Calmodulin
From Proteopedia
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
== 3D Structures of Calmodulin == | == 3D Structures of Calmodulin == | ||
| - | + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |
=== Native CaM === | === Native CaM === | ||
Revision as of 10:41, 7 March 2013
Calmodulin (CaM) – calcium modulated protein – regulates various protein targets. It is used by various proteins as calcium sensor and signal transducer by binding to their calcium binding domain (CBD). It undergoes conformational change upon binding Ca++ via its 4 EF hand motives and can undergo post-translational modification. More details on apo-CaM in Calcium-free Calmodulin.
The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative calmodulin, i.e. crystal structure of bovine brain Ca++ calmodulin in a compact form (1prw).
Contents |
Maximum Occurrence of Calmodulin Conformations
Maximum Occurrence, a method for making rigorous numerical assessments about the maximum percent of time that a conformer of a flexible macromolecule can exist and still be compatible with the experimental data, was used to probe the conformational disorder of Calmodulin[1].
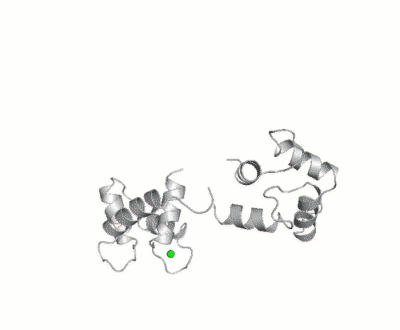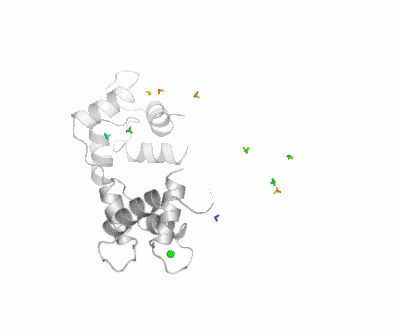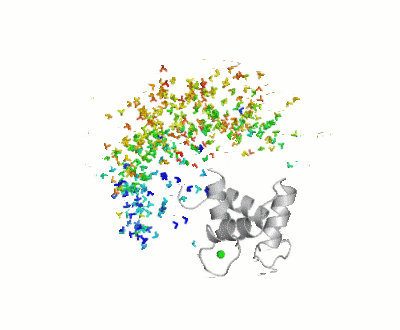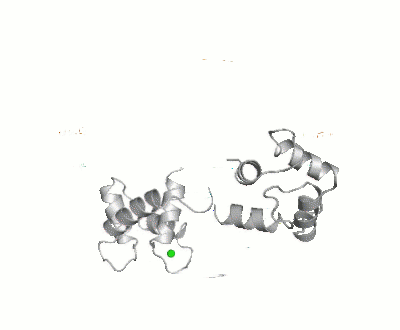
It was shown that the open (1cll) and closed (1prw) conformers can have MO of only 15% and 5% respectively.
Calmodulin in Motion
The clip represents Calmodulin in motion. At the beginning it is shown moving in the unbound form (ApoCaM), and it changes its conformation when Calcium ions are present in the medium (CaCaM).
Motion of ApoCaM is elaborated on the basis of 23 conformations derived from NMR file 1cfc, using the 3D animation program Blender, and according to a system to be published soon (Zini et al., manuscript in preparation). The transition from ApoCaM to CaCaM is elaborated with Blender starting with conformation 21 of 1cfc to arrive in conformation 11 of pdb file 1x02.
Surface rendering is also elaborated using Blender, and shows the lipophilic potential as a scale of white-black and smooth-rough, form the most lipophilic to the hydrophilic. Electrostatic potential is represented as a series of lines moving in the direction Positive to Negative, elaborated according to a scheme to be published soon (Andrei et al., in preparation). As most lines are moving towards Calmodulin, one can learn that the protein is slightly acidic (negative partial charges on its surface).
This movie was created by Andrei, Zini et al., of the Scientific Visualization Unit, Institute of Clinical Physiology - CNR of Itlay.
Conformational change of Calmodulin
|
,
3D Structures of Calmodulin
Updated on 07-March-2013
Native CaM
1prw, 1deg – bCaM - bovine
1up5 – cCaM – chicken
1clm, 1osa, 1exr – PtCaM - Paramecium tetraurelia
3cln – rCaM - rat
1x02, 1dmo – XlCaM – NMR - Xenopus laevis
2k61, 2k0e – hCaM – NMR - human
1y6w, 1cll - hCaM
4cln – DmCaM - Drosophila melanogaster
1rfj – CaM – potato
1ooj – CaM – Caenorhabditis elegans
Mutant CaM
1ahr – cCaM (mutant)
2k0j, 1sw8 – hCaM (mutant) – NMR
apo CaM
1lkj – yapoCaM – NMR -yeast
1cfc, 1cfd - XlapoCaM – NMR
1qx5 – rapoCaM – rat
CaM N-terminal
2i08 - hCaM N-terminal (mutant)
1j7o, 1j7p - hCaM N-terminal – NMR
1f70 - XlCaM N-terminal – NMR
2ro8, 2roa - sCaM N-terminal+Ca – NMR - soybean
2ro9, 2rob - sCaM C-terminal+Ca – NMR
3ifk, 3b32 – rCaM N-terminal
1f54, 1f55 – yapoCaM N-terminal – NMR
CaM C-terminal
1f71 - XlCaM C-terminal – NMR
1cmg – bCaM C-terminal – NMR
1fw4 - bCaM C-terminal
1cmf – bapoCaM C-terminal – NMR
2hf5 - hCaM EF2 EF3 – NMR
2lqp - hCaM EF3 EF4 – NMR
2kxw – PtapoCaM + IQ motif of NAV1.2 – NMR
2kz2 – CaM (mutant) – chicken
2rrt – XlCaM (mutant)
CaM+ cations (not calcium)
2ksz – sCaM N-terminal+Mg – NMR
1ak8 - bCaM N-terminal+Ce – NMR
2eqc – XlCaM C-terminal+Mg– NMR
2pq3 – rCaM+Zn
2v01 – hCaM+Pb
2v02 – hCaM+Ba
3uct – hCaM + Mn + Zn
3ucw - hCaM N-terminal + Mg
3ucy - hCaM N-terminal + Mg + Zn
1n0y – PtCaM+Pb
2lhh – yCaM + Ca - NMR
CaM small molecule complexes
3if7 – bCaM+sphingosylphosphorylcholine
1qiv, 1qiw – bCaM+DPDv
1a29, 1lin – bCaM+trifluoperazine
1ctr - hCaM+trifluoperazine
2kug, 2kuh - hCaM N-terminal EF1 EF2+halothane – NMR
2kdu – XlCaM+MUNC13-1 – NMR
1mux – XlCaM+W-7 – NMR
CaM complexed with protein CBD domains
3gp2 – cCaM+CaM kinase II δ chain
2dfs – cCaM+myosin 5A
2o5g – cCaM+ myosin light chain kinase peptide
2bcx – cCaM+ryanodine receptor 1 peptide
3gof, 2o60 – cCaM+nitric oxide synthase CBD
1niw - rCaM+nitric oxide synthase CBD
2hqw - rCaM+glutamate receptor peptide
3bxk, 3bxl, 4ehq – rCaM+ calcium channel peptide
1g4y, 3sjq, 4g27, 4g28 - rCaM+ potassium channel CBD
2ygg – rCaM + Na/H exchanger CBD
1qx7 – rapoCaM+potassium channel peptide
4gow – hCaM + potassium channel peptide
3hr4, 2ll6, 2ll7 - hCaM+nitric oxide synthase CBD
2x0g, 1yr5, 1wrz, 2y4v – hCaM+death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAP)
2kne – hCaM+PMCA C-terminal CBD
3ewt, 3ewv – hCaM+TNFR fragment
2w73, 2jzi, 2r28 – hCaM+Ser/Thr phosphatase CBD
3bya – hCaM+glutamate receptor peptide
3g43, 2vay, 2f3y, 2f3z, 2be6, 2lqc, 3oxq – hCaM+calcium channel CAV1.2
3dve, 3dvj, 3dvk, 3dvm - hCaM+calcium channel CAV2.2
4djc - hCaM+ sodium channel protein type V α subunit
4dck - hCaM+ sodium channel protein type V α subunit + fibroblast growth factor 13
2k0f – hCaM+myosin light chain kinase peptide – NMR
1zuz – hCaM+DRP kinase peptide
1l7z – hCaM+CAP-23/NAP-22 CBD
1cdl - hCaM+CaM dependent kinase CBD
1iwq - hCaM+MARCKS CBD
3sui – hCaM + capsaicin receptor peptide
2kn2 – sCaM C-terminal+NtMKP1 CBD – NMR
2x51, 4anj – DmCaM+pMyosin IV
2k3s – CaM+smoothelin-like protein 1 – NMR
1cff - XlCaM+ calcium channel CBD - NMR
1sy9 – XlCaM+olfactory channel peptide
1nwd – XlCaM+glutamate decarboxylase CBD
1iq5 – XlCaM+CaM dependent kinase CBD
1ckk - XlCaM+CaM dependent kinase CBD - NMR
2llo, 2llq – XlCaM EF-hand domain + estrogen receptor CBD – NMR
2ix7 – apoCaM+myosin-5A
2bbm, 2bbn - DmCaM+myosin light chain kinase
1mxe – DmCaM+rCaMKI CBD
2vas, 2vb6, 3gn4, 3l9i – DmCaM+myosin VI
2bki, 2bkh – CaM+myosin VI – pig
2fot - bCaM+α-II spectrin CBD
2f2o, 2f2p – bCaM+calcineurin CBD
1xa5 – bCaM+KAR-2
1cm1, 1cm4, 1cdm - bCaM+CaM dependent kinase CBD
2col, 1yrt, 1yru – BpCaM+adenyl cyclase – Bordetella pertussis
1zot – BpCaM C-terminal+adenyl cyclase
1xfu, 1xfv, 1xfw, 1xfx, 1xfy, 1xfz, 1y0v, 1sk6, 1pk0, 1lvc, 1k90, 1k93 - CaM+adenyl cyclase – Bacillus anthracis
2l1w – CaM+vacuolar calcium ATPase peptide – soybean – NMR
2lgf – hCaM + selectin peptide
1qs7, 1qtx – CaM+RS20 – Escherichia coli
1vrk – CaM (mutant)+RS20
3ek4, 3ek7, 3ek8, 3ekh, 3ekj, 3evr, 3evu, 3evv, 3o77, 3o78 – CaM/DFP/myosin light chain kinase
4ds7 – CaM + spindle pole body component 10 – Kluyveromyces lactis
See Also
Bibliography
- ↑ Bertini I, Giachetti A, Luchinat C, Parigi G, Petoukhov MV, Pierattelli R, Ravera E, Svergun DI. Conformational Space of Flexible Biological Macromolecules from Average Data. J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20822180 doi:10.1021/ja1063923
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Jaime Prilusky, Enrico Ravera, Daniel Moyano-Marino
