We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 127
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
== PBP2a and Ceftobiprole == | == PBP2a and Ceftobiprole == | ||
| - | |||
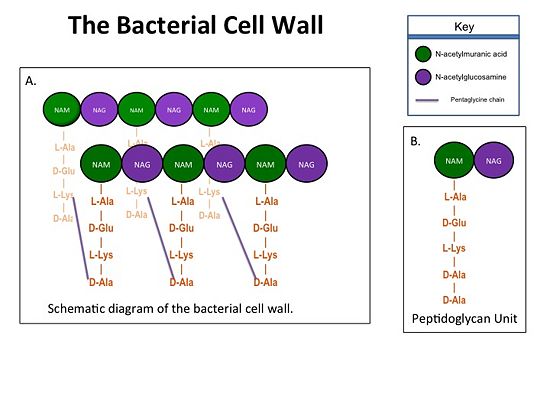
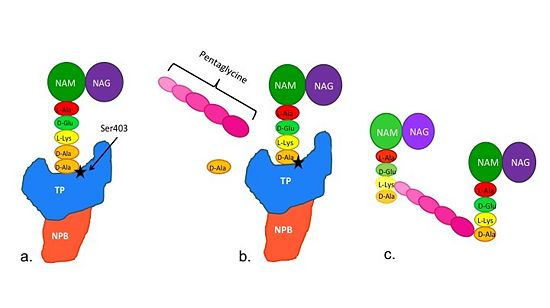
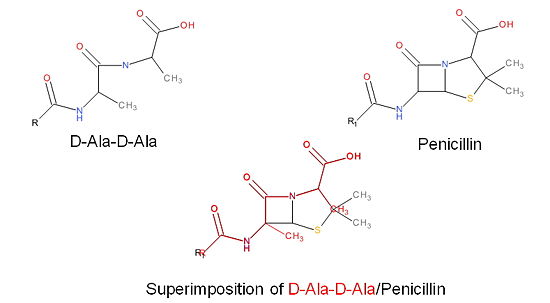
| - | MRSA becomes resistant to β-lactams by acquiring an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is | ||
| - | neither bound nor inhibited by β-lactams. Recently, two cephalosporins – <scene name='36/365380/Ceftobiprole/23'>ceftobiprole</scene> and | ||
| - | ceftaroline – that have anti-MRSA activity have been developed. Ceftobiprole is able to | ||
| - | inhibit PBP2a because additional chemical groups at the <scene name='36/365380/Ceftobiprole/12'>R2</scene> position of the cephalosporin backbone are able to interact with additional amino acid residues in PBP2a; specifically | ||
| - | <scene name='36/365380/Ceftobiprole/22'>Tyr446 and Met641</scene>. As a result of its tighter binding to PBP2a, ceftobiprole is able to more | ||
| - | efficiently react with the serine active site residue and therefore inhibit the activity of | ||
| - | PBP2a. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
MRSA becomes resistant to β-lactams by acquiring an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is | MRSA becomes resistant to β-lactams by acquiring an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is | ||
neither bound nor inhibited by β-lactams. Recently, two cephalosporins – | neither bound nor inhibited by β-lactams. Recently, two cephalosporins – | ||
| - | <scene name='37/372724/ | + | <scene name='37/372724/Medicine_interaction/4'>cefobiprole</scene> and |
ceftaroline – that have anti-MRSA activity have been developed. Ceftobiprole is able to | ceftaroline – that have anti-MRSA activity have been developed. Ceftobiprole is able to | ||
inhibit PBP2a because additional chemical groups at the | inhibit PBP2a because additional chemical groups at the | ||
| - | <scene name='37/372724/ | + | <scene name='37/372724/Medicine_interaction/3'>R2</scene> |
position of the cephalosporin backbone are able to interact with additional amino acid | position of the cephalosporin backbone are able to interact with additional amino acid | ||
residues in PBP2a; specifically | residues in PBP2a; specifically | ||
| - | <scene name='37/372724/ | + | <scene name='37/372724/Medicine_interaction/2'>Tyr446 and Met641</scene>. |
| - | + | <scene name='37/372724/Medicine_interaction/1'>The medicine</scene> shown as colors of the atom types ([[CPK]]) is able to more efficiently react with the serine active site residue and therefore inhibit the activity of pbp2a as a result of ceftobiprole <scene name='37/372724/R2_interaction/6'>tighter binding</scene> to pbp2a. unlike penicillin, this results in inhibition of pbp2a | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='37/372724/R2_interaction/6'>tighter binding</scene> | + | |
Revision as of 17:51, 15 August 2013
| |||||||||||