This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 713
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[Image:2fkl.png|left|200px|thumb|Caption]] | [[Image:2fkl.png|left|200px|thumb|Caption]] | ||
{{STRUCTURE_2fkl| PDB=2fkl | SCENE= }} | {{STRUCTURE_2fkl| PDB=2fkl | SCENE= }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=='''Introduction'''== | =='''Introduction'''== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 38: | ||
=='''Biological role'''== | =='''Biological role'''== | ||
| - | |||
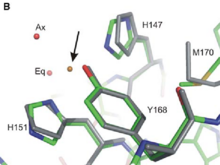
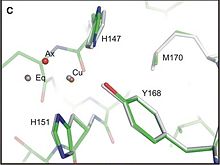
2FKL belong to the domain of APP which is able to bind Cu and zinc. Copper is an important metal to health. It acts as an indispensable catalytic and structural cofactor that drive many biological functions of our organism. But in particular situations like overcconcentration it can also become toxic for the cell. <ref> PMID:18030462</ref> | 2FKL belong to the domain of APP which is able to bind Cu and zinc. Copper is an important metal to health. It acts as an indispensable catalytic and structural cofactor that drive many biological functions of our organism. But in particular situations like overcconcentration it can also become toxic for the cell. <ref> PMID:18030462</ref> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 56: | ||
If the CuBD (located in E1 region) does contribute to APP dimerisation without Cu ions, that mean that the Cu binding may reduce AB production, either by shifting the monomer-dimer equilibrium to favor monomer form, or by re-orienting the dimer form, which disfavour the aB production. <ref> PMID : 18030462 <ref/> | If the CuBD (located in E1 region) does contribute to APP dimerisation without Cu ions, that mean that the Cu binding may reduce AB production, either by shifting the monomer-dimer equilibrium to favor monomer form, or by re-orienting the dimer form, which disfavour the aB production. <ref> PMID : 18030462 <ref/> | ||
| - | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 12:10, 5 January 2013
Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein copper-binding domain
| |||||||||
| 2fkl, resolution 2.50Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene: | APP (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| Related: | 1owt, 2fjz, 2fk1, 2fk2, 2fk3 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Contents |
Introduction
2FKL is located in a transmembrane protein called APP for Amyloid precursor protein. This domain going from residue 124 to 189 is localized in the extracellular part of APP just between the Growth Factor Domain (GFD) and the Acidic domain, in a region called Cu-Binding Domain which is able to bind Cu and Zinc.
This proteins plays a major role into the development of Alzheimer disease[1]. APP cleavage by BACE and gamma secretase gives ended rise to the Aβ peptide, which forms at the end an aggregation of amyloid plaques [2] .
As the interaction between copper ion and APP can modulate the production of Aβ peptide [3] and also the progression of Alzheimer disease, structural studies of the Cu-binding Domain of this protein give a lot of information for the development of novel therapeutics.
Structure
| |||||||||||
Additionnal Resources
PDB file of 2fkl
PDB file of 2fk1
PDB file of 2fk2
Alzheimer disease
References
- ↑ Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002 Oct 25;298(5594):789-91. PMID:12399581 doi:10.1126/science.1074069
- ↑ Kang J, Lemaire HG, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik KH, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Muller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19-25;325(6106):733-6. PMID:2881207 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/325733a0
- ↑ Kong GK, Miles LA, Crespi GA, Morton CJ, Ng HL, Barnham KJ, McKinstry WJ, Cappai R, Parker MW. Copper binding to the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein. Eur Biophys J. 2008 Mar;37(3):269-79. Epub 2007 Nov 21. PMID:18030462 doi:10.1007/s00249-007-0234-3
- ↑ Barnham KJ, McKinstry WJ, Multhaup G, Galatis D, Morton CJ, Curtain CC, Williamson NA, White AR, Hinds MG, Norton RS, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Parker MW, Cappai R. Structure of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein copper binding domain. A regulator of neuronal copper homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 2003 May 9;278(19):17401-7. Epub 2003 Feb 28. PMID:12611883 doi:10.1074/jbc.M300629200
- ↑ Kong GK, Miles LA, Crespi GA, Morton CJ, Ng HL, Barnham KJ, McKinstry WJ, Cappai R, Parker MW. Copper binding to the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein. Eur Biophys J. 2008 Mar;37(3):269-79. Epub 2007 Nov 21. PMID:18030462 doi:10.1007/s00249-007-0234-3
- ↑ PMID : 18030462 <ref></ref> for more information you can follow the link : Alzheimer disease The differents domains involved into the aB dimerisation aren't yet wery well known, but it seems that E1 and E2 are playing a major role. E1 contains the copper-binding site domain and also the Growth Factor-like Domain, rather than E2 contains the Central APP domain. Those two regions are located in the extracellurlar space. <ref> PMID : 20400860 </li> <li id="cite_note-6">[[#cite_ref-6|↑]] PMID : 18030462 <ref/> </li></ol></ref>
Contributors
Milène Walter, Andréa Mc Cann
sth to add : binding with cu