We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Hepatocyte growth factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='1shy' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human HGF β chain complex with HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains (PDB entry 1shy)' scene=''> '''Hepatocyte...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
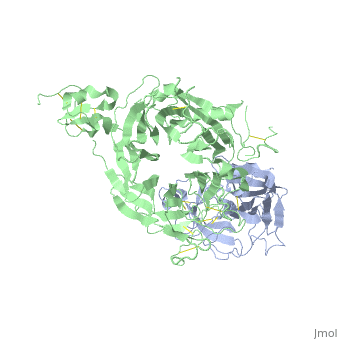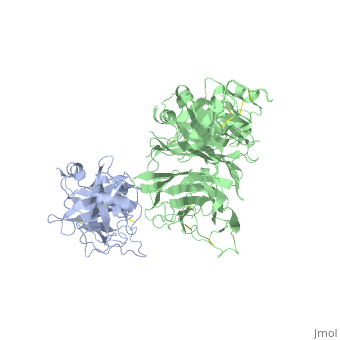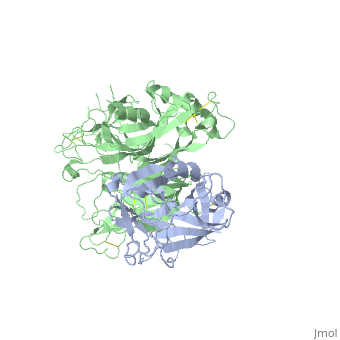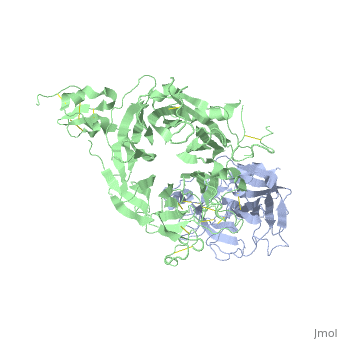
| - | + | <StructureSection load='1shy' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human HGF β chain (grey) complex with HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains (green) (PDB entry [[1shy]])' scene=''> | |
| - | <StructureSection load='1shy' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human HGF β chain complex with HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains (PDB entry [[1shy]])' scene=''> | + | |
'''Hepatocyte growth factor''' (HGF) regulates cell growth, motility and morphogenesis. HGF binds to proto-oncogene c-Met receptor and activates a tyrosine kinase signaling cascade. HGF precursor is cleaved by serine protease to α and β (residues 495-728) chains which form a disulfide bond to produce the active heterodimer. HGF NK1 variant is comprised of residues 28-210 containing the N-terminus and the first kringle domain of HGF. HGF NK2 variant is comprised of residues 28-289 containing the N-terminus and the first 2 kringle domains of HGF. | '''Hepatocyte growth factor''' (HGF) regulates cell growth, motility and morphogenesis. HGF binds to proto-oncogene c-Met receptor and activates a tyrosine kinase signaling cascade. HGF precursor is cleaved by serine protease to α and β (residues 495-728) chains which form a disulfide bond to produce the active heterodimer. HGF NK1 variant is comprised of residues 28-210 containing the N-terminus and the first kringle domain of HGF. HGF NK2 variant is comprised of residues 28-289 containing the N-terminus and the first 2 kringle domains of HGF. | ||
Revision as of 10:50, 12 May 2013
| |||||||||||