We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Michael Roberts/BIOL115 Myo
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== The Heme Group == | == The Heme Group == | ||
Now let's turn our attention to the main function of myoglobin - oxygen binding. | Now let's turn our attention to the main function of myoglobin - oxygen binding. | ||
| - | Oxygen is bound by a <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/1'>heme group</scene>, which sits in a hydrophobic pocket in the myoglobin protein. | + | Oxygen is bound by a <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/1'>heme group</scene>, (coloured red) which sits in a hydrophobic pocket in the myoglobin protein. |
Central to the heme group is an <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/3'>iron (Fe) atom</scene>. | Central to the heme group is an <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/3'>iron (Fe) atom</scene>. | ||
Revision as of 12:55, 1 May 2013
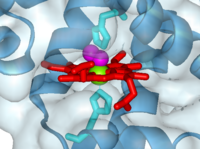
Myoglobin with oxygen bound to heme (1a6m)
The heme group and oxygen binding in myoglobin.
Myoglobin is a protein whose function is to store oxygen in muscle tissues. Like heamoglobin, it is red in colour, and it is myoglobin that gives muscle its strong red colour.
Myoglobin was the first globular protein for which the 3-dimensional structure was solved, back in the late 1950s. It gives its name to the 'globin fold', a common alpha domain motif. An alpha domain is a structural region composed entirley of alpha-helix.
Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.
| |||||||||||
