Chloride Intracellular Channel Protein 2
From Proteopedia
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
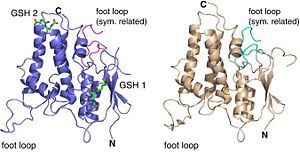
| - | [[Image:0.jpg|left|300px|thumb | + | [[Image:0.jpg|left|300px|thumb''Two different forms of CLIC2 which differ by 18 residues: form A (blue) and form B (grey).'']] |
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
| - | ''Two different forms of CLIC2 which differ by 18 residues: form A (blue) and form B (grey).'' | + | |
| - | + | ||
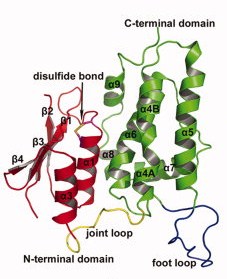
Contrary to each members of the CLICs family, CLIC 2 is a monomer, no matter if it is oxydated or reduiced. It is composed of 247 amino acids, has a weight of 28.4kDa and an isoelectric point at 5.44(crystal structure). The CLIC2 molecule is box shaped (60×60×35 Å) and consists of a four strand core and two helices on one side. Comparing sequence similarities, the core is supposed to adopt the canonical fold of the glutathione S-transferase (GST) superfamily. This has been confirmed by the crystal structure determination of human CLIC1 at 1.4 Å resolution. Then, by analyzing CLIC genes sequences, this protein appears to have two potential transmembrane domains that would correspond to helices α1 and α6 in the GST-like structure of the soluble form. Thanks to immunological, electrophysical and proteolysis studies, we can say that membrane form of CLIC proteins cross the lipid bilayer an odd number of times. | Contrary to each members of the CLICs family, CLIC 2 is a monomer, no matter if it is oxydated or reduiced. It is composed of 247 amino acids, has a weight of 28.4kDa and an isoelectric point at 5.44(crystal structure). The CLIC2 molecule is box shaped (60×60×35 Å) and consists of a four strand core and two helices on one side. Comparing sequence similarities, the core is supposed to adopt the canonical fold of the glutathione S-transferase (GST) superfamily. This has been confirmed by the crystal structure determination of human CLIC1 at 1.4 Å resolution. Then, by analyzing CLIC genes sequences, this protein appears to have two potential transmembrane domains that would correspond to helices α1 and α6 in the GST-like structure of the soluble form. Thanks to immunological, electrophysical and proteolysis studies, we can say that membrane form of CLIC proteins cross the lipid bilayer an odd number of times. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 54: | ||
What’s more, CLIC-2 has also a light catalytic activity glutathione transferase. | What’s more, CLIC-2 has also a light catalytic activity glutathione transferase. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
CLIC2 interacts with the RyR protein (those channels are called Ryanodine receptor RyR). and has by this interaction a huge role in calcium concentration regulation. Actually, CLIC2 is involved in maintaining calcium homeostasy by limiting calcium releases for cellular stock. | CLIC2 interacts with the RyR protein (those channels are called Ryanodine receptor RyR). and has by this interaction a huge role in calcium concentration regulation. Actually, CLIC2 is involved in maintaining calcium homeostasy by limiting calcium releases for cellular stock. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 63: | ||
Ryanodine is an alkaloid extracted from plants which modify the activity of intracellular chloride channels like those present on sarcoplasmic reticulum. At low concentrations (<10µM), ryanodine opens RyR leading to calcium release in the cytoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Whereas at high concentrations (>100µM), ryanodine inhibits RyR.. | Ryanodine is an alkaloid extracted from plants which modify the activity of intracellular chloride channels like those present on sarcoplasmic reticulum. At low concentrations (<10µM), ryanodine opens RyR leading to calcium release in the cytoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Whereas at high concentrations (>100µM), ryanodine inhibits RyR.. | ||
Furthermore, the binding of CLIC2 to domains 5 and 6 of RyR increases the interaction between these two domains and so stabilizes the closed state of the RyR channel. This aspect explain how CLIC2 can prevent from Ca2+ efflux from skeletal heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum. | Furthermore, the binding of CLIC2 to domains 5 and 6 of RyR increases the interaction between these two domains and so stabilizes the closed state of the RyR channel. This aspect explain how CLIC2 can prevent from Ca2+ efflux from skeletal heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum. | ||
| - | |||
A detail that worth being noticed, it is the fact that a small fraction of cardiac RyR or not totally inhibited by CLIC2. This can be explained by supposing that there exist many isoforms of RyR or simply because we still do not really know if CLIC2 interacts directly with RyR or with other component of the RyR complex. | A detail that worth being noticed, it is the fact that a small fraction of cardiac RyR or not totally inhibited by CLIC2. This can be explained by supposing that there exist many isoforms of RyR or simply because we still do not really know if CLIC2 interacts directly with RyR or with other component of the RyR complex. | ||
In addition with CLIC2, ryanodine and GST, RyR has many regulators including Ca2+ and Mg2+, ATP and calmodulin. All these regulators allow RyR channels to respond in synchrony with other cell processes even if CLIC2 remains one of the only a few cytosolic inhibitors of cardiac RyR2 channels, and may suppress their activity during diastole and during stress. The action of CLIC-2 in depressing RyR channel activity and regulating cytoplasmic Ca2+ stores suggests indirectly that it could be effective in preventing or reducing Ca2+ overload in conditions such as ischaemia, and in slowing apoptotic processes. | In addition with CLIC2, ryanodine and GST, RyR has many regulators including Ca2+ and Mg2+, ATP and calmodulin. All these regulators allow RyR channels to respond in synchrony with other cell processes even if CLIC2 remains one of the only a few cytosolic inhibitors of cardiac RyR2 channels, and may suppress their activity during diastole and during stress. The action of CLIC-2 in depressing RyR channel activity and regulating cytoplasmic Ca2+ stores suggests indirectly that it could be effective in preventing or reducing Ca2+ overload in conditions such as ischaemia, and in slowing apoptotic processes. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Those receptors are also involved in the physical bound to the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transversal tubules in squeletal muscle cells | Those receptors are also involved in the physical bound to the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transversal tubules in squeletal muscle cells | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
==3D structures of Chloride intracellular channel proteins== | ==3D structures of Chloride intracellular channel proteins== | ||
| Line 100: | Line 93: | ||
Proteins. 2008 Apr. PMID: 18186468 | Proteins. 2008 Apr. PMID: 18186468 | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
'''Blood leukocyte microarrays to diagnose systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis and follow the response to IL-1 blockade''' | '''Blood leukocyte microarrays to diagnose systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis and follow the response to IL-1 blockade''' | ||
Revision as of 09:32, 10 July 2013
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Chloride intracellular channel proteins
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Membrane Channels & Pumps
References
- ↑ Heiss NS, Poustka A. Genomic structure of a novel chloride channel gene, CLIC2, in Xq28. Genomics. 1997 Oct 1;45(1):224-8. PMID:9339381 doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4922
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Board PG, Parker MW. Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of chloride intracellular channel 2 (CLIC2). Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Nov 1;63(Pt, 11):961-3. Epub 2007 Oct 24. PMID:18007051 doi:10.1107/S1744309107049159
- ↑ Meng X, Wang G, Viero C, Wang Q, Mi W, Su XD, Wagenknecht T, Williams AJ, Liu Z, Yin CC. CLIC2-RyR1 interaction and structural characterization by cryo-electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):320-34. Epub 2009 Feb 4. PMID:19356589 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.059
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Littler DR, Brown LJ, Mazzanti M, Breit SN, Curmi PM, Dulhunty AF, Board PG, Parker MW. Structure of the Janus protein human CLIC2. J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 30;374(3):719-31. Epub 2007 Sep 20. PMID:17945253 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.041
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Board PG, Parker MW. Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of chloride intracellular channel 2 (CLIC2). Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Nov 1;63(Pt, 11):961-3. Epub 2007 Oct 24. PMID:18007051 doi:10.1107/S1744309107049159
- ↑ Meng X, Wang G, Viero C, Wang Q, Mi W, Su XD, Wagenknecht T, Williams AJ, Liu Z, Yin CC. CLIC2-RyR1 interaction and structural characterization by cryo-electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):320-34. Epub 2009 Feb 4. PMID:19356589 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.059
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Littler DR, Brown LJ, Mazzanti M, Breit SN, Curmi PM, Dulhunty AF, Board PG, Parker MW. Structure of the Janus protein human CLIC2. J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 30;374(3):719-31. Epub 2007 Sep 20. PMID:17945253 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.041
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Board PG, Parker MW. Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of chloride intracellular channel 2 (CLIC2). Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Nov 1;63(Pt, 11):961-3. Epub 2007 Oct 24. PMID:18007051 doi:10.1107/S1744309107049159
- ↑ Mi W, Li L, Su XD. 5,5'-Dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) modification of cysteine improves the crystal quality of human chloride intracellular channel protein 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Apr 18;368(4):919-22. Epub 2008 Feb 14. PMID:18280248 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.021
- ↑ Meng X, Wang G, Viero C, Wang Q, Mi W, Su XD, Wagenknecht T, Williams AJ, Liu Z, Yin CC. CLIC2-RyR1 interaction and structural characterization by cryo-electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):320-34. Epub 2009 Feb 4. PMID:19356589 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.059
- ↑ Mi W, Liang YH, Li L, Su XD. The crystal structure of human chloride intracellular channel protein 2: a disulfide bond with functional implications. Proteins. 2008 Apr;71(1):509-13. PMID:18186468 doi:10.1002/prot.21922
- ↑ Meng X, Wang G, Viero C, Wang Q, Mi W, Su XD, Wagenknecht T, Williams AJ, Liu Z, Yin CC. CLIC2-RyR1 interaction and structural characterization by cryo-electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):320-34. Epub 2009 Feb 4. PMID:19356589 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.059
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Board PG, Parker MW. Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of chloride intracellular channel 2 (CLIC2). Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Nov 1;63(Pt, 11):961-3. Epub 2007 Oct 24. PMID:18007051 doi:10.1107/S1744309107049159
- ↑ Cromer BA, Gorman MA, Hansen G, Adams JJ, Coggan M, Littler DR, Brown LJ, Mazzanti M, Breit SN, Curmi PM, Dulhunty AF, Board PG, Parker MW. Structure of the Janus protein human CLIC2. J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 30;374(3):719-31. Epub 2007 Sep 20. PMID:17945253 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.041
5,5'-Dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) modification of cysteine improves the crystal quality of human chloride intracellular channel protein 2.
Mi W, Li L, Su XD.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Apr 18. PMID: 18280248
The crystal structure of human chloride intracellular channel protein 2: a disulfide bond with functional implications.
Mi W, Liang YH, Li L, Su XD.
Proteins. 2008 Apr. PMID: 18186468
Blood leukocyte microarrays to diagnose systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis and follow the response to IL-1 blockade
Allantaz F, Chaussabel D, Stichweh D, Bennett L, Allman W, Mejias A, Ardura M, Chung W, Smith E, Wise C, Palucka K, Ramilo O, Punaro M, Banchereau J, Pascual V.
J Exp Med. 2007 Sep 3. PMID: 17724127
A recently identified member of the glutathione transferase structural family modifies cardiac RyR2 substate activity, coupled gating and activation by Ca2+ and ATP
Dulhunty AF, Pouliquin P, Coggan M, Gage PW, Board PG.
Biochem J. 2005 Aug 15.PMID: 15916532
CLIC-2 modulates cardiac ryanodine receptor Ca2+ release channels
Board PG, Coggan M, Watson S, Gage PW, Dulhunty AF.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Aug .PMID: 15147738
Interaction of Sedlin with chloride intracellular channel proteins
Fan L, Yu W, Zhu X.
FEBS Lett. 2003 Apr 10.PMID: 12681486
Differential expression of a chloride intracellular channel gene, CLIC4, in transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated conversion of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts
Rønnov-Jessen L, Villadsen R, Edwards JC, Petersen OW.
Am J Pathol. 2002 Aug .PMID: 12163372
Identification of a novel member of the chloride intracellular channel gene family (CLIC5) that associates with the actin cytoskeleton of placental microvilli
Berryman M, Bretscher A.
Mol Biol Cell. 2000 May.PMID: 10793131
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Céline Debarnot, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, David Canner, Eran Hodis