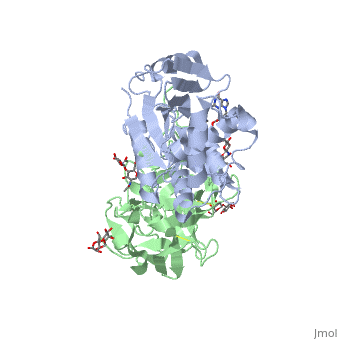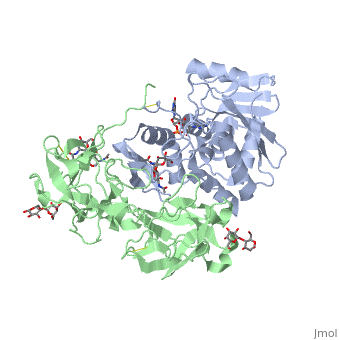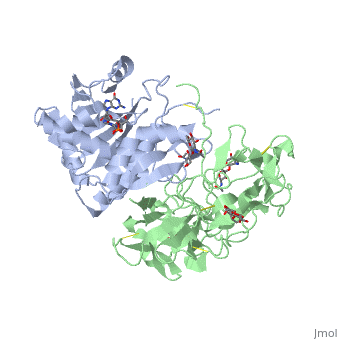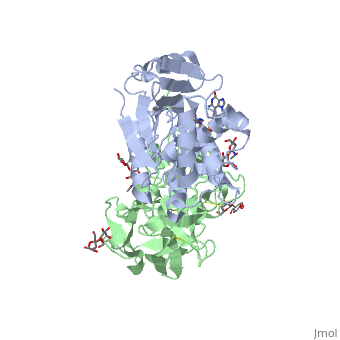
Ricin
From Proteopedia
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
The proposed mechanism of depurination utilizes the <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Conserved_residues/2'>conserved residues</scene> in the A chain. The aromatic ring structures of the substrate adenosine stack with the aromatic side chains of <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Tyr_stacking/1'>two tyrosine residues</scene>, Tyr 80 and 123, above and below. Hydrogen bonds form between the conserved arginine and a backbone carbonyl. The depurination reaction is aided by the protonation of N3 by Arg 180 and by ion pairing to Glu 177. A water molecule on the opposite side of the ribose is activated by hydrogen bonding to Arg 180. The activated water attacks C1' of the ribose, releasing the adenine and depurinated RNA fragment. This interferes with elongation factor binding to the ribosome, thus inhibiting [[translation|translation]]. | The proposed mechanism of depurination utilizes the <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Conserved_residues/2'>conserved residues</scene> in the A chain. The aromatic ring structures of the substrate adenosine stack with the aromatic side chains of <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Tyr_stacking/1'>two tyrosine residues</scene>, Tyr 80 and 123, above and below. Hydrogen bonds form between the conserved arginine and a backbone carbonyl. The depurination reaction is aided by the protonation of N3 by Arg 180 and by ion pairing to Glu 177. A water molecule on the opposite side of the ribose is activated by hydrogen bonding to Arg 180. The activated water attacks C1' of the ribose, releasing the adenine and depurinated RNA fragment. This interferes with elongation factor binding to the ribosome, thus inhibiting [[translation|translation]]. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Site of ricin modification of rRNA == | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='3u5d' size='400' side='right' caption='ribosomal RNA from Yeast(PDB entry [[3u5d]])' scene=''> | ||
| + | Ricin removes an adenine from a specific portion of the 28S rRNA called the <scene name='Taylor_sandboxk_ricin_rRNA_modification_site/Sarcin-ricin_loop/1'>sacrin-ricin loop</scene>, or SRL. This <scene name='Taylor_sandboxk_ricin_rRNA_modification_site/Depurination/1'>depurination</scene> leads to reduced binding of elongation factors to the ribosome and reduced synthesis of proteins. It also triggers apoptosis via activation of the JNK pathway <ref name="Iordanov">PMID: 9154836</ref>. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 05:49, 4 May 2013
Ricin is a potent cytotoxin that is synthesized in the endosperm cells of maturing seeds of the castor oil plant (Ricinus communis)[1]. Ricin belongs to a small multi-gene family[2] that is composed of eight members. Ricin is classified as a type II heterodimeric Ribosome Inactivating Protein[1] or RIPs. For toxins in Proteopedia see Toxins.
| |||||||||||
Site of ricin modification of rRNA
| |||||||||||
Updated April 2013
Ricin A chain (RTA)
1j1m, 1ift, 2aai, 1rtc – RTA
3lc9, 3mk9, 2vc4, 1uq4, 1uq5, 1obs, 3bjg, 3srp – RTA (mutant)
Ricin A chain binary complexes
3px8 – RTA preproricin + 7-carboxy-pterin
1br5, 1br6 - RTA + pterin derivative
3px9 - RTA preproricin + furanylmethyl-carbamoyl-pterin
3lc9, 3mk9, 2vc4, 1uq4, 1uq5, 1obs – RTA (mutant)
3hio – RTA + tetranucleotide
3ej5, 1il5 – RTA pyrimidine derivative
2p8n, 1ifs – RTA + adenine
2pjo, 2r2x – RTA + urea derivative
2r3d – RTA + acetamide
2vc3 - RTA (mutant) + acetate
1il3, 1il4, 1il9 – RTA + guanine derivative
1ifu, 1fmp – RTA + formycin
1obt - RTA (mutant) + AMP
1apg – RTA + RNA
3px8 – RTA + formycin monophosphate
Ricin B chain (RTB)
3nbc, 3nbd – CnRTB + lactose – Clitocybe nebularis
3nbe – CnRTB + lactose derivative
3phz – RTB + glycoside – Polyporus squamosus
Ricin A+B chains
2aai - RTA + RTB
3rtj - RTA + RTB + dinucleotide
See Also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID:8119491
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Montfort W, Villafranca JE, Monzingo AF, Ernst SR, Katzin B, Rutenber E, Xuong NH, Hamlin R, Robertus JD. The three-dimensional structure of ricin at 2.8 A. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5398-403. PMID:3558397
- ↑ Weston SA, Tucker AD, Thatcher DR, Derbyshire DJ, Pauptit RA. X-ray structure of recombinant ricin A-chain at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 9;244(4):410-22. PMID:7990130 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1739
- ↑ Rutenber E, Ready M, Robertus JD. Structure and evolution of ricin B chain. Nature. 1987 Apr 9-15;326(6113):624-6. PMID:3561502 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/326624a0
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Rapak A, Falnes PO, Olsnes S. Retrograde transport of mutant ricin to the endoplasmic reticulum with subsequent translocation to cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):3783-8. PMID:9108055
- ↑ Holmberg L, Nygard O. Depurination of A4256 in 28 S rRNA by the ribosome-inactivating proteins from barley and ricin results in different ribosome conformations. J Mol Biol. 1996 May 31;259(1):81-94. PMID:8648651 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0303
- ↑ Iordanov MS, Pribnow D, Magun JL, Dinh TH, Pearson JA, Chen SL, Magun BE. Ribotoxic stress response: activation of the stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 by inhibitors of the peptidyl transferase reaction and by sequence-specific RNA damage to the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop in the 28S rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jun;17(6):3373-81. PMID:9154836
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Ann Taylor, Joel L. Sussman, Douglas Read, Wayne Decatur, David Canner, Angel Herraez, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky, Andrea Gorrell