User:Michael Roberts/BIOL115 CaM
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:CaM.png|left|thumb|Crystal Structure of Calmodulin [[1cll]]]] | + | [[Image:CaM.png|left|250px|thumb|Crystal Structure of Calmodulin [[1cll]]]] |
<span style="font-size:150%">'''Sequence and structure of EF hands'''</span> | <span style="font-size:150%">'''Sequence and structure of EF hands'''</span> | ||
Revision as of 17:32, 22 April 2013
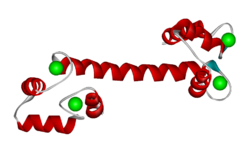
Sequence and structure of EF hands
The EF hand motif is present in a many proteins and it commonly bestows the ability to bind Ca2+ ions. It was first identified in parvalbumin, a muscle protein. Here we'll have a look at the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin, which possesses four EF hands. Calmodulin and its isoform, troponinC, are important intracellular Ca2+-binding proteins.
The structure below, obtained by X-ray crystallography, represents the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin. It has a dumbell-shaped structure with two identical lobes connected by a central alpha-helix. Each lobe comprises three α-helices joined by loops. A helix-loop-helix motif forms the basis of each EF hand.
Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.
| |||||||||||
External Resources. You can view a nice animation of the conformational change undergone by calmodulin upon calcium binding by following this link [1].
