We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 123
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Cell Wall Structure == | == Cell Wall Structure == | ||
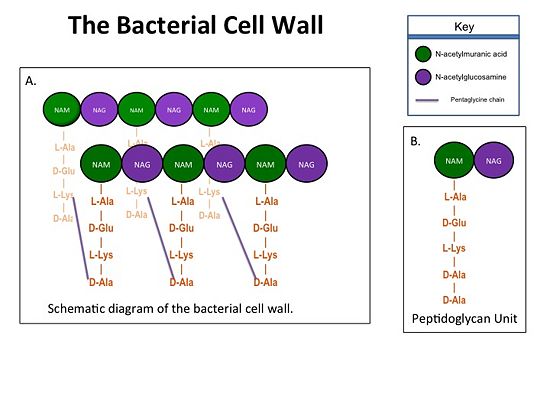
| - | The cell wall, which is composed of peptidoglycan, is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the bacterium. Peptidoglycan consists of N-acetylmuramic Acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) polymers. Rows of peptidoglycan cross-linked together with pentaglycine chains. The NAM residues have a five amino acid side chain that terminates with two D-Alanine (D-Ala) residues. | + | The cell wall, which is composed of peptidoglycan, is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the bacterium. Peptidoglycan consists of N-acetylmuramic Acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) polymers. Rows of peptidoglycan cross-linked together with pentaglycine chains. The NAM residues have a five amino acid side chain that terminates with two D-Alanine (D-Ala) residues. [[Image:Cell Wall 7 30 2013.jpg|thumb|alt= Alt text| Figure 1. A.Bacterial Cell Wall B.Peptidoglycan with D-Ala-D-Ala substrate |550px]] |
| + | |||
<StructureSection load='4DKI' size=550 side=right scene='2H4M'/Com_view/1'> | <StructureSection load='4DKI' size=550 side=right scene='2H4M'/Com_view/1'> | ||
Revision as of 18:20, 1 August 2013
, also known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBP), catalyze the cross-linking of peptidoglycan polymers during bacterial cell wall synthesis. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics, which include penicillins, cephalosporins and carbapenems, bind and irreversibly inhibit transpeptidases. The overuse and misuse of β-lactam antibiotics has led to strains of Staphylococcus aureus that are resistant to all β-lactams and are often only susceptible to “last resort antibiotics”, such as vancomycin.
Cell Wall Structure
The cell wall, which is composed of peptidoglycan, is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the bacterium. Peptidoglycan consists of N-acetylmuramic Acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) polymers. Rows of peptidoglycan cross-linked together with pentaglycine chains. The NAM residues have a five amino acid side chain that terminates with two D-Alanine (D-Ala) residues.
| |||||||||||