2bo5
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="2bo5" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="2bo5" /> '''BOVINE OLIGOMYCIN SENSITIVITY CONFERRAL PROT...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:2bo5.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="2bo5" size=" | + | [[Image:2bo5.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="2bo5" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="2bo5" /> | caption="2bo5" /> | ||
'''BOVINE OLIGOMYCIN SENSITIVITY CONFERRAL PROTEIN N-TERMINAL DOMAIN'''<br /> | '''BOVINE OLIGOMYCIN SENSITIVITY CONFERRAL PROTEIN N-TERMINAL DOMAIN'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | The peripheral stalk of ATP synthase holds the alpha3beta3 catalytic | + | The peripheral stalk of ATP synthase holds the alpha3beta3 catalytic subcomplex stationary against the torque of the rotating central stalk. In bovine mitochondria, the N-terminal domain of the oligomycin sensitivity conferral protein (OSCP-NT; residues 1-120) anchors one end of the peripheral stalk to the N-terminal tails of one or more alpha-subunits of the F1 subcomplex. Here we present the solution structure of OSCP-NT and an NMR titration study of its interaction with peptides representing N-terminal tails of F1 alpha-subunits. The structure comprises a bundle of six alpha-helices, and its interaction site contains adjoining hydrophobic surfaces of helices 1 and 5; residues in the region 1-8 of the alpha-subunit are essential for the interaction. The OSCP-NT is similar to the N-terminal domain of the delta-subunit from Escherichia coli ATP synthase (delta-NT), except that their surface charges differ (basic and acidic, respectively). As the charges of the adjacent crown regions in their alpha3beta3 complexes are similar, the OSCP-NT and delta-NT probably do not contact the crowns extensively. The N-terminal tails of alpha-subunit tails are probably alpha-helical, and so this interface, which is essential for the rotary mechanism of the enzyme, appears to consist of helix-helix interactions. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 2BO5 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bos_taurus Bos taurus]. Active as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H(+)-transporting_two-sector_ATPase H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.6.3.14 3.6.3.14] Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 2BO5 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bos_taurus Bos taurus]. Active as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H(+)-transporting_two-sector_ATPase H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.6.3.14 3.6.3.14] Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2BO5 OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Category: H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase]] | [[Category: H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Carbajo, R | + | [[Category: Carbajo, R J.]] |
| - | [[Category: Kellas, F | + | [[Category: Kellas, F A.]] |
| - | [[Category: Montgomery, M | + | [[Category: Montgomery, M G.]] |
[[Category: Neuhaus, D.]] | [[Category: Neuhaus, D.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Runswick, M | + | [[Category: Runswick, M J.]] |
| - | [[Category: Walker, J | + | [[Category: Walker, J E.]] |
[[Category: alpha-subunit]] | [[Category: alpha-subunit]] | ||
[[Category: atp synthase]] | [[Category: atp synthase]] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category: transport]] | [[Category: transport]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 16:39:51 2008'' |
Revision as of 14:39, 21 February 2008
|
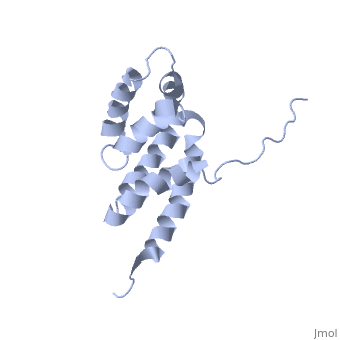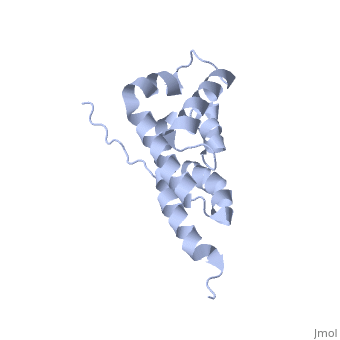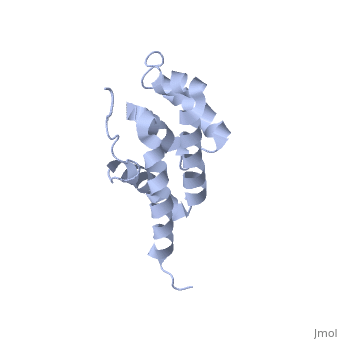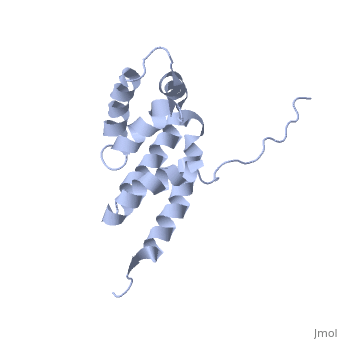
BOVINE OLIGOMYCIN SENSITIVITY CONFERRAL PROTEIN N-TERMINAL DOMAIN
Overview
The peripheral stalk of ATP synthase holds the alpha3beta3 catalytic subcomplex stationary against the torque of the rotating central stalk. In bovine mitochondria, the N-terminal domain of the oligomycin sensitivity conferral protein (OSCP-NT; residues 1-120) anchors one end of the peripheral stalk to the N-terminal tails of one or more alpha-subunits of the F1 subcomplex. Here we present the solution structure of OSCP-NT and an NMR titration study of its interaction with peptides representing N-terminal tails of F1 alpha-subunits. The structure comprises a bundle of six alpha-helices, and its interaction site contains adjoining hydrophobic surfaces of helices 1 and 5; residues in the region 1-8 of the alpha-subunit are essential for the interaction. The OSCP-NT is similar to the N-terminal domain of the delta-subunit from Escherichia coli ATP synthase (delta-NT), except that their surface charges differ (basic and acidic, respectively). As the charges of the adjacent crown regions in their alpha3beta3 complexes are similar, the OSCP-NT and delta-NT probably do not contact the crowns extensively. The N-terminal tails of alpha-subunit tails are probably alpha-helical, and so this interface, which is essential for the rotary mechanism of the enzyme, appears to consist of helix-helix interactions.
About this Structure
2BO5 is a Single protein structure of sequence from Bos taurus. Active as H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase, with EC number 3.6.3.14 Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit., Carbajo RJ, Kellas FA, Runswick MJ, Montgomery MG, Walker JE, Neuhaus D, J Mol Biol. 2005 Aug 26;351(4):824-38. PMID:16045926
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 16:39:51 2008
Categories: Bos taurus | H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase | Single protein | Carbajo, R J. | Kellas, F A. | Montgomery, M G. | Neuhaus, D. | Runswick, M J. | Walker, J E. | Alpha-subunit | Atp synthase | Beta-subunit | Binding interface | Cf(1) | Chemical shift mapping | Chemical shift perturbations | Hydrogen ion transport | Hydrolase | Ion transport | Mitochondrion | Nmr | Oscp | Peripheral stalk | Protein-protein interactions | Titration | Transit peptide | Transport