This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Prp40
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
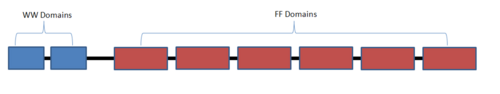
==The first FF domain (FF1)== | ==The first FF domain (FF1)== | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <Structure load='1o6w' size='250' thumb='false' align='left' caption='Figure 2: N terminal (blue) to C terminal (red) ribbon representation of the consecutive WW domains of Prp40, [[1o6w]]' scene='Sandbox_504/Start_scene_ff1/1'/> | ||
| - | |||
The <scene name='Sandbox_504/Start_scene_ff1/1'>FF1 domain of Prp40 is comprised of three alpha helices</scene>, and one 310 helix located between α2 and α3. Helices are composed of the following residues, <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_a1/1'>α1</scene> (134-146), <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_a2/2'>α2</scene> (154-163), <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_310/1'>310</scene> (167-170), and <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_a3/1'>α3</scene> (175-187). The core domain is made up of a series of aromatic and aliphatic residues. A type 1 β-turn is exhibited by the residues Asp149, Ser150, Thr151, and Trp152<ref name ="gasch"/>. | The <scene name='Sandbox_504/Start_scene_ff1/1'>FF1 domain of Prp40 is comprised of three alpha helices</scene>, and one 310 helix located between α2 and α3. Helices are composed of the following residues, <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_a1/1'>α1</scene> (134-146), <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_a2/2'>α2</scene> (154-163), <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_310/1'>310</scene> (167-170), and <scene name='Sandbox_504/Ff1_a3/1'>α3</scene> (175-187). The core domain is made up of a series of aromatic and aliphatic residues. A type 1 β-turn is exhibited by the residues Asp149, Ser150, Thr151, and Trp152<ref name ="gasch"/>. | ||
==The fourth FF domain (FF4)== | ==The fourth FF domain (FF4)== | ||
| - | + | <scene name='Sandbox_504/Start_scene_ff4/1'>Domain FF4 of Prp40</scene> exhibits compact four helical bundle fold comprised of an α1-α2-310-α3 topology. The composition of each helix is a follows <scene name='Sandbox_504/A1_of_ff4/1'>α1</scene> (Glu489-Thr507), <scene name='Sandbox_504/A2_of_ff4/1'>α2</scene> (Trp519-Leu526), <scene name='Sandbox_504/310_of_ff4/1'>310</scene> (Tyr532-Gly536) and <scene name='Sandbox_504/A3_of_ff4/1'>α3</scene> (Asp539-Phe549). There are a series of interactions between the different helices, for example Tyr532 is in contact with Phe500, Leu503, Ser523, and Arg542. A difference between FF1 and FF4 is the presence of five extra amino acids in F4 which gives the <scene name='Sandbox_504/Loop_of_ff4/1'>loop</scene> located between α 1 and α2 an extra turn. This insertion however does not increase the flexibility of F4 as compared to F1<ref name ="bonet"/>. | |
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | < | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Domain FF4 of Prp40 exhibits compact four helical bundle fold comprised of an α1-α2-310-α3 topology. The composition of each helix is a follows <scene name='Sandbox_504/A1_of_ff4/1'>α1</scene> (Glu489-Thr507), <scene name='Sandbox_504/A2_of_ff4/1'>α2</scene> (Trp519-Leu526), <scene name='Sandbox_504/310_of_ff4/1'>310</scene> (Tyr532-Gly536) and <scene name='Sandbox_504/A3_of_ff4/1'>α3</scene> (Asp539-Phe549). There are a series of interactions between the different helices, for example Tyr532 is in contact with Phe500, Leu503, Ser523, and Arg542. A difference between FF1 and FF4 is the presence of five extra amino acids in F4 which gives the <scene name='Sandbox_504/Loop_of_ff4/1'>loop</scene> located between α 1 and α2 an extra turn. This insertion however does not increase the flexibility of F4 as compared to F1<ref name ="bonet"/>. | + | |
| - | + | ||
=Additional Resources= | =Additional Resources= | ||
*[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2KFD Prp40 FF4 domain, in the RCSB Protein Data Bank] | *[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2KFD Prp40 FF4 domain, in the RCSB Protein Data Bank] | ||
Revision as of 09:17, 8 April 2013
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
- Prp40 FF4 domain, in the RCSB Protein Data Bank
- SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE PRP40 WW DOMAIN PAIR OF THE YEAST SPLICING FACTOR PRP40, in the RCSB Protein Data Bank
- First FF domain of Prp40 Yeast Protein, in the RCSB Protein Data Bank
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bonet R, Ruiz L, Morales B, Macias MJ. Solution structure of the fourth FF domain of yeast Prp40 splicing factor. Proteins. 2009 Dec;77(4):1000-3. PMID:19722265 doi:10.1002/prot.22547
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Wiesner S, Stier G, Sattler M, Macias MJ. Solution structure and ligand recognition of the WW domain pair of the yeast splicing factor Prp40. J Mol Biol. 2002 Dec 6;324(4):807-22. PMID:12460579
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Gasch A, Wiesner S, Martin-Malpartida P, Ramirez-Espain X, Ruiz L, Macias MJ. The structure of Prp40 FF1 domain and its interaction with the crn-TPR1 motif of Clf1 gives a new insight into the binding mode of FF domains. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 6;281(1):356-64. Epub 2005 Oct 27. PMID:16253993 doi:10.1074/jbc.M508047200
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 van der Feltz C, Anthony K, Brilot A, Pomeranz Krummel DA. Architecture of the Spliceosome. Biochemistry. 2012 Apr 10. PMID:22471593 doi:10.1021/bi201215r
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Sperling J, Azubel M, Sperling R. Structure and function of the Pre-mRNA splicing machine. Structure. 2008 Nov 12;16(11):1605-15. PMID:19000813 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.011
- ↑ Zhang L, Xu T, Maeder C, Bud LO, Shanks J, Nix J, Guthrie C, Pleiss JA, Zhao R. Structural evidence for consecutive Hel308-like modules in the spliceosomal ATPase Brr2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Jul;16(7):731-9. Epub 2009 Jun 14. PMID:19525970 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1625
- ↑ Zhang L, Xu T, Maeder C, Bud LO, Shanks J, Nix J, Guthrie C, Pleiss JA, Zhao R. Structural evidence for consecutive Hel308-like modules in the spliceosomal ATPase Brr2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Jul;16(7):731-9. Epub 2009 Jun 14. PMID:19525970 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1625
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Cramer P, Bushnell DA, Kornberg RD. Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 angstrom resolution. Science. 2001 Jun 8;292(5523):1863-76. Epub 2001 Apr 19. PMID:11313498 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1059493
- ↑ Phatnani HP, Greenleaf AL. Phosphorylation and functions of the RNA polymerase II CTD. Genes Dev. 2006 Nov 1;20(21):2922-36. PMID:17079683 doi:10.1101/gad.1477006
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Morris DP, Greenleaf AL. The splicing factor, Prp40, binds the phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 22;275(51):39935-43. PMID:10978320 doi:10.1074/jbc.M004118200