Group:MUZIC:Telethonin
From Proteopedia

| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
Telethonin accumulation is restricted to striated muscle, being found mostly in skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is one of the major components of the sarcomere and localizes to the Z-disc. It was also reported to localize to the nucleus.<ref>PMID:12379311 </ref>, <ref name="a"> PMID:16678796 </ref> | Telethonin accumulation is restricted to striated muscle, being found mostly in skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is one of the major components of the sarcomere and localizes to the Z-disc. It was also reported to localize to the nucleus.<ref>PMID:12379311 </ref>, <ref name="a"> PMID:16678796 </ref> | ||
| - | Studies on | + | Studies on the telethonin structure by Zou et al. <ref name="b"> PMID:16407954 </ref> report that it is made up of <scene name='User:Marcia_Ivonne_Pena_Paz/workbench/Telethonin/Telethonin_nter_cter/1'>five stranded antiparallel β-sheets extended by two wing-shaped β-hairpin motifs (A-B, C-D). These two motifs are related by an approximate two-fold symmetry, which generates an almost perfect palindromic arrangement.</scene> (N-terminal in blue and C-ter in orange). This structure is only found in the presence of <scene name='Group:MUZIC:Telethonin/Titin_teletonin/1' titin </scene>, Telethonin might adopt a different fold in its absence. |
The structure of Telethonin was determined using X-ray crystallography. <ref>PMID:12446666</ref>,<ref name="b" /> The shape and architecture of the complex of Titin/Telethonin was studied by small-angle- X-ray scattering (SAXS) and then compared to the crystallographic models. <ref>PMID:16713295</ref> | The structure of Telethonin was determined using X-ray crystallography. <ref>PMID:12446666</ref>,<ref name="b" /> The shape and architecture of the complex of Titin/Telethonin was studied by small-angle- X-ray scattering (SAXS) and then compared to the crystallographic models. <ref>PMID:16713295</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:20, 8 January 2013
Contents |
Telethonin
Also known as T-Cap or Titin Cap protein.
Introduction
Telethonin is a small protein composed of 167 amino acids with a molecular weight of 19KDa; its expression is predominantly specific to striated muscle belonging to the structural machinery of the sarcomere and locating to the Z-disk. Telethonin acts as multifunctional protein linking Titin and other proteins implicated in sarcomere structure and signalling pathways.
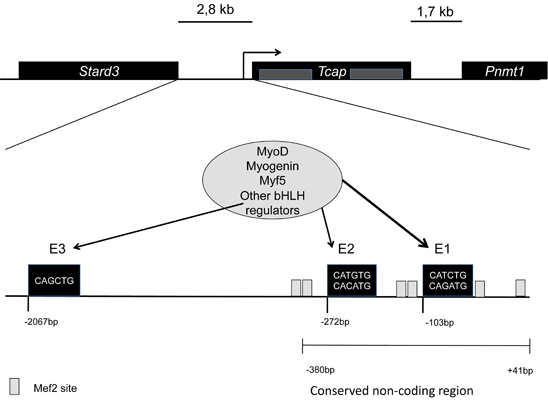
It is encoded by the Tcap gene in mice (Mus musculus), and TCAP in humans (Homo sapiens), no known homologues have been reported for this gene. In mice it is located in chromosome 11, in humans in the long arm of chromosome 17. Tcap is encoded by two exons, and has non-conserved intragenic sequences. The gene is flanked by two other genes, namely Stard3 upstream separated by 2,8kb, and Pnmt1 downstream separated by 1,7kb. It has three conserved E-box elements at -103bp (E1), -272bp (E2), and -2067bp (E3).
For the full activation of the gene the regulation of E1 is highly important. MyoD plays an important role in this regulation all through development, while myogenin mainly during late differentiation into myoblasts. [1]
Tcap is one of the most abundant transcripts in skeletal muscle [2] and it does not have different levels of expression in different types of fibers in skeletal muscle; levels of expression of Tcap are lower in neonatal compared to adult striated muscle. The transcript is accumulated in a linear pattern similar to that of the myosin heavy chain [3]. In these same studies it was reported that denervation leads to decrease in the expression of Tcap transcript, suggesting that locomotor activity is a potential regulator of its maintenance.
|
Sequence Annotation
Telethonin is comprised of 167 amino acids, the sequence of human, mouse, bovine, porcine Telethonin is available from Uniprot.
Structure
Telethonin accumulation is restricted to striated muscle, being found mostly in skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is one of the major components of the sarcomere and localizes to the Z-disc. It was also reported to localize to the nucleus.[4], [5]
Studies on the telethonin structure by Zou et al. [6] report that it is made up of (N-terminal in blue and C-ter in orange). This structure is only found in the presence of