This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
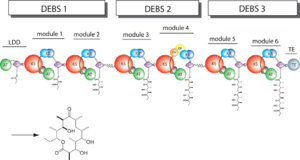
After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the beta-position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. | After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the beta-position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
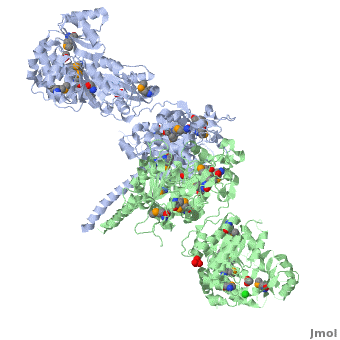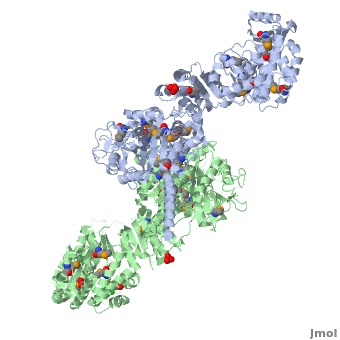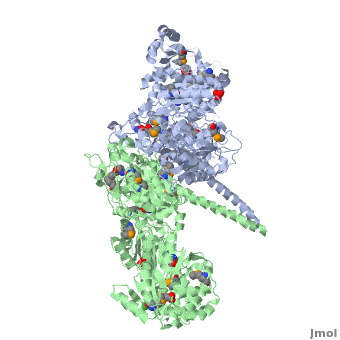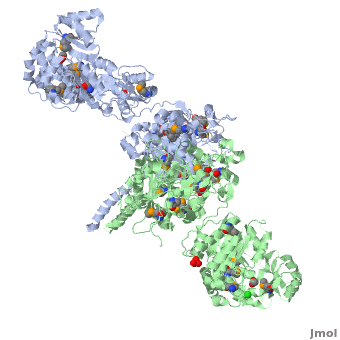
===Ketosynthase-acyltransferase (KS-AT)=== | ===Ketosynthase-acyltransferase (KS-AT)=== | ||
Molecular Playground banner: KS-AT The "builder" and the "gatekeeper". | Molecular Playground banner: KS-AT The "builder" and the "gatekeeper". | ||
| - | + | Structure of the homodimers of ketosynthase-acyltransferase didomain of module 5 from DEBS ([[2hg4]]). | |
| - | + | <scene name='User:Tsung-Yi_Lin/6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase/Ks-at_dimer/2'>KS-AT dimer</scene> | |
| - | + | ||
The AT domain is responsible for selecting the building blocks which become incorporated into the polyketide chain, most often in the form of malonyl-CoA derivatives. Each polyketide synthase AT is exquisitely selective for one substrate type and the DEBS ATs are selective for (S)-methylmalonyl CoA. In this way it functions as the "gatekeeper", preventing erroneous building blocks from becoming incorporated into the growing chain. the methylmalonyl group is transferred by the AT to the ACP, from where it can become incorporated into the polyketide by the KS domain. | The AT domain is responsible for selecting the building blocks which become incorporated into the polyketide chain, most often in the form of malonyl-CoA derivatives. Each polyketide synthase AT is exquisitely selective for one substrate type and the DEBS ATs are selective for (S)-methylmalonyl CoA. In this way it functions as the "gatekeeper", preventing erroneous building blocks from becoming incorporated into the growing chain. the methylmalonyl group is transferred by the AT to the ACP, from where it can become incorporated into the polyketide by the KS domain. | ||
The KS accepts the "in-progress" polyketide from its upstream module, and then catalyzes the decarboxylative condensation of ACP-bound malonyl CoA derivatives with the in-progress chain. This results in an ACP-bound β-ketothioester which is processed by any other β-carbon tailoring domains present within the module. | The KS accepts the "in-progress" polyketide from its upstream module, and then catalyzes the decarboxylative condensation of ACP-bound malonyl CoA derivatives with the in-progress chain. This results in an ACP-bound β-ketothioester which is processed by any other β-carbon tailoring domains present within the module. | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='User:Tsung-Yi_Lin/6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase/Ks-at_dimer/2'>KS-AT dimer</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
===Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)=== | ===Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)=== | ||
Revision as of 12:09, 1 May 2013
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Tsung-Yi Lin, Alexander Berchansky, Lawrence Sheringham Borketey, Joel L. Sussman, Jon Amoroso, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky