin bound to SLe(X) and PSGL-1. Cell. 2000 Oct 27;103(3):467-79. PMID : [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11081633 11081633] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Kansas GS, Saunders KB, Ley K, et al (1994). "A role for the epidermal growth factor-like domain of P-selectin in ligand recognition and cell adhesion". J Cell Biol 124 (4): 609–18. PMID 7508943. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Phan UT, Waldron TT, Springer TA (2006). "Remodeling of the lectin-EGF-like domain interface in P- and L-selectin increases adhesiveness and shear resistance under hydrodynamic force". Nat Immunol 7 (8): 883–9. doi:10.1038/ni1366. PMID 16845394. | ||
| + | |||
== '''Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors''' == | == '''Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors''' == | ||
Delphine Trelat, Cécile Ehrhardt | Delphine Trelat, Cécile Ehrhardt | ||
Revision as of 14:25, 3 January 2013
|
Crystal structure of P-selectin lectin/EGF domains complexed with SLeX
Contents |
Introduction
Selectins are proteins that are include in a family of cell adhesion receptor involved in the leukocyte extravasation. There are 3 kinds of selectins :
E selectin localized in endothelial cells, L selectin found in leukocytes, and P selectins in platelets and endothelial cells.
In this page we will be focused only on P-Selectin.
3D structure
P-Selectin is a protein composed by 162 amino-acids residues in 4 different chains A, B, C and D. There are many domains in this protein. Three types of domains represent the extracellular part of the protein : the EGF domain, the lectin domain and nine consensus repeat (CR) domains. Finally, we find a transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic domain.
Different role of the P-selectin
Role in leukocyte extravasation
Leukocyte extravasation is the movement of leukocytes out of the circulatory system. First, the leukocyte is attracted by cytokines, secreted near the site of infection. Then, this leukocyte slows down and begin rolling along the surface of the vessel. He binds then tightly the vessel and immobilizates himself. Finally, he passes through gaps between epithelial cells. By this mecanism, the leukocyte arrives on the site of infection to neutralize the infection agent.
Role in platelets recruitment
Role in cancer
External resources
Protein Data Bank file 1G1R
References
1. http://cro.sagepub.com/content/10/3/337.full.pdf
2. Somers WS, Tang J, Shaw GD, Camphausen RT. Insights into the molecular basis of leukocyte tethering and rolling revealed by structures of P- and E-selectin bound to SLe(X) and PSGL-1. Cell. 2000 Oct 27;103(3):467-79. PMID : 11081633
3. Kansas GS, Saunders KB, Ley K, et al (1994). "A role for the epidermal growth factor-like domain of P-selectin in ligand recognition and cell adhesion". J Cell Biol 124 (4): 609–18. PMID 7508943.
4. Phan UT, Waldron TT, Springer TA (2006). "Remodeling of the lectin-EGF-like domain interface in P- and L-selectin increases adhesiveness and shear resistance under hydrodynamic force". Nat Immunol 7 (8): 883–9. doi:10.1038/ni1366. PMID 16845394.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
Delphine Trelat, Cécile Ehrhardt