Poly(A) Polymerase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:2q66.png|left|170px]] | [[Image:2q66.png|left|170px]] | ||
[[Poly(A) Polymerase]] (polynucleotide adenylytransferase, [[EC Number|EC]] 2.7.7.19) is the enzyme responsible for adding a polyadenine tail to the 3' end of a nascent pre-mRNA transcript. Its substrates are ATP and RNA. The poly(A) tail that poly-A polymerase adds to the 3' end of the pre-mRNA transcript is important for nuclear export, translation and stability of the mRNA. | [[Poly(A) Polymerase]] (polynucleotide adenylytransferase, [[EC Number|EC]] 2.7.7.19) is the enzyme responsible for adding a polyadenine tail to the 3' end of a nascent pre-mRNA transcript. Its substrates are ATP and RNA. The poly(A) tail that poly-A polymerase adds to the 3' end of the pre-mRNA transcript is important for nuclear export, translation and stability of the mRNA. | ||
| - | + | __NOTOC__ | |
==Determinants of ATP Recognition== | ==Determinants of ATP Recognition== | ||
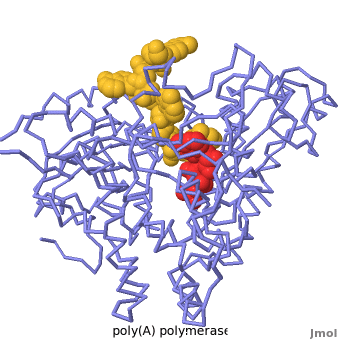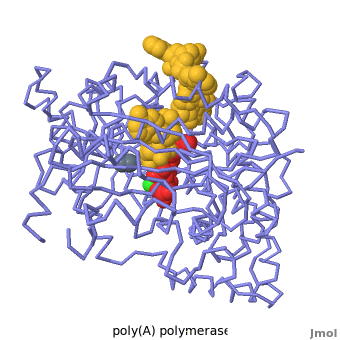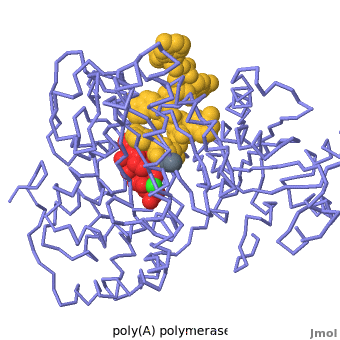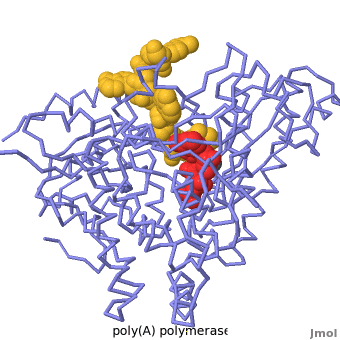
<StructureSection load='2q66' scene='Proteopedia:Main_page_develop/2q66_initial/3' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of Yeast Poly(A) Polymerase with ATP and oligo(A) (PDB entry [[2q66]])'> | <StructureSection load='2q66' scene='Proteopedia:Main_page_develop/2q66_initial/3' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of Yeast Poly(A) Polymerase with ATP and oligo(A) (PDB entry [[2q66]])'> | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 27 February 2013
Poly(A) Polymerase (polynucleotide adenylytransferase, EC 2.7.7.19) is the enzyme responsible for adding a polyadenine tail to the 3' end of a nascent pre-mRNA transcript. Its substrates are ATP and RNA. The poly(A) tail that poly-A polymerase adds to the 3' end of the pre-mRNA transcript is important for nuclear export, translation and stability of the mRNA.
Determinants of ATP Recognition
| |||||||||||
This section complements the article on Poly(A) Polymerase in the Molecule of the Month Series. See also Teaching Scenes, Tutorials, and Educators' Pages.
3D structures of poly(A) polymerase
3aqk, 3aql, 3aqm, 3aqn – PAP residues 18-431 – Escherichia coli
1jsz - VvPAP regulatory subunit residues 1-307 – Vaccinia virus
1jte, 1eam - VvPAP regulatory subunit residues 1-307 (mutant)
2hhp, 2o1p – yPAP - yeast
1q79, 1f5a - bPAP-α - bovine
Poly(A) polymerase complex
3er8, 3er9, 3erc – VvPAP catalytic subunit + RNA
2ga9 - VvPAP catalytic subunit + CAP-specific mRNA methyltransferase + ATP
2gaf - VvPAP catalytic subunit (mutant) + CAP-specific mRNA methyltransferase
1jtf, 2vp3 - VvPAP regulatory subunit residues 1-307 (mutant) + M7GPPPG
1b42, 1bky, 1eqa, 3mag, 3mct, 4dcg, 1av6, 1p39, 1v39 - VvPAP regulatory subunit residues 1-297 (mutant) + purine derivative + adenosylhomocysteine
1vp3 - VvPAP regulatory subunit + adenosylhomocysteine
1vp9 - VvPAP regulatory subunit (mutant) + adenosylhomocysteine
1vpt - VvPAP regulatory subunit (mutant) + adenosylmethionine
3c66 - yPAP residues 1-526 + Fip1 peptide
2q66 – yPAP + polyA + ATP
1q78 – bPAP-α + Mg + ATP
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Translation
For additional examples of transferases, see: Transferase
- PDB entry 2q66
Reference
Mechanism of poly(A) polymerase: structure of the enzyme-MgATP-RNA ternary complex and kinetic analysis., Balbo PB, Bohm A, Structure. 2007 Sep;15(9):1117-31. PMID:17850751
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Eran Hodis, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, OCA, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky, David S. Goodsell, Eric Martz