We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 123
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load= size=450 side='right' scene='36/365380/4dki_cartoon/ | + | <StructureSection load= size=450 side='right' scene='36/365380/4dki_cartoon/16'> |
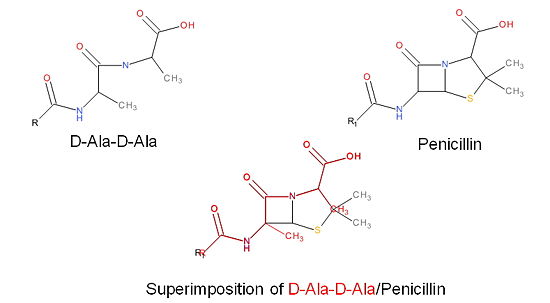
Transpeptidase (TP), also known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBP), catalyze the cross-linking of peptidoglycan polymers during bacterial cell wall synthesis. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics, which | Transpeptidase (TP), also known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBP), catalyze the cross-linking of peptidoglycan polymers during bacterial cell wall synthesis. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics, which | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Structure of a Resistant Transpeptidase == | == Structure of a Resistant Transpeptidase == | ||
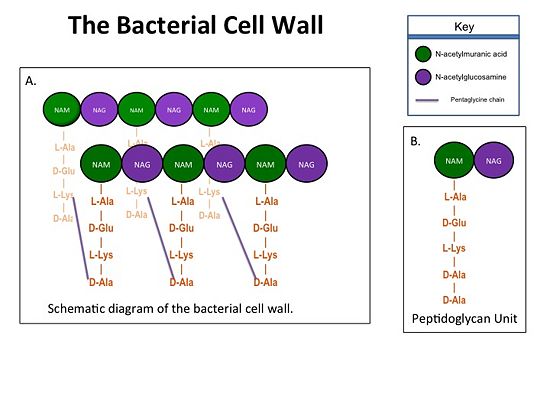
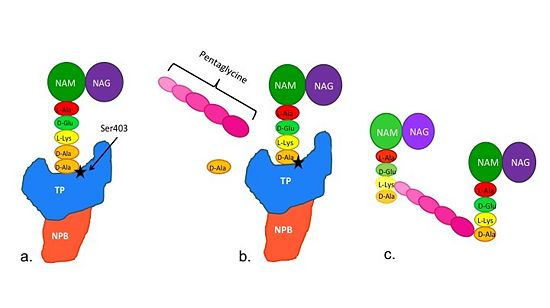
| - | Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is resistant to all β-lactams because it acquires an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is not bound or inhibited by any β-lactams. PBP2a is composed of two domains: a <font color='orange'><b>non-penicillin binding domain </b><scene name='36/365380/4dki_cartoon/ | + | Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is resistant to all β-lactams because it acquires an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is not bound or inhibited by any β-lactams. PBP2a is composed of two domains: a <font color='orange'><b>non-penicillin binding domain </b><scene name='36/365380/4dki_cartoon/17'>(NPB) </scene></font> and a <font color='dodgerblue'><b>transpeptidase <scene name='36/365380/4dki_cartoon/18'>(TP)</scene> binding domain </b></font>. The NBP domain of PBP2a is anchored in the cell membrane, while the TP domain “sits” in the periplasm with its active site facing the inner surface of the cell wall. The active site contains <scene name='36/365380/Ser403/15'>a serine residue at position 403 (ser403)</scene> which catalyzes the cross-linking of the peptidoglycan rows with pentaglycine cross-links. |
Revision as of 14:44, 15 August 2013
| |||||||||||