1z99
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="1z99" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1z99" /> '''Solution structure of Crotamine, a myotoxin ...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1z99.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1z99" size=" | + | [[Image:1z99.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1z99" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="1z99" /> | caption="1z99" /> | ||
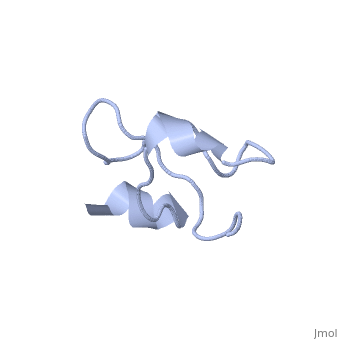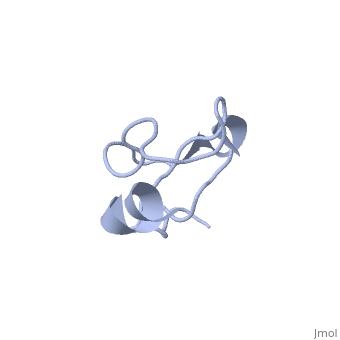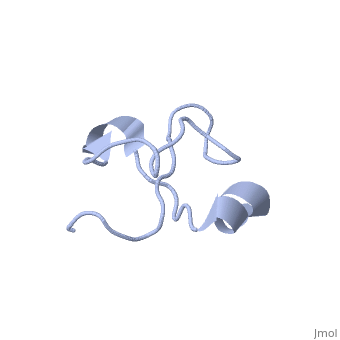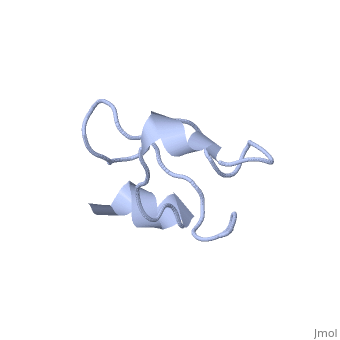
'''Solution structure of Crotamine, a myotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus'''<br /> | '''Solution structure of Crotamine, a myotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | Crotamine is one of four major components of the venom of the South | + | Crotamine is one of four major components of the venom of the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus. Similar to its counterparts in the family of the myotoxins, it induces myonecrosis of skeletal muscle cells. This paper describes a new NMR structure determination of crotamine in aqueous solution at pH 5.8 and 20 degrees C, using standard homonuclear 1H NMR spectroscopy at 900MHz and the automated structure calculation software ATNOS/CANDID/DYANA. The automatic NOESY spectral analysis included the identification of a most likely combination of the six cysteines into three disulfide bonds, i.e. Cys4-Cys36, Cys11-Cys30 and Cys18-Cys37; thereby a generally applicable new computational protocol is introduced to determine unknown disulfide bond connectivities in globular proteins. A previous NMR structure determination was thus confirmed and the structure refined. Crotamine contains an alpha-helix with residues 1-7 and a two-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet with residues 9-13 and 34-38 as the only regular secondary structures. These are connected with each other and the remainder of the polypeptide chain by the three disulfide bonds, which also form part of a central hydrophobic core. A single conformation was observed, with Pro13 and Pro21 in the trans and Pro20 in the cis-form. The global fold and the cysteine-pairing pattern of crotamine are similar to the beta-defensin fold, although the two proteins have low sequence homology, and display different biological activities. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1Z99 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crotalus_durissus_terrificus Crotalus durissus terrificus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1Z99 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crotalus_durissus_terrificus Crotalus durissus terrificus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1Z99 OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Category: Crotalus durissus terrificus]] | [[Category: Crotalus durissus terrificus]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Azevedo, W | + | [[Category: Azevedo, W F.de.]] |
[[Category: Bettendorff, P.]] | [[Category: Bettendorff, P.]] | ||
[[Category: Fadel, V.]] | [[Category: Fadel, V.]] | ||
[[Category: Herrmann, T.]] | [[Category: Herrmann, T.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Oliveira, E | + | [[Category: Oliveira, E B.]] |
[[Category: Wuthrich, K.]] | [[Category: Wuthrich, K.]] | ||
[[Category: Yamane, T.]] | [[Category: Yamane, T.]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category: myotoxin]] | [[Category: myotoxin]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 16:13:20 2008'' |
Revision as of 14:13, 21 February 2008
|
Solution structure of Crotamine, a myotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus
Overview
Crotamine is one of four major components of the venom of the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus. Similar to its counterparts in the family of the myotoxins, it induces myonecrosis of skeletal muscle cells. This paper describes a new NMR structure determination of crotamine in aqueous solution at pH 5.8 and 20 degrees C, using standard homonuclear 1H NMR spectroscopy at 900MHz and the automated structure calculation software ATNOS/CANDID/DYANA. The automatic NOESY spectral analysis included the identification of a most likely combination of the six cysteines into three disulfide bonds, i.e. Cys4-Cys36, Cys11-Cys30 and Cys18-Cys37; thereby a generally applicable new computational protocol is introduced to determine unknown disulfide bond connectivities in globular proteins. A previous NMR structure determination was thus confirmed and the structure refined. Crotamine contains an alpha-helix with residues 1-7 and a two-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet with residues 9-13 and 34-38 as the only regular secondary structures. These are connected with each other and the remainder of the polypeptide chain by the three disulfide bonds, which also form part of a central hydrophobic core. A single conformation was observed, with Pro13 and Pro21 in the trans and Pro20 in the cis-form. The global fold and the cysteine-pairing pattern of crotamine are similar to the beta-defensin fold, although the two proteins have low sequence homology, and display different biological activities.
About this Structure
1Z99 is a Single protein structure of sequence from Crotalus durissus terrificus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Automated NMR structure determination and disulfide bond identification of the myotoxin crotamine from Crotalus durissus terrificus., Fadel V, Bettendorff P, Herrmann T, de Azevedo WF Jr, Oliveira EB, Yamane T, Wuthrich K, Toxicon. 2005 Dec 1;46(7):759-67. Epub 2005 Sep 26. PMID:16185738
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 16:13:20 2008