This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Quinone reductase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='2f1o.pdb' size='500' frame='true' align='right' scene='2f1o/Com_view/2' caption='NADPH dehydrogenase complex with FAD and dicoumarol [[2f1o]]'> | ||
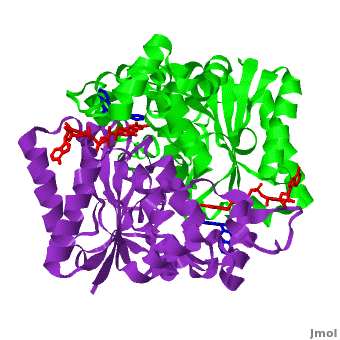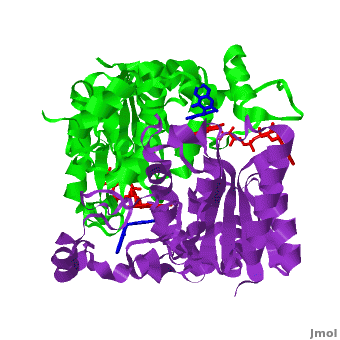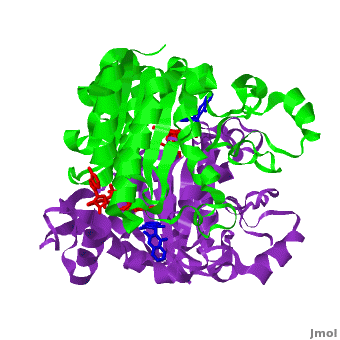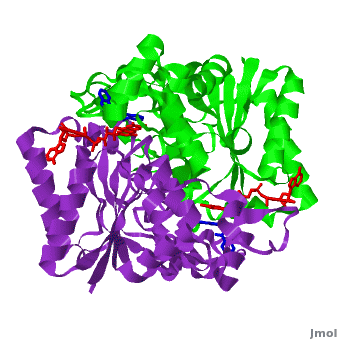
[[Image:2f1o1.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of NADH quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) with inhibitor dicoumarol [[2f1o]]]] | [[Image:2f1o1.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of NADH quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) with inhibitor dicoumarol [[2f1o]]]] | ||
| - | + | ||
| Line 40: | Line 41: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='2f1o.pdb' size='500' frame='true' align='right' scene='2f1o/Com_view/2' caption='NADPH dehydrogenase complex with FAD and dicoumarol [[2f1o]]'> | ||
| - | |||
The crystal structure of human NQO1 in complex with dicoumarol was determined at 2.75 Å resolution ([[2f1o]]). NQO1 is a <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/6'>physiological homodimer</scene> composed of two interlocked monomers. <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/7'>Two catalytic sites</scene> are formed and are present at the dimer interface (<font color='red'><b>FAD is colored red</b></font> and <font color='blue'><b>dicoumarol is colored blue</b></font>). Therefore, each from these two <scene name='2f1o/Active_site/3'>dicoumarol-hNQO1 binding sites</scene> is formed by both monomers. <font color='cyan'><b>Dicoumarol is colored cyan</b></font>, <font color='orange'><b>FAD in orange</b></font>, nitrogens and oxygens are shown in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPK_coloring CPK colors]. NQO1 <font color='blueviolet'><b>chain A is colored blueviolet</b></font> and <font color='lime'><b>chain C in lime</b></font>. NQO1 residues, participating in ligand interactions, are shown as stick representation and are labeled (A and C refer to the NQO1 chains). H-bonds are shown by dashed lines with their distances. | The crystal structure of human NQO1 in complex with dicoumarol was determined at 2.75 Å resolution ([[2f1o]]). NQO1 is a <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/6'>physiological homodimer</scene> composed of two interlocked monomers. <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/7'>Two catalytic sites</scene> are formed and are present at the dimer interface (<font color='red'><b>FAD is colored red</b></font> and <font color='blue'><b>dicoumarol is colored blue</b></font>). Therefore, each from these two <scene name='2f1o/Active_site/3'>dicoumarol-hNQO1 binding sites</scene> is formed by both monomers. <font color='cyan'><b>Dicoumarol is colored cyan</b></font>, <font color='orange'><b>FAD in orange</b></font>, nitrogens and oxygens are shown in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPK_coloring CPK colors]. NQO1 <font color='blueviolet'><b>chain A is colored blueviolet</b></font> and <font color='lime'><b>chain C in lime</b></font>. NQO1 residues, participating in ligand interactions, are shown as stick representation and are labeled (A and C refer to the NQO1 chains). H-bonds are shown by dashed lines with their distances. | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 1 August 2013
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D Structures of Quinone reductase
Updated on 01-August-2013
Quinone reductase type 1
3jsx – hQR1 + coumarine derivative
2f1o – hQR1 + dicoumarol
1kbo, 1kbq – hQR1 + indole derivative
Quinone reductase type 2
3fw1, 1qr2 – hQR2 - human
3o2n, 3g5m, 3gam – hQR2 + PET agent
3ovm, 3owh, 3owx – hQR2 + carbamate derivative
3ox1, 2qx4, 2qx6, 2qx8, 2qx9, 2qwx – hQR2 + acetamide derivative
3ox2 - hQR2 + indole derivative
3ox3 - hQR2 + carboxamide derivative
2qmy – hQR2 + adrenochrome
2qr2 – hQR2 + menadione
2qmz – hQR2 + dopamine
1sg0 – hQR2 + resveratol
3nhu, 3nhs, 3nhr, 3nhp, 3nhl, 3nhk, 3nhj, 3nhf, 3nfr, 3nhw, 3nhy, 3uxe, 3uxh - hQR2 + quinoline derivative
3te7, 3tem, 3tzb – hQR2 + acridine derivative
2bzs, 1xi2, 1zx1, 3o73 – hQR2 + anti-cancer prodrug
4fgj, 4fgk, 4fgl – hQR2 + anti-malaria drug<be />
Sulfide-quinone reductase
3hyv – AaSQR – Aquifex aeolicus
3hyw – AaSQR + decylubiquinone
3hyx – AaSQR + Aurachin C
NADPH-quinone reductase
3ha2 – NQR – Pediococcus pentosaceus
1dxq, 1d4a - hNQR
1yb5 – hNQR + NADP
1gg5, 1h66, 1h69, 1qbg - hNQR + anti-cancer prodrug
1dxo - hNQR + quinone derivative
1qrd – QR + bicarbon blue + duroquinone - rat
4gi5 – QR + FAD – Klebsiella pneumoniae
References
- Faig M, Bianchet MA, Talalay P, Chen S, Winski S, Ross D, Amzel LM. Structures of recombinant human and mouse NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductases: species comparison and structural changes with substrate binding and release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 28;97(7):3177-82. PMID:10706635 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.050585797
- Asher G, Dym O, Tsvetkov P, Adler J, Shaul Y. The crystal structure of NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 in complex with its potent inhibitor dicoumarol. Biochemistry. 2006 May 23;45(20):6372-8. PMID:16700548 doi:10.1021/bi0600087