Trypsin
From Proteopedia
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Comparison to Chymotrypsin and Elastase== | ==Comparison to Chymotrypsin and Elastase== | ||
| - | < | + | |
| + | <scene name='Sandbox_32/Chymotrypsin/1'>Structure of Chymotrypsin and Elastase.</scene> | ||
Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase are all digestive enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Each of these enzymes has different specificities in regards to the side chains next to the peptide bond. Chymotrypsin prefers a large hydrophobic residue, trypsin is specific for a positively charged residue, and elastase prefers a small neutral residue. Chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase are all proteins that contain a catalytic mechanism and hydrolyze peptides using the serine protease mechanism. Chymotrypsin and elastase are both homologs of Trypsin since they are 40% alike in structure and composition <ref> Pratt, C.W., Voet, D., Voet, J.G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry - Life at the Molecular Level - Third Edition. Voet, Voet and Pratt, 2008. </ref>. In the <scene name='Sandbox_32/Chymotrypsin/2'>Chymotrypsin</scene> structure shown the alpha helices are blue, the beta sheets are green, and the remainder of the protein is red. In the <scene name='Sandbox_32/Elastase/2'>Elastase</scene> structure shown the alpha helices are in red, the beta sheets are yellow, and the remainder of the protein is orange. | Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase are all digestive enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Each of these enzymes has different specificities in regards to the side chains next to the peptide bond. Chymotrypsin prefers a large hydrophobic residue, trypsin is specific for a positively charged residue, and elastase prefers a small neutral residue. Chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase are all proteins that contain a catalytic mechanism and hydrolyze peptides using the serine protease mechanism. Chymotrypsin and elastase are both homologs of Trypsin since they are 40% alike in structure and composition <ref> Pratt, C.W., Voet, D., Voet, J.G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry - Life at the Molecular Level - Third Edition. Voet, Voet and Pratt, 2008. </ref>. In the <scene name='Sandbox_32/Chymotrypsin/2'>Chymotrypsin</scene> structure shown the alpha helices are blue, the beta sheets are green, and the remainder of the protein is red. In the <scene name='Sandbox_32/Elastase/2'>Elastase</scene> structure shown the alpha helices are in red, the beta sheets are yellow, and the remainder of the protein is orange. | ||
Revision as of 11:59, 16 July 2013
| |||||||||||
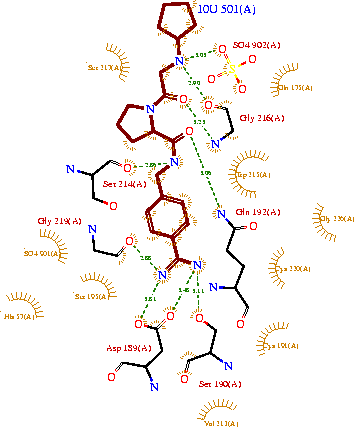
3D structures of Trypsin
Updated on 16-July-2013
Cationic trypsin
3nk8, 3nkk, 3mi4, 3mfj, 3iti, 2d8w, 2by5, 2by6, 2by7, 2by8, 2by9, 2bya, 2blv, 2blw, 2a7h, 1s0q, 1uto, 1utp, 1utq, 1utn, 1n6x, 1n6y, 1hj9, 2ptn, 3ptn, 5ptp, 3t25, 3t26, 3t27, 3t28, 3t29, 3unr, 4i8g, 4i8h, 4i8j, 4i8k, 4i8l - bTry1 - bovine
3qk1 – bTry1 (mutant)
1utk, 1utj, 1utl, 1utm, 1hj8 – Try1 – Salmon
1trn – hTry1 – human
3ljj, 3ljo, 3a7t, 3a7v, 3a7w, 3a7x, 3a7y, 3a7z, 3a80, 3a81, 3a82, 3a83, 3a84, 3a85, 3a86, 3a87, 3a88, 3a89, 3a8b, 3a8a, 3a8c, 3a8d, 3m35, 3aas, 3aau, 3aav, 3gy2, 3gy3, 3gy4, 3gy5, 3gy6, 3gy7, 3gy8, 2zq1, 2zq2, 2zhd, 2zfs, 2zft, 2zdk, 2zdl, 2zdm, 2zdn, 2oxs, 2otv, 2g8t, 2g5n, 2g5v, 2ah4, 2fx4, 2fx6, 1yp9, 2ayw, 1y3u, 1y3v, 1y3w, 1y3x, 1y3y, 1tx8, 1tx7, 1s0r, 1rxp, 1o2q, 1o2r, 1o2s, 1o2t, 1o2u, 1o2v, 1o2w, 1o2x, 1o2y, 1o2z, 1o30, 1o31, 1o32, 1o33, 1o34, 1o35, 1o36, 1o37, 1o38, 1o39, 1o3a, 1o3b, 1o3c, 1o3d, 1o3e, 1o3f, 1o3g, 1o3h, 1o3i, 1o3j, 1o3k, 1o3l, 1o3m, 1o3n, 1o3o, 1o3p, 1o2l, 1o2k, 1o2j, 1o2i, 1o2h, 1o2m, 1o2n, 1o2o, 1o2p, 1lqe, 1oyq, 1eb2, 1k1i, 1k1j, 1k1l, 1k1m, 1k1n, 1k1o, 1k1p, 1g36, 1j8a, 1jir, 1g3b, 1g3c, 1g3d, 1g3e, 1g9i, 1f0t, 1f0u, 1c1n, 1c1o, 1c1p, 1c1q, 1c1r, 1c1s, 1c1t, 1c2d, 1c2e, 1c2f, 1c2g, 1c2h, 1c2i, 1c2j, 1c2k, 1c2l, 1c2m, 1qbn, 1qbo, 1qb9, 1qb1, 1qb6, 1qa0, 1qcp, 1ce5, 2bza, 1az8, 1xuf, 1xug, 1bju, 1bjv, 1xuh, 1xui, 1xuj, 1xuk, 1auj, 2tio, 1tio, 1aq7, 3ati, 3atk, 3atl, 3atm, 3rxa, 3rxb, 3rxc, 3rxd, 3rxe, 3rxf, 3rxg, 3rxh, 3rxi, 3rxj, 3rxk, 3rxl, 3rxm, 3rxo, 3rxq, 3rxr, 3rxs, 3rxt, 3rxu, 3rxv - bTry1 + small molecule inhibitor
1v2j, 1v2l, 1v2m, 1v2n, 1v2o, 1v2p, 1v2q, 1v2r, 1v2s, 1v2t, 1v2u, 1v2v, 1v2w, 3plb, 3plk, 3plp, 3pm3, 3pmj, 3pwb, 3pwc, 3pyh, 3q00, 3unq, 3uns, 3uop, 3upe, 3uqo, 3uqv, 3uuz, 3uwi, 3uy9, 3v0x, 3v12, 3v13 - bTry1 (mutant) + small molecule inhibitor
3m7q, 2xtt, 3e8l, 3otj, 3i29, 3d65, 2qyi, 2qn5, 2o9q, 2plx, 2cmy, 2iln, 2uuy, 2j9n, 2g81, 2age, 2agg, 2agi, 2ftl, 2ftm, 2fi3, 2fi4, 2fi5, 1zr0, 1ox1, 1p2i, 1p2j, 1p2k, 1ejm, 1f2s, 3bte, 3btq, 3btd, 3btf, 3btg, 3bth, 3btk, 3btm, 3btt, 3btw, 2btc, 1sbw, 1taw, 1smf, 1ppc, 1ppe, 1pph, 2tld, 1tab, 1tpa, 1c9t, 1ezx, 2f3c, 3rdz – bTry1 + proteinase inhibitor
4b2b, 4b1t, 4b2a, 4b2c – bTry1 (mutant) + eglin (mutant)
2ra3, 1oph, 3veq - bTry1 (mutant) + proteinase inhibitor
1jrs, 1jrt, 1sfi, 1yyy, 1zzz, 4abi – bTry1 + polypeptide
1c5p, 1c5q, 1c5r, 1c5s, 1c5t, 1c5u, 1c5v, 1ghz, 1gi0, 1gi1, 1gi2, 1gi3, 1gi4, 1gi5, 1gi6, 1gj6, 1mts, 1mtu, 1mtv, 1mtw, 1ql7, 1ql8, 1ql9, 1v2k, 1y59, 1y5a, 1y5b, 1y5u, 3rxp, 4ab8, 4ab9, 4aba, 4abb, 4abd, 4abe, 4abf, 4abg, 4abh, 3vpk – bTry1 + inhibitor
4abj – bTry1 + Try inhibitor 1
2eek – Try1 + inhibitor – Atlantic cod
Cationic trypsinogen
1tgc, 1tgt, 2tga, 2tgt, 1tgb, 1tld, 1tpo - bTryp1
1ntp - β-bTry1 – Neutron diffraction
1d6r, 4tpi, 1tgs, 2tgp, 3tpi, 2tpi, 2ptc - bTryp1 + proteinase inhibitor
1max, 1may, 1btp, 1bty, 1tps, 1tyn, 1tng, 1tnh, 1tni, 1tnj, 1tnk, 1tnl, 1gbt, 1tpp, 3ptb - bTry1 + small molecule inhibitor
1btw, 1btx, 1btz - bTry1 + polypeptide
Anionic trypsin
2zpq, 2zpr, 2zps, 1mbq – Try2 – Chum salmon
1bit, 2tbs - AsTry2 – Atlantic salmon
2sta, 2stb, 1bzx - AsTry2 + proteinase inhibitor
1a0j - AsTry2 + small molecule inhibitor
1ane, 1bra - rTry2]] - rat
1amh, 1dpo, 1anb, 1anc, 1and, 1trm, 2trm - rTry2 (mutant)
3fp6, 3tgi, 1brb, 1brc – rTry2 + proteinase inhibitor
3fp7, 3fp8, 1ykt, 1ylc, 1yld, 1co7, 1k9o, 1slu, 1slv, 1slw, 1slx - rTry2 (mutant) + proteinase inhibitor
1j14, 1j15, 1j16, 1j17 - rTry2 (mutant) + small molecule inhibitor
Anionic trypsinogen
1f5r, 1f7z, 3tgk, 1ezs, 1ezu, 3tgj - rTryp2 (mutant) + proteinase inhibitor
1fy8 - rTryp2 + proteinase inhibitor
Trypsinogen
1tgn – bTryp
2tgd – bTryp + inhibitor
Mesotrypsin
3l33 – hTry3 (mutant) + amyloid β A4
3l3t - hTry3 residues 28-251 (mutant) + amyloid β precursor
2r9p – hTry3 (mutant) + BPTI
Brain trypsin
1h4w – hTry4 + small molecule inhibitor
Neurotrypsin
2k4r, 2k51 – rNTry Kringle domain – NMR
Streptomyces griseus trypsin
3i77, 3i78, 1os8, 1sgt – SGT – Streptomyces griseus
3beu, 2fmj – SGT (mutant)
1oss - SGT (mutant) + small molecule inhibitor
1s81 – pTry – pig
1aks - α-pTry
1ept - ε-pTry
1mct - β-pTry + proteinase inhibitor
3myw, 1yf4, 1z7k, 1tx6, 1v6d, 1uhb, 1h9h, 1h9i, 1eja, 1c9p, 1avw, 1avx, 1ldt, 1tfx, 1an1, 4an7 – pTry + proteinase inhibitor
2a31, 2a32, 1s5s, 1s6f, 1s6h, 1s82, 1s83, 1s84, 1s85, 1fmg, 1fn6, 1fni, 1qqu – pTry + small molecule inhibitor
2vu8 – Try + proteinase inhibitor – mold
2g51, 2g52, 2g55, 1xvo, 1pq5, 1pq7 – FoTry – Fusarium oxysporum
1ppz, 1pqa, 1try - FoTry + small molecule inhibitor
1xvm, 1pq8, 1fn8, 1fy4, 1fy5, 1gdn, 1gdq, 1gdu – FoTry + polypeptide
2f91 – Try-hepatopancreas - Crayfish
References
- ↑ Trypsin. 2010. 30 October 2010 <http://www.worthington-biochem.com/tyr/default.html>
- ↑ Trypsin. 30 October 2010 <http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/life-science/metabolomics/enzyme-explorer/analytical-enzyme/trypsin.html>.
- ↑ Image From: http://chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/MAT500/Peptidase1.html
- ↑ Trypsin. 2010. 30 October 2010 <http://www.worthington-biochem.com/tyr/default.html>
- ↑ Pratt, C.W., Voet, D., Voet, J.G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry - Life at the Molecular Level - Third Edition. Voet, Voet and Pratt, 2008.
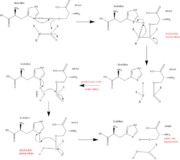
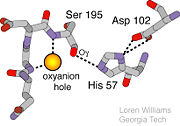
- ↑ Structural Biochemistry. 10 June 2010. 30 October 2010.<http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Enzyme/Catalytic_Triad>.
- ↑ Image From:

- ↑ Williams, Loren. Georgia Tech. http://www2.chemistry.gatech.edu/~1W26/bcourse_information/6521/protein/serine_protease/triad_1/html.
- ↑ Structural Biochemistry. 10 June 2010. 30 October 2010.<http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Enzyme/Catalytic_Triad>.
- ↑ Pratt, C.W., Voet, D., Voet, J.G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry - Life at the Molecular Level - Third Edition. Voet, Voet and Pratt, 2008.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Eran Hodis, Leah Bowlin, David Canner, Glenn Jones, Ben Hallowell, Karl Oberholser, Jaime Prilusky